Scientists at Kanazawa University in a joint effort with groups from Toyama Prefectural University and BioSeeds Corporation report in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces the recognizable proof of a particle with improved antiproliferative movement in malignant growth cells. The fundamental biomolecular component is the restraint of a chemical that is overproduced in a few kinds of malignant growth.
Nutrient D3 has significant organic capacities, including keeping up with bone mineral thickness, which limits the gamble of bone crack. Be that as it may, nutrient D3 is likewise accepted to have anticancer action, as low nutrient D3 levels and the related overproduction of a compound called CYP24 are connected to an unfortunate guess for malignant growth patients. Particles that cutoff or hinder the activity of CYP24 and atoms that impersonate the capacity of nutrient D3 are these days exceptionally investigated as expected antiproliferative specialists for malignant growth treatment.
In any case, large numbers of the inhibitors and D3 analogs combined so far have shown deficient clinical reaction, as well as undesired aftereffects. Presently, Madhu Biyani from Kanazawa University and partners have distinguished a DNA-determined particle that ties to and hinders the capacity of CYP24 and shows promising antiproliferative movement. The examination group additionally gives nitty gritty experiences into the pertinent sub-atomic cycles at play.
The researchers screened countless DNA aptamers — bits of single-abandoned DNA with specific three-layered structures that can tie to explicit objective particles and have a practical impact after restricting. They searched for DNA aptamers that tight spot to CYP24 yet not to the comparative catalyst CYP271B, which is answerable for the union of nutrient D3.
An underlying longlist of 18 aptamer competitors was decreased to 11 agents with explicit sub-atomic designs. The analysts actually look at the CYP24 restraint action of the 11 agent aptamers in vitro. Four applicants bringing about the hindrance of CYP24 however not in that frame of mind of CYP27B1 stayed, of which one (Apt-7) was held for additional review.
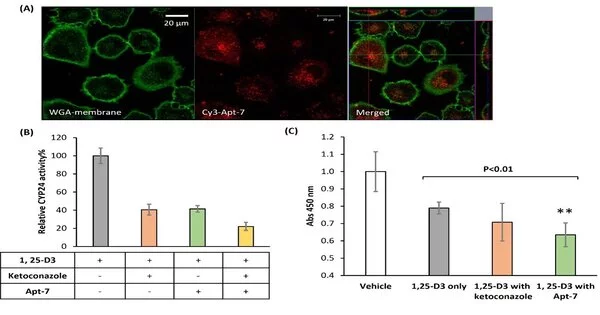
Figure 2.Internalization of aptamer into A549 cells is fundamental for CYP24 restraint and upgrading 1, 25-D3 intervened cell-development hindrance. (A) Internalization of Aptamer into A549 cells. A549 cellular breakdown in the lungs cells were treated with 500 nM aptamer Apt-7 and had their layers stained green (Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) Conjugates). Confocal microscopy uncovered the intracellular sign, got from assimilated aptamer (red fluorescence, Cy3). (B) Apt-7 represses the CYP24-intervened catabolism of 1,25-D3 in A549 cells. After 18 h of aptamer treatment, 1, 25-D3 metabolite change proportion and relative CYP24 not entirely settled by HPLC. (C) Apt-7 improves the counter proliferative capacity of 1, 25-D3 in A549 cells.
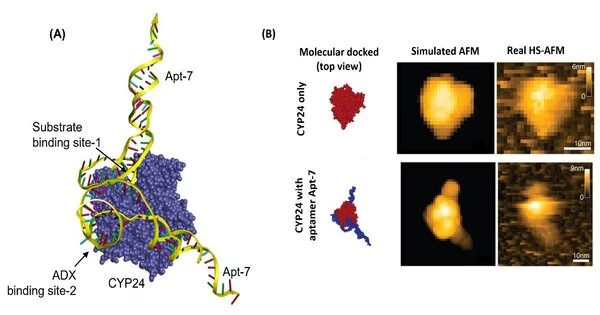
Biyani and partners performed reenactments of Apt-7 restricting to CYP24. A sub-atomic docking situation was gotten, which they checked tentatively by looking at the way of behaving of a combination of nutrient D3 and CYP24 with and without Apt-7. The reenactments and the analyses showed that Apt-7 outcomes in the restraint of CYP24 movement, and that what happens is that the aptamer likely obstructs the catalyst’s dynamic site. The scientists likewise performed high velocity nuclear power microscopy on the limiting of CYP24 and Apt-7 progressively, affirming the sub-atomic docking situation got from recreations.
At last, the examination group concentrated on the impact of Apt-7 at the cell level by acquainting the particle with malignant growth cells. They noticed huge CYP24 hindrance for a malignant growth cell line known to overexpress the CYP24 compound, subsequently showing antiproliferative action. Citing Biyani and partners, these discoveries “obviously described and suggested that a DNA aptamer-based particle could be a promising lead contender for anticancer treatment.”
More information: Madhu Biyani et al, Novel DNA Aptamer for CYP24A1 Inhibition with Enhanced Antiproliferative Activity in Cancer Cells, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c22965