A group of scientists, including individuals from Peking College and WuXi AppTec (Tianjin) Co., Ltd., has planned and fabricated a robotized carbohydrate synthesizer that creates polysaccharides of record-breaking length. In their paper distributed in the diary Nature Blend, the gathering depicts how they assembled their gadget and its potential purposes. Hanchao Cheng and Peng George Wang with the Southern College of Science and Innovation in China, have distributed a News and Perspectives piece in a similar diary issue framing the work by the group in China.
As Cheng and Wang note, carbs play a vital part in science—they are a biochemical wellspring of energy. Furthermore, as they likewise note, normally occurring carbs will generally be primarily vague, and that implies they are comprised of combinations of atoms, making them very intricate.
Thus, obvious carbs are valued. Sadly, blending them has been shown to be troublesome, especially as they become bigger. In this new effort, scientists have devised a method for accelerating the cycle—a robotized synthesizer—one that beats issues related to different machines intended to do likewise.
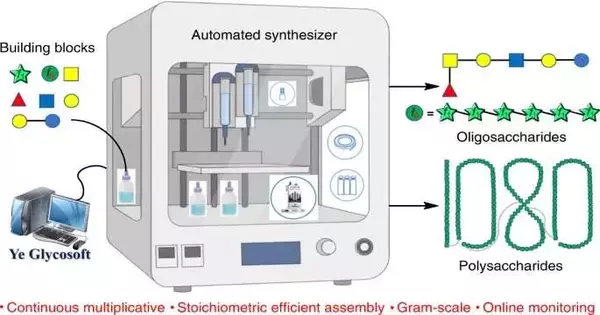
The synthesizer made by the group has three sections: a blending framework, a framework for checking progress, and programming that is utilized to control the equipment. The synthesizer includes a stirrer, intensity controls, and a light that is utilized to impel light-induced responses.
It also has a robotized injector framework for controlling material conveyance into the framework and a mechanized cleaning framework to avoid contamination.The synthesizer works by PC controlling the progression of reagents into a holder and dealing with the development of snake-like monosaccharides. The checking framework constantly concentrates on the responses that are occurring to ensure they are being done accurately.
One of the upsides of utilizing such a framework, Cheng and Wang note, is that it has no requirement for safeguarding gatherings, which are veils utilized on receptive parts. In manual cycles, such gatherings will generally add additional moves toward the cycle, making it more muddled.
The outcome is improved yields and longer glycans. Testing of the gadget showed it was fit for making polysaccharides comprised of 1,080 sugar moieties, which included 4,320 stereo genic focuses — the longest kind of glycan blended to date. The group utilized their gadget to make a few medications that are now available in a more effective way.
More information: Wenlong Yao et al, Automated solution-phase multiplicative synthesis of complex glycans up to a 1,080-mer, Nature Synthesis (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s44160-022-00171-9
Hanchao Cheng et al, Machine assembly of carbohydrates with more than 1,000 sugar units, Nature (2022). DOI: 10.1038/d41586-022-02927-x
Journal information: Nature Synthesis , Nature