A group of manufactured researchers at the Hong Kong College of Science and Innovation (HKUST) has as of late found a way that could increment engineered mRNA’s protein creation proficiency by up to multiple times, and that implies the viability of mRNA immunizations and medications—ffor example, those utilized against malignant growth, Coronavirus, or other hereditary infections—will be significantly supported with even less measurement of the mRNAs.
mRNAs can be orchestrated to show our cells making any sort of proteins, for example, antigens, compounds, and chemicals, which are fundamental in battling contamination and controlling physical processes, so mRNA is seemingly a favored choice for immunizations and treatment for the vast majority of various types of sickness.
Notwithstanding, high doses and repeated infusions are frequently expected for mRNA medications and immunizations to create an adequate measure of protein in the body, so upgrading mRNA’s viability—llike by expanding its protein creation proficiency—is a hot subject among researchers, as our safe framework, for instance, could work better with additional specific antibodies.
Presently, a group led by Prof. Becki Kuang Yi, collaborator teacher at the Branch of Compound and Organic Designing at HKUST, has found a way that could improve both the life expectancy and productivity of mRNA.
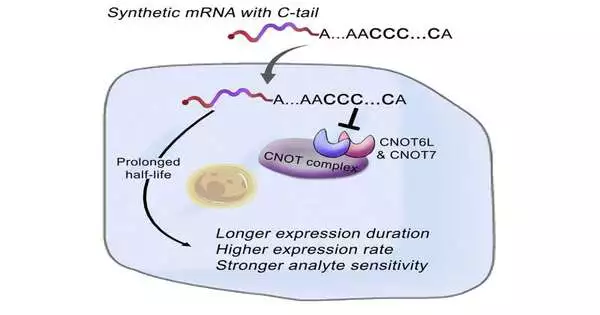
The improved mRNA tail would protect it from rapid debasement and allow it to stay in the cell for a longer period of time, increasing protein creation productivity by up to tenfold.
Prof. Kuang’s group discovered improved sequences that could produce 3 to 10 times the amount of proteins as unoptimized tail arrangements commonly used for manufactured mRNAs on both human cells and mice after designing various mRNA tail arrangements. The duration of protein production is also increased.
This new innovation will not only reduce the number and quantity of infusions required for mRNA medications and immunizations, but it may also reduce the cost of medications.It can likewise be utilized alongside other mRNA improvement advancements to synergistically support protein production.
“Expanding the protein creation of manufactured mRNA is by and large useful for all mRNA medications and antibodies,” said Prof. Kuang.
When compared to the unoptimized tail, the upgraded mRNA tail (right) can still blend protein (colored in brilliant green) 48 hours after conveyance to cells.
“In a joint effort with Sun Yat-Sen College, our group is currently investigating the utilization of improved tails for mRNA disease immunizations on creatures.” “We also anticipate collaborating with pharmaceutical companies to move this innovation into the pipelines of mRNA therapeutics and antibodies to benefit society.”
The discovery was recently published online in the journal Atomic Treatment—Nucleic Acids.
mRNA medications and immunizations stand out lately because of their viability in safeguarding us against extreme states of specific transmittable illnesses, for example, the coronavirus, and their high potential in dealing with ongoing illnesses like malignant growths.
More information: Cheuk Yin Li et al, Cytidine-containing tails robustly enhance and prolong protein production of synthetic mRNA in cell and in vivo, Molecular Therapy—Nucleic Acids (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.10.003