Both Rocky and Icy Bodies Were Identified Among the Debris on the Surface of a White Dwarf Star.
“Draw out your dead!” rings in the air in the exemplary film “Monty Python and the Holy Grail,” a happy lined up with what’s going on around a white small star in a close by planetary framework. The dead star is “ringing” its own chime, shouting to the “dead” to gather at its strides. The white, diminutive person is all that remains after a sun-like star has depleted its atomic fuel and removed the majority of its external material, pulverizing objects in the planetary framework that circle it. What’s left is a band of players with capricious circles that, regardless of fights that they “aren’t dead yet!”, will at last be caught by the focal star.
How would we be aware? The bodies consumed by the star leave obvious “fingerprints”-got by the Hubble Space Telescope and other NASA observatories-on its surface. The ghostly proof shows that the white diminutive person is redirecting both rough metallic and frigid material-trash from the two its framework’s internal and external scopes. Uncovering proof of cold bodies is interesting since it suggests that a “water supply” may be normal on the edges of planetary frameworks, working on the opportunities for the development of life as far as we might be concerned.
A star’s final breaths have so viciously upset its planetary framework that the dead star abandoned, called a “white midget,” is redirecting garbage from both the framework’s internal and external compasses. This is whenever space experts first notice a small white star that is consuming both rough metallic and cold material, the elements of planets. Chronicled information from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and other NASA observatories was fundamental in diagnosing this instance of astronomical barbarianism. The discoveries assist in depicting the savage idea of advanced planetary frameworks and can educate space experts regarding the cosmetics of recently shaped frameworks.
A Dead Star Is Caught Ripping Apart a Planetary System
A star’s final breaths have so brutally disturbed its planetary framework that the dead star’s abandoned, called a “white midget,” is redirecting trash from both the framework’s inward and external compasses. This is whenever space experts first notice a small white star that is consuming both rough metallic and frigid material, the elements of planets.
Documented information from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and other NASA observatories was fundamental in diagnosing this instance of astronomical human flesh consumption. The discoveries assist in portraying the rough idea of developed planetary frameworks and can enlighten stargazers concerning the cosmetics of recently shaped frameworks.
The discoveries depend on investigating material caught by the environment of the nearby white small star G238-44. A white midget is the remaining parts of a star like our Sun after it sheds its external layers and quits consuming atomic combinations. “We have never seen both of these sorts of items accumulating on a white midget simultaneously,” said Ted Johnson, the lead specialist and late University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) single guy’s alumni. “By concentrating on these white midgets, we desire to acquire a superior understanding of planetary frameworks that are as yet unblemished.”
G238-44 Planetary System
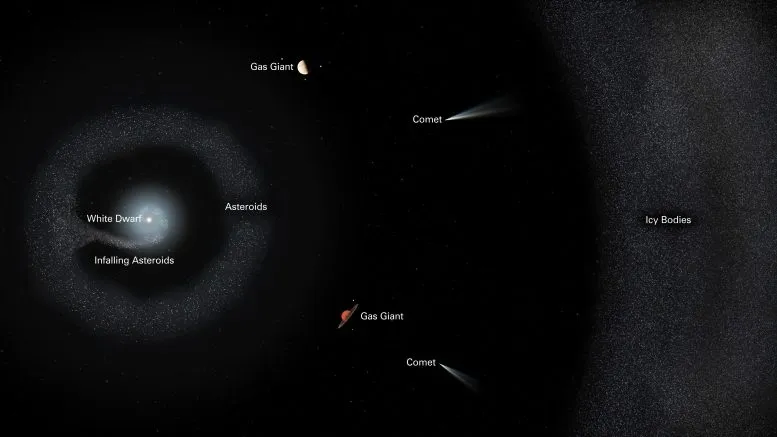
This delineated chart of the planetary framework G238-44 follows its annihilation. The small white star is at the focal point of the activity. An extremely weak growth plate is comprised of the bits of broken bodies falling onto the white, diminutive person. The excess space rocks and planetary bodies make up a repository of material encompassing the star. In any case, bigger gas monster planets might still exist in the framework. A lot further away is a belt of frigid bodies, for example, comets, which likewise eventually feed the dead star.
