Despite the fact that blockchain is best known for facilitating computerized cash transfers, scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Edge Public Lab are utilizing it to track a different type of trade: it is the first time blockchain has been used to approve correspondence among gadgets on the electric matrix.
The task is critical for the ORNL-led Darknet drive to gain control of the country’s power structure by gradually shifting its exchanges to acquire strategies.
Digital dangers have grown as a result of two-way communication between matrix power gadgets and gear, as well as new cutting-edge gadgets ranging from solar-powered chargers to electric vehicle chargers and smart home hardware.By giving a trust system to correspondence among electrical gadgets, an ORNL research group led by Raymond Borges Hink is expanding the strength of the electric matrix.
“This architecture provides us with a completely new power to respond to anomalies in real time. In the long term, we could detect an illegal system change faster, track down its source, and provide more reliable failure analysis. The purpose is to mitigate the impact of a cyberattack or equipment failure.”
Raymond Borges Hink
The group fostered a system to identify strange actions, including information control, mocking, and illegal changes to gadget settings. These drills could cause rolling blackouts as breakers are thwarted by security devices.
“This system gives us an absolutely new capacity to quickly answer oddities,” Borges Hink said. “Over the long haul, we could more rapidly recognize an unapproved framework change, track down its source, and give a more reliable disappointment examination. The objective is to restrict the harm brought about by a cyberattack or gear disappointment.”
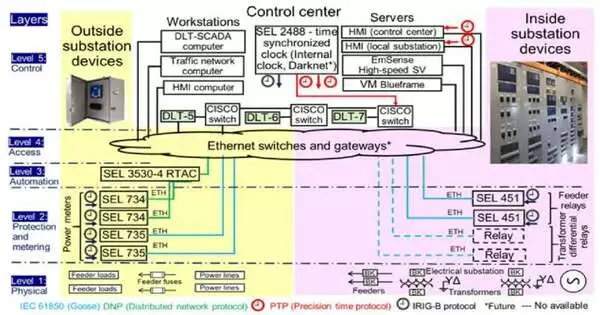
The methodology utilizes an altered-safe blockchain to spread setup and functional information needlessly across various servers. The information and gear settings are continually checked against a factual gauge of typical voltage, recurrence, breaker status, and power quality. Gear settings are gathered at regular intervals and contrasted with the last great setup saved in the blockchain. This permits fast acknowledgment of when and how settings were changed, whether those changes were approved, and what caused them.
“Our framework decides in close proximity to ongoing issues whether an issue was triggered by a cyberattack or by normal events,” Borges Hink explained.”This is the main execution of blockchain empowering such an information approval between a substation, a control place, and a metering framework.”
This sort of checking requires handling a huge amount of data. The blockchain utilizes a cryptographic strategy called hashing, where a numerical calculation is performed on the mass information to address it as numbers in the blockchain. This recovers energy and reduces the space expected to store information. The blockchain processes many exchanges each second for each keen matrix gadget, approving the items.
Scientists showed the system in a proving ground inside DOE’s Matrix Exploration and Mixing Center, or Network C, at ORNL. Under the authority of ORNL’s Emilio Piesciorovsky, the high-level security lab involves business-grade equipment in a closed electrical circle to copy the design of a genuine substation.
This is an okay method for mimicking cyberattacks or unplanned misconfigurations. The group’s approval system can identify both. Analysts are stretching out the way to deal with integrating interchanges among sustainable power sources and various utilities.
More information: Gary Hahn et al, Oak Ridge National Laboratory Pilot Demonstration of an Attestation and Anomaly Detection Framework using Distributed Ledger Technology for the Power Grid Infrastructure, Oak Ridge National Laboratory (2022). DOI: 10.2172/1887685