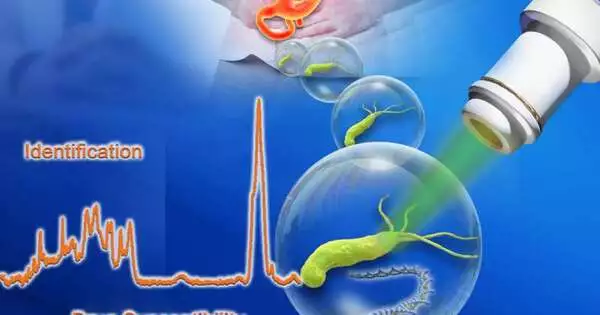
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), the microscopic organisms that can cause human gastritis, peptic ulcers and stomach disease, contaminates about portion of the total populace. It is fundamental to distinguish the disease and select the right blend of delicate anti-microbials rapidly. Current apparatuses, nonetheless, are restricted, principally on the grounds that H. pylori are slow-developing and difficult to develop.
Scientists from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their partners at State Key Laboratory of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention (ICDC) of China CDC and Qingdao Municipal Hospital have fostered a clinical instrument called Clinical Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Ramanometry for Helicobacter pylori (CAST-R-HP) that holds guarantee as a strong new device in the determination and treatment of H. pylori contaminations.
Their discoveries were distributed on June 18 in the diary Clinical Chemistry.
“The present culture-based antimicrobial susceptibility testing is very slow and takes at least a week to complete,”
Prof. Zhang Jianzhong from the State Key Laboratory of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control
In engaging H. pylori, specialists and medical services experts need devices that are quick, dependable and touchy for microbe ID and antimicrobial weakness tests, alongside extensive change profiling that uncovers the microorganisms’ obstruction systems.
Current techniques for distinguishing H. pylori and distinguishing touchy anti-infection agents for destruction treatment are bacterial culture and medication awareness testing in light of endoscopic gastric mucosal examples.
“The ongoing society based antimicrobial helplessness testing is excessively sluggish and expects basically seven days of completion time,” said Prof. Zhang Jianzhong from the State Key Laboratory of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control, ICDC of China CDC, a senior creator of the review.
The group has concocted a methodology that performs quick microorganism ID, digestion restraint based antimicrobial weakness tests, and great single-cell entire genome sequencing for divulging antimicrobial obstruction systems. Their methodology gives more noteworthy than 98% exactness and is fruitful at exact one-cell goal working straightforwardly from biopsy tests.
The center advances, called D2O-tested Ramanometry and Raman-enacted Cell Sorting and Sequencing (RACS-Seq), are coordinated in the CAST-R-HP instrument.
“The way of life independency, speed, high goal and extensive data yield propose CAST-R-HP as an incredible asset for determination and treatment of H. pylori contaminations, presently at single-cell accuracy,” said Xu Jian, one more senior creator of the review and Director of Single-Cell Center at QIBEBT.
Looking forward to future examination, the group will investigate ways of facilitating speed up the CAST-R-HP, for instance, by fostering a microfluidics-based chip to improve the follow number of cells straightforwardly from the H. pylori tainted biopsy tissue. This chip advancement could additionally decrease the time required to circle back of the metabolic-restraint based antimicrobial powerlessness test from approximately three days to under 24 hours.
“Our subsequent stage is completely survey the utility of the work process for all the first-line and second-line anti-toxins being used for the treatment of H. pylori diseases,” said Liu Min from the Single-Cell Center at QIBEBT, the main creator of the paper.
The group’s CAST-R-HP could likewise be utilized to plan H. pylori heterogeneity at the genome level. “By empowering distinguishing proof, drug defenselessness tests, and entire genome-based source following at single-cell goal, CAST-R-HP shouldn’t simply work with exact anti-infection organization for H. pylori contamination, yet decrease the gamble of medication opposition in the overall human populaces,” added Xu Jian.
More information: Min Liu et al, Single-Cell Identification, Drug Susceptibility Test, and Whole-genome Sequencing of Helicobacter pylori Directly from Gastric Biopsy by Clinical Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Ramanometry, Clinical Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/hvac082