The discoveries are likewise captivating on the grounds that little frigid items are credited with colliding with and “watering” dry, rough planets in our planetary group. Billions of years prior, comets and space rocks are remembered to have conveyed water to Earth, starting the circumstances important for life as far as we might be concerned. The cosmetics of the bodies identified pouring onto the white bantam infers that frosty repositories may be normal among planetary frameworks, said Johnson.
“Life as far as we might be concerned requires a rough planet covered with various components like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen,” said Benjamin Zuckerman, UCLA teacher and co-creator. “The overflows of the components we see on this white person seem to require both a rough and an unpredictable rich parent body-the main model we’ve found among investigations of many white midgets.”
Destruction Derby
Speculations of planetary framework development depict the progress between a red monster star and white bantam stages as a turbulent cycle. The star rapidly loses its external layers and its planets’ circles emphatically change. Little articles, similar to space rocks and bantam planets, can wander excessively near goliath planets and be sent plunging toward the star. This study affirms the genuine size of this rough and tumultuous stage, showing that 100 million years after the start of its white bantam stage, the star can all the while catch and consume material from its space rock belt and Kuiper belt-like areas.
The assessed absolute mass at last eaten up by the white midget in this study might be something like the mass of a space rock or a small moon. While the presence of somewhere around two articles that the white diminutive person is consuming isn’t straightforwardly estimated, it’s probable one is metal-rich like a space rock and another is a frigid body like what’s found at the edge of our planetary group in the Kuiper belt.
However, cosmologists have indexed more than 5,000 exoplanets, but the main planet where we have some immediate information on its inside cosmetics is Earth. The white bantam barbarianism gives a special chance to dismantle planets and see if they were tough where it really counts when they initially conformed to the star.
The group estimated the presence of nitrogen, oxygen, magnesium, silicon, and iron, among different components. The discovery of iron in an unusually high overflow is evidence of the metallic centers of earthbound planets such as Earth, Venus, Mars, and Mercury.Startlingly high nitrogen overflows drove them to close off the presence of frigid bodies. “The best fit for our information was an almost two-to-one blend of Mercury-like material and comet-like material, which is comprised of ice and residue,” Johnson said. “Iron metal and nitrogen ice each recommend ridiculously various states of planetary development.” There is no realized nearby planet group object with so great a deal of both. “
The Passing of a Planetary System
At the point when a star like our Sun ventures into a swelled red monster late in its life, it will shed mass by puffing off its external layers. One outcome of this could be the gravitational dispersion of little objects like space rocks, comets, and moons by any excess enormous planets. Like pinballs in an arcade game, the enduring items can be tossed into exceptionally unpredictable circles.
“After the red monster stage, the white small star that remains is conservative-no bigger than Earth.” “The unpredictable planets wind up getting extremely near the star and experience strong flowing powers that destroy them, making a vaporous and dusty plate that in the long run falls onto the white bantam’s surface,” Johnson made sense of.
The analysts are checking out a definitive situation for the Sun’s development, 5 billion years from now. Earth may be completely disintegrated alongside the internal planets. However, the circles of a significant number of the space rocks in the vital space rock belt will be gravitationally irritated by Jupiter and will ultimately fall onto the white bantam that the remainder of the Sun will turn into.
For nearly two years, researchers from UCLA, the University of California, San Diego, and Kiel University in Germany have attempted to unravel this mystery by dissecting the components identified on the white small star known as G238-44. Their examination incorporates information from NASA’s retired Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE), the Keck Observatory’s High Resolution Echelle Spectrometer (HIRES) in Hawaii, and the Hubble Space Telescope’s Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) and Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS).
The group’s outcomes were introduced at an American Astronomical Society (AAS) public interview on Wednesday, June 15, 2022.
The Hubble Space Telescope is the result of a global collaboration between NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, deals with the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science activities. STScI is being worked on for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, in Washington, D.C.





