A group of specialists from the College of Warsaw in Poland, the Foundation Pascal CNRS in France, the Tactical College of Innovation in Poland and the English College of Southampton have shown that controlling the purported extraordinary points is conceivable. Interestingly, physicists observed the destruction of excellent foci from various decadence foci.You can find out about the disclosure that might add to the making of current optical gadgets in the most recent Nature Correspondences.
The universe around us is made of rudimentary particles, the vast majority of which have their antiparticles. At the point when a molecule and an antiparticle, that is to say, matter and antimatter, meet one another, destruction happens. Physicists have for quite some time had the option of delivering quasiparticles and quasiantiparticles—rudimentary excitations: charge, vibration, energy—caught in issue, most frequently in gems or fluids.
“The universe of quasiparticles can be extremely muddled, albeit strangely, the actual quasiparticles assist with improving the depiction of quantum peculiarities,” makes sense to Jacek Szczytko from the Workforce of Physical Science at the College of Warsaw.
“Without quasiparticles, it would be hard to figure out the activity of semiconductors, light-producing diodes, superconductors, and some quantum PCs. Indeed, even conceptual numerical ideas can become quasiparticles as long as they can be executed in actual frameworks. One of such unique ideas is excellent focus.
“The universe of quasiparticles can be exceedingly intricate, but ironically, the quasiparticles themselves assist simplify the understanding of quantum processes,”
Jacek Szczytko from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw.
Scholars from Establishment Pascal CNRS in France, Guillaume Malpuech and Dmitry Solnyshkov, make sense of it.
“The purported ‘extraordinary focuses’ are explicit framework boundaries prompting the shared characteristic of two distinct arrangements that can exist in frameworks with misfortunes, for example, those wherein the motions gradually blur over the long run,” says Malpuech.
“They permit the production of effective sensors, single-mode lasers, or unidirectional vehicles.” “What is significant is that each remarkable point has a non-zero topological charge—a specific numerical element that depicts the basic mathematical properties and permits you to figure out which uncommon point will be the ‘antiparticle’ for another extraordinary point,” adds Solnyshkov.
Researchers from the College of Warsaw and the Tactical College of Innovation, in collaboration with scientists from the CNRS and the College of Southampton, examined the optical resonator loaded up with fluid gem. Fluid gems are an extraordinary type of issue wherein certain bearings are recognized notwithstanding their fluid structure.
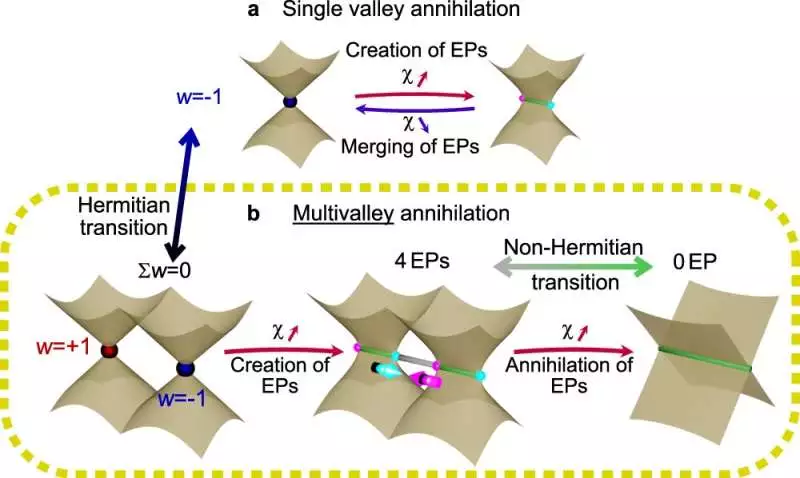
Contrast between recent thoughts about EP destruction and this work. a Normal EP destruction where just a solitary Dirac valley is involved. DPs are made from EPs while expanding the relative non-Hermiticity. On the other hand, they consolidate and structure a DP when the relative non-hermiticity diminishes. The obliteration of EPs is portrayed in this work, including different valleys. 4 EPs are made from 2 DPs while expanding the relative non-Hermiticity. At the point when it is expanded further, the EPs meet and obliterate it, leaving the framework with next to no peculiarity. The winding number here is w.Credit: NatureInterchanges (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33001-9
It could be examined, for example, by a light pillar, which acts differently depending on the direction of a rate comparable to the optical tomahawks of the fluid precious stone.This component, joined with the simple tunability by an outer electric field, is the reason for the activity of normal fluid gem shows (LCD). Spellbound light — that is, a particular bearing of vibrations of the electric field of an electromagnetic wave — impeccably “faculties” the heading of optical tomahawks, and these are connected with the course of the stretched particles of the fluid precious stone.
“In the lead research, the fluid gem layer was put between two level mirrors,” makes sense to Wiktor Piecek from the Tactical College of Innovation in Warsaw. “The entire construction makes an optical hole through which only light with a particular frequency can pass.”
This condition is met for the supposed cavity reverberation modes—that is, light with a specific tone (energy), polarization, and bearing of spread. This relates to a circumstance where a photon that falls into the depression can bob on various occasions between the two mirrors.
The presence of a fluid gem, the direction of which can be changed by applying a voltage, permits the energy of the cavity modes to be tuned. Moreover, the reverberation condition changes when the light is occurrence at a point, which specifically can lead different pit modes to converge with one another, for example, having a similar energy notwithstanding the unique polarization of the light.
For the particular direction of the fluid gem considered in the article, the two different hole modes ought to converge just for the four explicit rate points of light while thinking about an optimal design with next to no misfortunes. Truth be told, the light caught in the hole can get away from through flawed reflects or be dispersed.
The typical time the photon stays inside the microcavity is not set in stone based on spectroscopic estimations. Besides, because of the direction of the fluid gem layer, a distinction was seen in the dissipation of light captivated along and opposite to the pivot of the fluid precious stone. Subsequently, at the spot of every decline point for a glorified lossless depression, a couple of purported extraordinary foci were noticed for which both the energy and lifetime of the photon in the hole are very similar.
Mateusz Krol, who is the main creator of the distribution, describes the examination: “In the tried framework, it was seen that the place of uncommon focuses can be constrained by changing the voltage applied to the cavity. Most importantly, as the electric predisposition is decreased, the uncommon focuses made from various decline focuses draw nearer to one another, and for a reasonably low voltage, they cross-over. As the oncoming focuses have an inverse topological charge, they destroy them at the hour of the experience, so they vanish, leaving no extraordinary focuses. “
“This sort of topological peculiarity conduct, for example, the demolition of extraordinary focuses from various decadence focuses, has been noticed interestingly. Prior work showed the obliteration of uncommon places, but they showed up and vanished at the very same decline focuses, “adds Ismael Septembre, a Ph.D. understudy at the CNRS.
Uncommon focus has been seriously concentrated on in various areas of physical science lately. “Our revelation will permit the making of optical gadgets whose topological properties can be constrained by voltage,” finishes up Barbara Pietka from the Workforce of Material Science at the College of Warsaw.
More information: M. Król et al, Annihilation of exceptional points from different Dirac valleys in a 2D photonic system, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33001-9
Journal information: Nature Communications





