People are predisposed to reason about how various actual items in their environment behave.These actual thinking abilities are amazingly important for tackling regular issues, as they can assist us with picking more viable activities to accomplish explicit objectives.
Some PC researchers have been attempting to repeat these thinking skills in man-made reasoning (man-made intelligence) specialists to work on their exhibition on unambiguous errands. Up to this point, nonetheless, a solid way to train and survey the actual thinking capacities of man-made intelligence calculations has been lacking.
Cheng Xue, Vimukthini Pinto, Chathura Gamage, and partners, a group of scientists at the Australian Public College, have as of late presented Phy-Q, a new testbed intended to fill this hole in the literature. Their testbed, presented in a paper in Nature Machine Knowledge, incorporates a progression of situations that explicitly survey a man-made intelligence specialist’s actual thinking capacities.
“Physical reasoning is a key feature for AI agents to operate in the real world, and we discovered that there are no complete testbeds and a measure to evaluate AI agents’ physical reasoning intelligence,”
Vimukthini Pinto
“Actual thinking is a significant capacity for man-made intelligence specialists to work in reality, and we realized that there are no complete testbeds and an action to assess man-made intelligence specialists’ actual thinking knowledge,” Pinto told Tech Xplore.”Our primary goals were to present a specialist cordial testbed alongside an action for actual thinking knowledge, assessing the most recent man-made intelligence specialists alongside the general population for their actual thinking capacities, and giving direction to the specialists in the AIBIRDS rivalry, a long running contest for actual thinking held at the IJCAI and coordinated by Prof. Jochen Renz.”
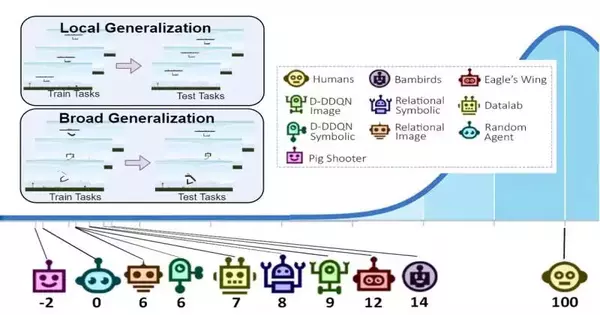
The Phy-Q testbed contains 15 different actual thinking situations that attract motivation from the circumstances in which babies get their actual abilities to think and the true cases in which robots could have to utilize these capacities. For each situation, the scientists made a few supposed “task layouts,” modules that permit them to gauge the generalizability of a man-made intelligence specialist’s abilities in both nearby and more extensive settings. Their testbed incorporates a total of 75 errand formats.
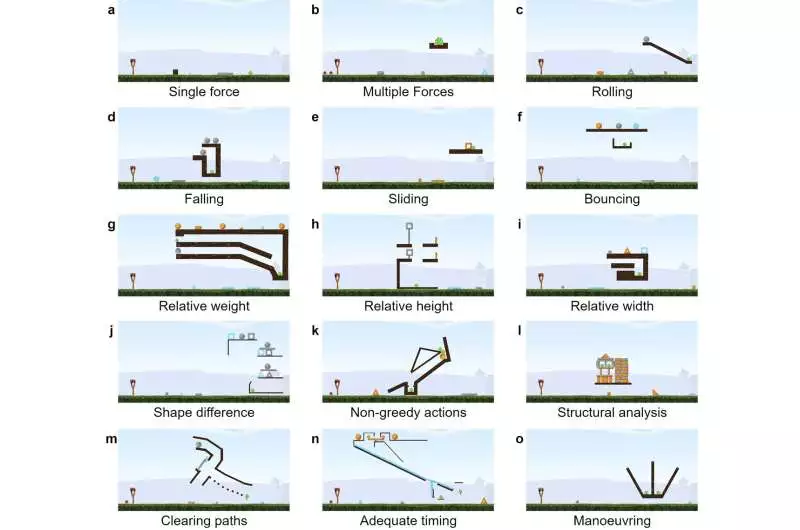
Screen captures of model errands in Phy-Q addressing the 15 actual situations The slingshot with birds is arranged on the left of the errand. The objective of the specialist is to kill every one of the green pigs by shooting birds from the slingshot. The dim, earth-colored objects are static stages. The items with different varieties are dynamic and dependent upon the physical science of the climate.
“Through nearby speculation, we assess the capacity of a specialist to sum up inside a given errand layout, and through wide speculation, we assess the capacity of a specialist to sum up between various undertaking formats inside a given situation,” Gamage made sense of. “In addition, we measure the Phy-Q, the actual thinking remainder, an action triggered by the human intelligence level, in addition to joining the broad speculation execution in the 15 actual situations.”
The scientists demonstrated the viability of their testbed by utilizing it to run a progression of man-made intelligence specialist assessments. The aftereffects of these tests propose that the actual thinking abilities of man-made intelligence specialists are still definitely less advanced than human capacities, hence there is as yet a huge opportunity to get better around here.
“From this review, we saw that the man-made intelligence frameworks’ actual thinking abilities are far beneath the level of people’s capacities,” Xue said. “Also, our analysis shows that specialists with high nearby speculation capacity struggle to learn the fundamental actual thinking rules and fail to thoroughly summarize. We now welcome individual analysts to use the Phy-Q testbed to improve their natural thinking artificial intelligence frameworks.”
The Phy-Q testbed could before long be utilized by scientists overall to efficiently assess their man-made intelligence model’s actual thinking capacities across a progression of actual situations. This could thus assist engineers with recognizing their models’ assets and shortcomings so they can further develop them likewise.
In their next examinations, the creators intend to join their actual thinking testbed with open-world learning. The last option is an emerging research area that focuses on working on the capacity of man-made intelligence specialists and robots to adjust to new circumstances.
“In reality, we continually experience novel circumstances that we have not encountered previously, and as people, we are able to adjust to those clever circumstances effectively,” the creators added. “Also, for a specialist who works in reality, it is critical to have capacities to identify and adjust to novel circumstances, in addition to actual thinking abilities.” “As a result, our future research will focus on advancing the development of artificial intelligence specialists who can perform real-world thinking tasks in a variety of novel situations.”
More information: Cheng Xue et al, Phy-Q as a measure for physical reasoning intelligence, Nature Machine Intelligence (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s42256-022-00583-4