Nanophotonic light producers are conservative and adaptable gadgets with boundless applications in applied material science. Ki Youthful Lee and an investigation group in physical science and design in China and the UK propose to foster a topological pillar producer construction of submicron-sized images with high effectiveness and versatile bar molding limits in another report currently distributed on Science Advances.
The proposed gadget worked with a profoundly attractive and effective microlight producer to identify different applications, including shows, strong state light discovery, optical interconnects, and media communications.
Photonic topological peculiarities
Topological connection point states have a phenomenally high resistance to natural unsettling influences with exceptional actual properties.Numerous analysts in arithmetic and photonics have broadly examined the photonic topological peculiarities because of their commitment across broadcast communications, information handling, and sensor applications.
In this review, Lee and partners investigated novel far-field optical properties related to non-Hermitian topological photonics. They demonstrated how a topological intersection metasurface composed of two directed mode reverberation gratings can function as capable submicron scale light producers with high quantum productivity and a versatile shaft forming limit.
During the trials, the group utilized an intersection containing two unmistakable directed mode full gratings that were contiguous to each other without any gaps. In such designs, the flawed Jackiw-Rebbi (JR) state at the intersection—which compares to a generally significant relativistic model—discharged a tight light emission. The cycle was driven by pit quantum electrodynamic coupling and electromagnetic channeling impacts. During the review, the group investigated a basic hypothesis of topological bar outflow and directed thorough mathematical examinations.
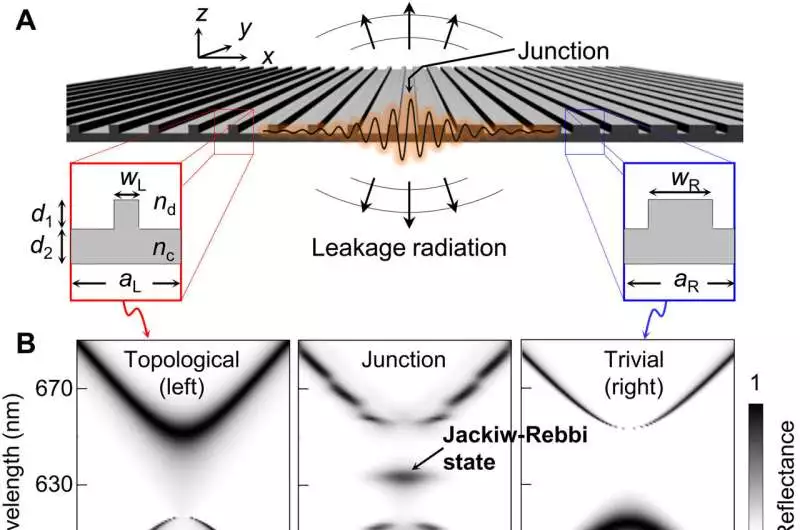
Principal properties of the cracked JR state in a topological intersection metasurface (A) Diagram of a topological intersection formed by two distinct slight film subwavelength gratings.(B) Point subordinate reflection spectra for the left unit cell in the topological stage (left), the right unit cell in the minor stage (right), and their intersection (center). (C) Electric field plentifulness Ey of the broken JR state at frequency JR = 633 nm We utilize the limited component technique (Comsol Multiphysics) for this estimation.
Spillage radiation from a Jackiw-Rebbi (JR) state
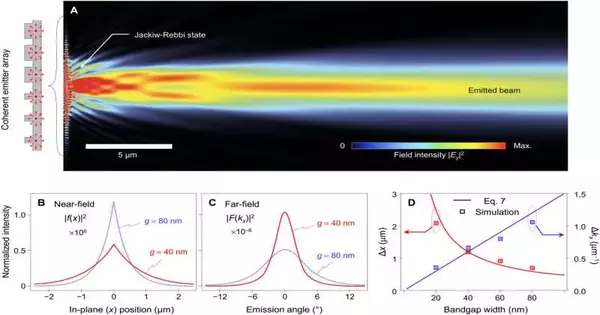
Lee et al. studied the defective JR state confined at a photonic topological intersection metasurface with a high-record film. Under unambiguous circumstances, the first-request diffraction from the JR state prompted bar spillage radiation towards the encompassing foundation, empowering trademark elements of spillage radiation to be assembled during the review.
