The period during and after medical clinic consolidations and acquisitions is a particularly weak time for patient information whenever the opportunity of a network safety break dramatically increases, as per research by a College of Texas at Dallas doctoral understudy.
Simply the declaration of a consolidation is sufficient to set off expanded information breaks, said Nan Forebearing, a Ph.D. competitor in financial matters in the School of Monetary, Political, and Strategy Sciences.
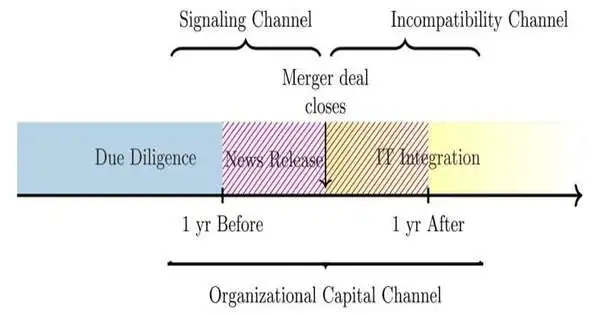
Fore bearing examined emergency clinic consolidation records and filed information break revealing from the Branch of Wellbeing and Human Administrations from 2010 to 2022 and found that in a two-year window around emergency clinic combination—one year before an arrangement is shut and one year later—the likelihood of information breaks in consolidation targets, purchasers, and venders dramatically increased.
“When two information systems are combined, hackers can take advantage. Despite the fact that most hospitals employ electronic medical record (EMR) systems, they may be from different vendors and have varied features.”
Clement’s Ph.D. advisor.
The likelihood of an information break during the two-year window was 6%, compared to a 3% likelihood of an information break for emergency clinics that converged throughout the informational index but were not inside the two-year window.
“The time paving the way to and following the consolidation bargain marking is for sure a more dangerous period,” Lenient said.
In July in Geneva, Lenient introduced her examination in a companion exploration paper at The 22nd Studio on the Financial Matters of Data Security, a gathering for an interdisciplinary grant on data security and protection. Her work was singled out for the Best Paper Grant.
Merciful expressed that while it is widely known in the network safety and medical services ventures that consolidations are a delicate time for information weaknesses, the impact she found is sensational.
“Consolidations are a period that we ought to zero in on and pursue security arrangements,” she said.
Dr. Daniel G. Arce, Ashbel Smith Teacher and program head of financial matters, said Forgiving’s exploration is significant in light of the fact that it digs into the reasons for network safety breaks as opposed to simply relationships.
“Now that ransomware has turned into a major event hunting peculiarities and medical clinics are carefully targeted, lives are yet to be determined,” said Arce, who is Merciful’s Ph.D. counsel.
Merciful likewise found that hacking and insider wrongdoing expanded when a clinic consolidation or securement was reported, even before any arrangements were made or the union of assets started. Utilizing information from Google Patterns, she tracked down an association between expansions in searches for an objective clinic’s name and expansions in the hacking movement, which she said may be connected to expanded media consideration of the impacted emergency clinics.
Inconsistency between the two medical clinics’ data frameworks can also prompt hackers to exploit weaknesses.
“At the point when you consolidate two data frameworks, that is a period that programmers can make use of,” Lenient said. “Although most emergency clinics utilize electronic clinical record (EMR) frameworks, they could emerge out of various merchants and have various highlights.”
Ransomware assaults, which disturb medical service administrations, happen all the more regularly during this timeframe too, she noted, and understanding the explanations behind the enormous scope of information breaks in the medical care industry is especially critical to keeping away from general wellbeing crises and keeping up with monetary market dependability.
“Medical clinics are the basic framework that contacts each American,” Lenient said. “Imagine a scenario where there’s a basic medical procedure required, but unexpectedly there’s a ransomware assault, and everything is down, and the next closest emergency clinic is 100 miles away,” she said. “I’m centered around tracking down accepted procedures for shielding medical clinic information from ransomware assaults and hacking; however, tragically, I don’t figure we can 100 percent forestall information breaks or hacking exercises.”
Provided by University of Texas at Dallas