The popularity of routine well-being checks is growing.An exploration group from the Institute of Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ICCAS) has recently fostered a living material for ongoing testing of lactate, a biomarker for disease.
Lactate is a significant analyte in bioprocess designing, sports medication, and clinical consideration, and it is likewise a solid biomarker of cancer age, metastasis, and repeat. Compact biosensors with great execution for checking the lactate content in body liquids are popular.
Living materials are another sort of biohybrid material comprising living components (microbes, mammalian cells, growths, green growth, and so on) and fake useful materials. Profiting from the mix of their separate benefits, living materials are utilized for biosensing, biosynthesis, and biomedical research. Formed polymers (CPs) are characterized by a delocalized electronic design that permits electron movement.
By additional modification of the CP spine utilizing water-solvent side chains, a progression of novel water-dissolvable formed polymers (WSCPs) were planned and blended with great water-dissolvability, photoelectric property, and biocompatibility. WSCPs are supposed to be great fake useful materials for building living materials and bioelectronic gadgets.
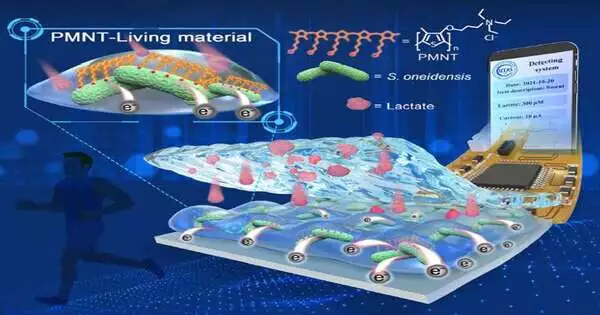
Driven by Prof. Wang Shu and Prof. Bai Haotian, the ICCAS group built a living material with cationic polythiophene (PMNT) and Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. The PMNT could contribute to the biofilm development and enhance the bioelectronic process inside S. oneidensis MR-1; hence, the built-in living materials could speed up the oxidization cycle from lactate and improve the outward electron mobility rate.
The material was then used to create an adaptable bioelectronic gadget for lactate location in physiological liquids (sweat, pee, and plasma) and growth cells through additional practical module mixing and designing innovation handling. Every one of the gathered electrical transmissions assembled by the adaptable bioelectronic gadget could be remotely moved to a compact cell phone for perusing and examining.
This work gives another system for coordinating the natural action of living cells and the optoelectronic properties of CPs for planning living materials. The adaptable and wearable electronic gadgets, in view of the new living materials, have likely applications for individual wellbeing monitoring from now on.
The review was published in Science Advances.
More information: Zenghao Wang et al, Flexible bioelectronic device fabricated by conductive polymer–based living material, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo1458