In view of the restricted shaft discharge related to the flawed JR Express, the group examined the emanation properties of light sources close to the topological intersection. The radiation design, which showed a thin pillar transmitted in the optical far field, was created using the limited component technique.The group then revealed the possibility of designing a suitable structure, in which two grinding locales would have indistinguishable Dirac masses to achieve ideal evenness of the transmitted bar.
During these investigations, the tight shaft emanation from isotropic light sources followed the specific diffraction properties of radiation spillage from the JR state. The group also looked for outside hotspots for the proposed radiating impact, which they accomplished by acquainting changes with the trial arrangement, for example, a decreased file contrast and in an upward direction coupled multi-facet waveguides, among other changes.
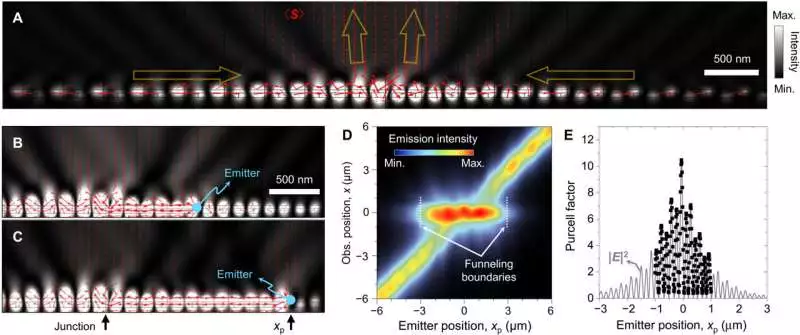
Electromagnetic channeling and Purcell upgrade of inside sources (A) Distribution of optical power-stream (time-normal Poynting vector St; red bolts) for a topological intersection with bandgap size g = 40 nm for close field force conveyance (dark level thickness).(B and C) An optical power stream energized by a solitary isotropic source located 1 and 2 m away from the intersection (xP = 1 and 2 m), individually (D) Source-position (xP): subordinate far-field power circulation on a perception plane 3.5 m over the grinding surface as an element of xP. (E) Purcell considers the appropriation correlation with the JR state’s close field force dissemination.
Dirac mass control is used to level top pillar age.(A) Dissemination of Dirac mass m(x) for level top bar ageIt has three levels at m′ = 0.634, 0, and +0.635 m1, and related JR state power profiles and produced bar profiles are plotted together for references. (B) Electric field power Ey2 design from the construction configuration in light of the Dirac mass dissemination in (A). The gadget structure in this reenactment has three grinding areas of various fill factors at F = 0.264, 0.46, and 0.7, compared to the three Dirac mass levels.
Versatile pillar molding
The idea of pillar molding is significant for the majority of general uses of light sources. The depicted topological radiating impact allows for direct control of the shaft shape from the source. The researchers portrayed the Dirac mass dissemination expected to produce the normal pillar profile.
For example, to produce a level top shaft, a zero Dirac mass district can be broadened—aacross the ideal width and around the intersection of the gadget. The results of the directed mode reverberation Dirac mass guideline can subsequently be productively applied to shaft molding applications.
Viewpoint
Along these lines, Ki Youthful Lee and partners proposed a topological intersection metasurface for effective pillar emanation. They used hole quantum electrodynamics coupling with electromagnetic piping impacts to achieve productive light radiating from inner producers by mimicking the trademark field conveyances of a defective Jackiw-Rabbi state at the intersection.
The proposed design is vital for the making of effective miniature light producers because it provides solid limitation, high quantum proficiency, and versatile bar molding limits. These properties are critical for various applications, including the improvement of show pixels, laser machining, and media communications applications. Because of their capacity to function as time-turned around producers, the proposed gadgets are also well-suited for use as effective optical locators. The researchers propose that the review results be improved further to foster new optical effects and corresponding gadget applications that outperform any current specialized limits.
More information: Ki Young Lee et al, Topological beaming of light, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add8349
Alexander Cerjan et al, Experimental realization of a Weyl exceptional ring, Nature Photonics (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41566-019-0453-z