Humble potatoes are a rich source of dietary carbohydrates for people and, additionally, of starches for various modern applications. Texas A & M AgriLife researchers are figuring out how to modify the proportion of potatoes’ two starch atoms — amylose and amylopectin — to increase both culinary and modern applications.
For instance, waxy potatoes, which are high in amylopectin content, have applications in the creation of bioplastics, food additives, cements, and liquor.
“The information and knowledge gathered from these two trials will assist us in introducing other desirable features in this extremely important crop.”
Rathore
Two articles as of late published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences and the Plant Cell, Tissue, and Organ Culture diaries frame how CRISPR innovation can propel the purposes of the world’s biggest vegetable harvest.
The two papers incorporate the work done by Stephany Toinga, Ph.D., who was an alumni understudy in the lab of Keerti Rathore, Ph.D., an AgriLife Research plant biotechnologist in the Texas A&M Institute for Plant Genomics and Biotechnology and Department of Soil and Crop Sciences. Likewise, co-writing the two papers was Isabel Vales, Ph.D., an AgriLife Research potato raiser in the Texas A & M Department of Horticultural Sciences. Toinga is presently a Texas A & M AgriLife Research postdoctoral partner with Vales.
“The data and information we acquired from these two examinations will assist us with presenting other helpful attributes in this vital harvest,” Rathore said.
Potato realities
Potatoes are the No. 1 vegetable yield overall and the third most significant human food crop, just behind rice and wheat in the world. Potatoes are grown in the north of 160 nations on 40.8 million sections of land and act as a staple nourishment for in excess of a billion people.
Rathore said. With a medium-sized potato providing roughly 160 calories, for the most part gotten from starch, the tubers comprise a significant energy hotspot for some individuals around the world. Potatoes additionally provide other essential supplements, including nutrients and minerals.
Tubers from one of the altered lines of potatoes in the Texas A & M AgriLife study. If these are planted in soil, they will grow into a typical potato plant with normal-sized tubers.Photo courtesy of Texas A&M AgriLife/Stephany Toinga
Potatoes are a cool-season crop that is generally delicate to intensity and dry spell pressure. The harvest likewise experiences irritations, for example, Colorado insects, aphids, and nematodes, as well as sicknesses including early and late curse, zebra chip, Fusarium dry decay, and various viral illnesses. The late scourge was the reason for the Irish potato starvation.
Starch is key for both dietary and modern purposes.
How much starch is in potato tubers is the fundamental variable that decides a potato’s utilization. According to Vales, high-starch potatoes are frequently used to make processed food sources such as French fries, chips, and dried out potatoes.
She said potatoes with low to medium starch levels are regularly utilized for the new or table financial exchange. For the new market, extra significant contemplations are tuber appearance, including skin surface, skin tone, tissue tone, and tuber shape. As of late, specialty potato types with various shapes, like fingerlings; more modest sizes; and red, purple, or yellow skin and tissue tones are becoming well known in light of their comfort in cooking and expanded health benefits.
Potato tuber shape is less significant for modern purposes than it is for human utilization, Vales said. Potato tubers with outer disfigurements brought about by intensity or dry season pressure or different elements can be diverted to heap uses, including nourishment for canines and cows. Furthermore, potato starch can deliver ethanol for fuel or in drinks like vodka; a biodegradable substitute for plastics; or glues, covers, surface specialists, and fillers for drugs, material, wood and paper ventures, and different areas.

For modern applications, the amount and kind of starch in a potato are significant considerations.
Toinga said starches higher in amylopectin are attractive for handling food and other modern applications because of their remarkable useful properties. For instance, such starches are the favored structure for use as a stabilizer and thickener in food items and as an emulsifier in salad dressings. In view of its freeze-defrost soundness, amylopectin starch is utilized in frozen food sources. Also, potatoes rich in amylopectin starch yield higher ethanol levels compared with those with different starches.
The advantages of reproducing potatoes with select starches
Toinga said that creating potato cultivars with changed starch could open new doors. Potatoes with high amylopectin and low amylose, similar to the quality altered Yukon Gold strain she depicted in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, have modern applications beyond customary purposes.
Interestingly, potatoes with high amylose levels and low amylopectin would be attractive for human utilization, Vales said. In this way, amylose behaves like fiber and doesn’t free glucose as effectively as amylopectin, in this way bringing about a lower glycemic index and making potatoes more satisfactory for individuals with diabetes.
A knockout line in culture that has delivered little potatoes called microtubers. Photo courtesy of Texas A&M AgriLife/Stephany Toinga
CRISPR/Cas9 makes new choices.
CRISPR/Cas9 innovation has extended the toolset accessible to reproducers, Vales said, and it addresses a more straightforward, quicker means to integrate wanted characteristics into popular business crop assortments. Regular reproduction is an extensive cycle that can require 10–15 years.
Furthermore, she said, because of the intricate idea of the potato genome, producing new cultivars with the right supplement of advantageous attributes is a challenge for customary rearing. Atomic reproducing has improved rearing efficiencies, and quality alteration utilizing the CRISPR/Cas9 innovation adds one more degree of refinement.
“We used the Agrobacterium technique to convey the CRISPR reagents into potatoes since it is dependable, effective, and most affordable compared with any remaining conveyance strategies,” Rathore said.
In the primary review, featured in the Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture article, a potato line containing four duplicates of gfp, a jellyfish quality that permits a fluorescence-based representation of the quality’s movement, was focused on for change utilizing the CRISPR/Cas9 framework, Toinga said.
Fundamentally, this venture gave a simple to-see attribute that empowered specialists to upgrade the system.
“Loss of the trademark green fluorescence and sequencing of the gfp quality following CRISPR treatment showed that it is feasible to upset every one of the four duplicates of the gfp quality, subsequently affirming that it ought to be feasible to change each of the four alleles of a local quality in the tetraploid potato,” Rathore said.
A superior Yukon Gold cultivar.
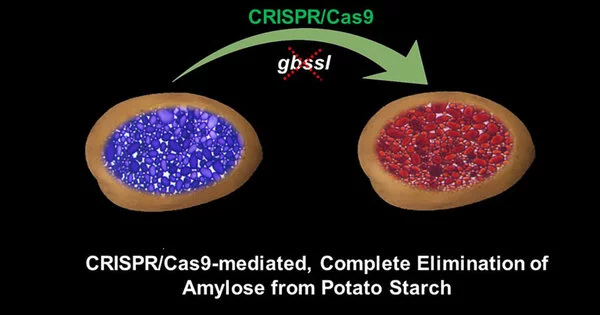
Among the different potato cultivars assessed in the primary review, the Yukon Gold strain recovered the best, so it was utilized for the subsequent review. In the subsequent knockout review, described in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the local quality gbss in the tetraploid Yukon Gold strain was focused on to really dispense with amylose. The outcome was a potato with a starch rich in amylopectin and low in amylose.
“One of the knockout occasions, T2-7, showed ordinary development and yield qualities, but was totally without any trace of amylose,” Toinga said.
That tuber starch, T2-7, could track down modern applications in the paper and material areas such as cements and fasteners, bioplastics, and ethanol ventures. Tuber starch from this trial strain, as a result of its freeze-defrost steadiness without the requirement for substance changes, ought to likewise be valuable in delivering frozen food sources. Potatoes with amylopectin as the restrictive type of starch ought to yield more ethanol for modern use or to make cocktails.
As the subsequent stage for these examinations, the T2-7 strain has been self-pollinated and crossed with the Yukon Gold strain contributor and other potato clones to wipe out the transgenic components.