While looking for the reasons for sickness and developing new therapies, having an exact understanding of the hereditary fundamentals is totally crucial. Würzburg scientists have contrived another method for this reason.
Obsessive cycles are typically characterized by altered quality action in the impacted phones.Thus, acquiring an exact image of quality movement can give way to the improvement of new, designated treatments. Whether these treatments then function as we would expect them to can also be confirmed by looking at qualities and the cycles they initiate.
It is no big surprise that research is centered around strategies and methods that give point-by-point data about the hereditary movement of individual cells. An examination group at the College of Würzburg (JMU) has now fostered a strategy that is a huge enhancement to the techniques used to date. Researchers from the Foundation for Sub-atomic Contamination Science (IMIB) and the Helmholtz Organization for RNA-based Disease Exploration (HIRI) were involved. They have introduced the aftereffects of their figure in the ebb and flow problem of the diary Nucleic Acids Exploration.
Investigation of an engineered transcriptome
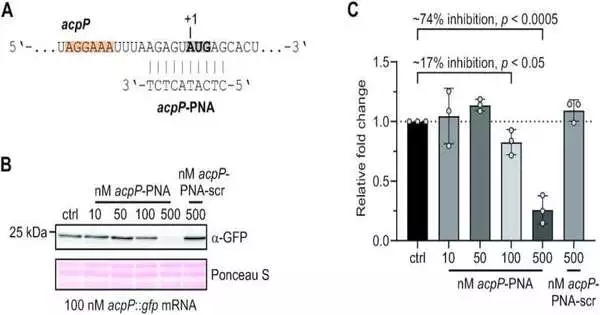
“We have fostered a strategy that can be utilized to dissect the translational scene of a completely adaptable engineered transcriptome, at the end of the day, one outside the cell,” is the means by which Jörg Vogel makes sense of the focal result of the review. Vogel heads the Organization for Sub-atomic Disease Science at JMU and is the Overseer of HIRI as well as the chief creator of the review. The new method has been given the logical name INRI-seq, which is short for in vitro Ribo-seq.
“We have developed a technique that can be used to analyze the translational landscape of a fully customizable synthetic transcriptome, that is, one that exists outside of the cell.”
Jörg Vogel explains the central outcome of the study.
A transcriptome is an assortment of the relative multitude of qualities that are dynamic in a cell at a given moment. It consists of the amount of the current mRNA—the carriers of the diagrams for proteins from the cell core to the ribosomes. Ribosomes are the “protein manufacturing plants” of the phone; this is where interpretation of the nucleotide succession of the mRNA into the amino acid corrosive grouping of a protein happens.
Refinement of equivalent strategies:
On a fundamental level, INRI-seq is a refinement of similar strategies that seek after similar objectives yet give less exact outcomes or have different weaknesses. For instance, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) decides the convergence of mRNA in cells, permitting conclusions to be drawn about their dynamic qualities. In any case, the last protein overflow doesn’t generally relate to the particular mRNA fixations.
A more precise strategy is ribosome profiling (Ribo-seq). In recent years, this has become one of the primary techniques for estimating protein blends straightforwardly in a vast way. “While Ribo-seq has incredibly advanced the investigation of interpretation-related processes, the technique has not been without restrictions,” says Jörg Vogel.
Various restrictions on Ribo-seq
For example, it is a significant test to identify feeblely communicated qualities with Ribo-seq, keeping numerous qualities from being kept in a similar manner, concentrating on plans. Likewise, a Ribo-seq investigation of microorganisms from significant biological environments, for example, the human stomach, is troublesome since a considerable number of them can’t be refined in the research center.
A further deficiency, as Vogel makes sense of, is the way that “on the unthinking level, Ribo-seq-based investigations of particles influencing interpretation, like exceptional anti-infection agents, can be hampered by cell reactions.” Since Ribo-seq is performed on living cells, recognizing immediate and backhanded impacts on translation can be troublesome.
To overcome a portion of these constraints, the researchers from Würzburg have created INRI-seq for the worldwide investigation of interpretation in a sans cell climate. In addition, INRI-seq utilizes a monetarily accessible in vitro interpretation framework joined with an in vitro-blended, completely adaptable transcriptome that permits better control of individual mRNA levels.
“WithINRI-seq, for instance, it is at this point excessive for interpretation balancing substances to navigate cell layers or to separate ribosomes from an enormous number of living cells,” says Vogel, framing the benefits of the strategy. “You likewise need significantly less of the frequently costly substances that you need to study, for example, another anti-infection that must be delivered on a limited scale. Additionally, it sets aside time and cash. “
Increased examination success rate
The exploration group showed how well the framework functions utilizing an artificially created transcriptome of the bacterium Escherichia coli. INRI-seq identified nearly multiple times more locations where interpretation processes are initiated when compared to an actually comparable concentration on residing cells, demonstrating its high responsiveness.
Hence, Vogel and his group are in no doubt that “INRI-seq bears extraordinary potential as an elective technique for concentrating on interpretation cycles and, accordingly, substances that can impact these cycles.”
More information: Jens Hör et al, INRI-seq enables global cell-free analysis of translation initiation and off-target effects of antisense inhibitors, Nucleic Acids Research (2022). DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac838
Journal information: Nucleic Acids Research