Cellular breakdown in the lungs is a main source of death in Japan and across the globe. Among every one of the tumors, cellular breakdown in the lungs has perhaps the lowest five-year endurance rates. Smoking tobacco and utilizing tobacco-based items is known to add to the improvement of cellular breakdown in the lungs. It is undeniably true that the dynamic fixings in various natural products reduce the risk of ongoing illnesses, including disease.
“Sarunashi” (Actinidia arguta) is an eatable natural product developed in Japan’s Okayama Prefecture. Scientists from Okayama College, led by Dr. Sakae ArimotoKobayashi, an academic partner in the Staff of Drug Sciences at Okayama College, demonstrated that sarunashi squeeze and its constituent isoquercetin (isoQ) help prevent and reduce cellular breakdown in the lungs using a mouse model.
A. arguta is one of the most extravagant wellsprings of polyphenols and L-ascorbic acid. Already, the analysts had shown the inhibitory impact of sarunashi juice (sar-j) on mutagenesis, irritation, and mouse skin tumorigenesis. They had recognized the parts of A. arguta responsible for the countermutagenic impacts as water-solvent and intensity-touchy phenolic compounds. Hence, the scientists proposed the polyphenolic compound isoQ as a component with anticarcinogenic potential.
“The goal of this work was to look into the chemopreventive effects of A. arguta juice and its constituent isoQ on 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK)-induced lung cancer in A/J mice, as well as the possible pathways underlying A. arguta’s antitumorigenic activities.”
Dr. Arimoto‑Kobayashi
“In this review, we attempted to examine the chemopreventive impacts of A. arguta squeeze and its comprising part isoQ on 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK)-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice and recognize the potential systems-basic counter tumorigenic impacts of A. arguta,” says Dr. ArimotoKobayashi.
To this end, the group prompted growth development in mice utilizing NNK, a known disease-causing compound present in tobacco products. Utilizing a progression of tests and controls, the group concentrated on the impacts of sar-j and isoQ on lung tumorigenesis in mice.
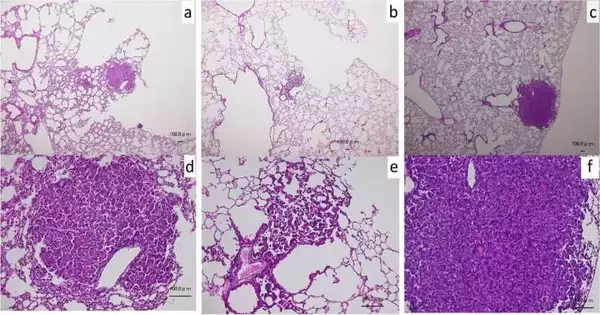
The results were encouraging: the number of cancer knobs per mouse lung in the group that received NNK infusions and oral doses of A. arguta juice was significantly lower than in the NNK-infused group.Furthermore, the oral administration of isoQ reduced the number of knobs in the mouse lungs.
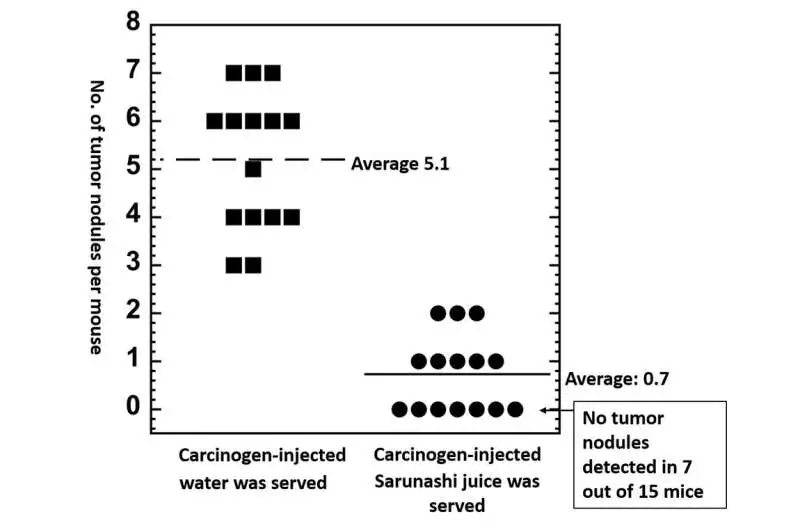
In a concentrate developed by scientists from Okayama College, Actinidia arguta (sarunashi) juice decreased growth knobs in cancer-causing agent-uncovered mice.
Then, the group kicked things off by finding a logical system of activities. NNK and 1-methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine, or “MNNG,” are known mutagens—specialists that trigger DNA changes. The researchers therefore devised a series of tests to investigate the effect of sar-j and isoQ on NNK- and MNNG-mediated mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535, a bacterial strain commonly used for detecting DNA changes.
As expected, the mutagenicity of NNK and MNNG identified using S. typhimurium TA1535 decreased in the presence of sar-j.However, when comparable tests were conducted using S. typhimurium YG7108, a strain lacking key proteins responsible for DNA repair, Sar-J was unable to reduce the mutagenic effects of NNK and MNNG.Based on this fundamental belief, the researchers reasoned that Sar-J appears to intervene in its antimutagenic effect by hastening DNA repair.
At last, utilizing cell-based tests, the group likewise showed that Sar-J stifled the activity of “Akt,” a key protein engaged in disease flagging. It’s obviously true that Akt and a related protein called “PI3K” move past being enacted in a few human tumors.
Co-creator Katsuyuki Kiura, a teacher in the Branch of Sensitivity and Respiratory Medication, Okayama College Clinic, says, “Sar-j and isoQ decreased NNK-prompted lung tumorigenesis.” Sar-j specifically targets both the inception and development, or movement ventures, during carcinogenesis, specifically through the antagonist of mutagenesis, the sensation of alkyl DNA adduct fix, and the concealment of Akt-interceded development flagging.”IsoQ may contribute to the organic effects of Sar-j to some extent by concealing Akt phosphorylation, but it may not be the super dynamic fix.”
Their discoveries were distributed on December 9, 2022, in Qualities and Climate.
In outline, the review shows that lung tumorigenesis in mice was stifled following the oral admission of Sar-J. Although clinical trials are warranted, the constituents of sar-j, including isoQ, appear to be appealing candidates for chemoprevention.
More information: Jun Takata et al, Chemopreventive effects and anti-tumorigenic mechanisms of Actinidia arguta, known as sarunashi in Japan toward 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK)- induced lung tumorigenesis in a/J mouse, Genes and Environment (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s41021-022-00255-0