A study conducted at the University of So Paulo (USP) in Brazil and depicted in an article published in the journal Logical Reports suggests that calming drugs commonly used by children may be linked to dental polish deformities (DEDs), which are currently seen in around 20% of children worldwide.
The researchers, who collaborated with the Ribeiro Preto Dental School (FORP-USP) and School of Drug Sciences (FCFRP-USP), investigated the effects of celecoxib and indomethacin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), as the first step on the pain-relieving stepping stool, followed by paracetamol.
Recently, dental specialists at FORP-USP’s Dental Veneer Center, who investigate and manage the issue on a regular basis, have noticed a significant increase in the number of children seeking treatment for torment, white or yellow tooth spots, and dental responsiveness and delicacy.At times, basic biting can crack the kids’ teeth. Every one of these are old-style side effects of DEDs of the sort known as polish hypomineralization, whose causes are inadequately perceived.
“These significant findings were only possible due to the efforts of FORP-Dental USP’s Enamel Clinic and collaboration with Lcia Helena Faccioli, a professor at FCFRP-USP. She made an important contribution to our understanding of the role of lipidic mediators in inflammatory disorders of the teeth.”
Francisco de Paula-Silva, a professor in FORP-USP’s Pediatric Department.
Because of this issue, dental rot as well as carious sores show up sooner and more regularly in these patients, whose reclamations are less gluey and will generally bomb more. Studies have shown they might need to supplant restorations multiple times more frequently over a long period than individuals with sound teeth.
A particular incident stirred the scientists’ interest in particular: the patients’ ages. The main periods of life when DEDs structure are when the disorder is regular, frequently with high fever.
“These illnesses are commonly treated with NSAIDs, which hinder the action of cyclooxygenase [COX, a key fiery enzyme] and lessen the creation of prostaglandin [which likewise advances inflammation],” said Francisco de Paula-Silva, a teacher in FORP-USP’s Pediatric Division and last writer of the article. “Nonetheless, COX and prostaglandin are known to be physiological for dental polish, and we hence contemplated whether these medications meddled in the typical arrangement of this design.”
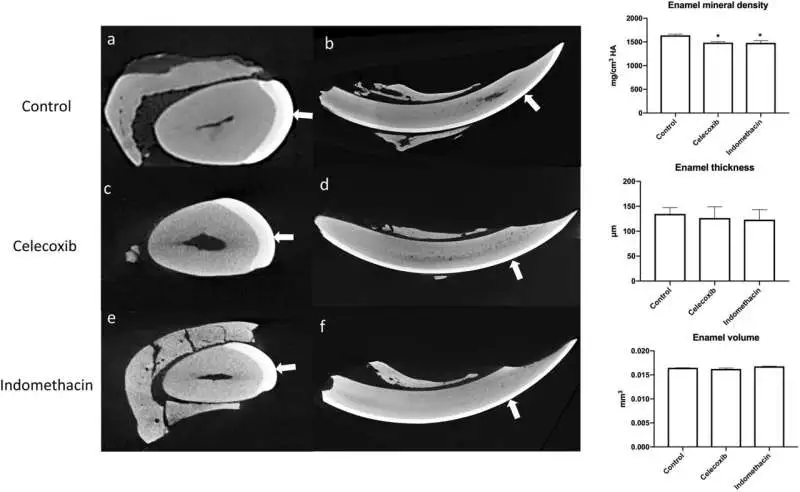
Miniature figured examination (CT) of mandibular incisors Hub pictures (a, c, and e) show the polish layer of the three gatherings. The adult veneer portion, which will emit in the oral pit, is depicted in the sagittal images (b, d, and f) with white bolts.
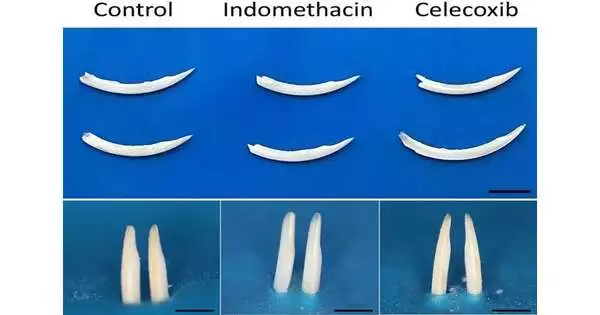
The analysts utilized rodents to concentrate on the issue, as these creatures have incisors that develop constantly, which works with examination. The rodents were treated with celecoxib and indomethacin for 28 days, after which basically no distinctions in their teeth were apparent to the unaided eye. Nonetheless, when the analysts started removing the teeth, they found that the teeth broke more easily without any problem.
An examination in view of imaging and the compound piece proposed that dental mineralization had been impacted. The teeth contained below-average amounts of calcium and phosphate, which are vital to dental finish arrangement, and mineral thickness was low.
When the analysts investigated the reasons for this, they discovered changes in proteins expected for mineralization and cell separation, indicating that the medications had undoubtedly influenced the piece of dental polish.
Following stages
“At this moment, the concentrate basically offers us a sign of the character of another player that might be engaged in the improvement of DEDs.” “Until now we’ve been absolutely in obscurity,” said Paula-Silva. “We just accomplished these significant discoveries because of the endeavors of FORP-USP’s Dental Polish Center and cooperation with Lcia Helena Faccioli, a teacher at FCFRP-USP. She made a vital commitment to how we might interpret the pretended “lipidic go-betweens” connected with fiery illnesses that influence teeth.
The gathering intends to lead a clinical report fully intent on confirming the outcomes of the creature model exploration.”We will examine the clinical history of the kids with DEDs and their utilization of these medications, and we’ll set up a clinical report that will relate the two datasets to check whether exactly the same thing happens to people.” Assuming this is correct, we can make recommendations regarding which medications should not be used for which patients.”We can likewise assist with working out a proper treatment convention in the future,” said Paula-Silva, contrasting this present circumstance with that of antibiotic medication, an anti-toxin not suggested for kids since it causes tooth staining.
One more significant highlight that should be addressed is the unpredictable utilization of non-prescription medications, an issue that seems to have deteriorated as pediatric consideration has become more normalized, although substantial data on this isn’t yet accessible.
More information: Juliana de Lima Gonçalves et al, Enamel biomineralization under the effects of indomethacin and celecoxib non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Scientific Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19583-w
Journal information: Scientific Reports