An examination group from the Graduate School of Informatics, Nagoya University, has made a major stride towards making a brain network with metamemory through a PC-based development try. Their paper shows up in Scientific Reports.
Lately, there has been quick advancement in planning computerized reasoning innovations utilizing brain networks that emulate mind circuits. One objective of this field of exploration is understanding the development of metamemory to utilize it to make computerized reasoning with a human-like brain.
Metamemory is the interaction by which we find out if we recall what we had for supper yesterday and, afterward, utilize that memory to choose whether to eat something else this evening. While this might appear to be a straightforward inquiry, note that it includes a mind-boggling process. Metamemory is significant on the grounds that it affects an individual’s knowledge of their own memory capacities and changes their way of behaving likewise.
“Understanding metamemory is critical for elucidating the evolutionary underpinnings of the human mind and consciousness, A fully human-like artificial intelligence, which can be engaged with and enjoyed like a family member in a person’s home, is one that has some metamemory, or the ability to remember things it has previously heard or learnt.”
lead author Professor Takaya Arita.
According to lead creator Professor Takaya Arita, understanding metamemory is critical to clarifying the transformative premise of the human psyche and awareness.”A genuinely human-like man-made consciousness, which can be connected with and delighted in like a relative in an individual’s house, is computerized reasoning that has a specific measure of metamemory, as it can recollect things that it once heard or learned.”
While considering metamemory, scientists frequently utilize a “postponed matching-to-test task.” In people, this undertaking comprises of the member seeing an item, like a red circle, recalling it, and afterward participating in a test to choose what they had recently seen from numerous comparable items. Right responses are compensated and wrong responses are rebuked. Nonetheless, the subject can decide to avoid the test regardless to procure a more modest prize.
A human playing out this errand would normally utilize their metamemory to consider the event in the event that they saw the item. Assuming that they recollected it, they would step through the exam to get the greater prize, and assuming they were uncertain, they would try not to gamble with the punishment and get the more modest award, all things considered. Past investigations detailed how monkeys could carry out this undertaking too.
The Nagoya University group, including Professor Takaya Arita, Yusuke Yamato, and Reiji Suzuki of the Graduate School of Informatics, made a fake brain network model that played out the deferred matching-to-test task and broke down how it acted.
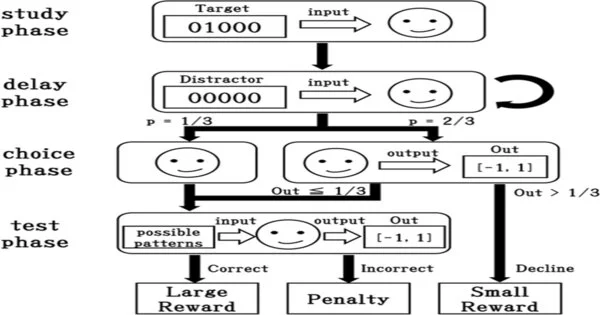
The deferred match-to-test task presented the departure choice. Image courtesy of Scientific Reports (2022).DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10173-4
Regardless of beginning from irregular brain networks that didn’t actually have memory work, the model had the option to develop to the point that it performed in basically the same manner as the monkeys in past examinations. The brain organization could analyze its recollections, keep them, and separate the results. The knowledge had the option to do this without needing any support or mediation by the scientists, proposing its credibility as having metamemory components. “The requirement for metamemory relies upon the client’s current circumstance.” “Subsequently, man-made consciousness should have a metamemory that adjusts to its current circumstance by learning and developing,” says Professor Arita of the finding. “The central issue is that man-made brainpower learns and develops to make a metamemory that adjusts to its current circumstances.”
Making versatile knowledge with metamemory is a major advance towards gaining machines that have an experience like our own. The group is energetic about what’s to come: “This accomplishment is supposed to give hints to the acknowledgment of computerized reasoning with a ‘human-like brain’ and even cognizance.”