Research driven by the College of Tübingen, Germany, alongside accomplices at Stanford College, Emory College, and the Cincinnati Youngsters’ Emergency Clinic Clinical Center, U.S., has investigated baby-safe reactions following SARS-CoV-2 contaminations during the underlying long stretches of life.
In a paper named “Multi-omics examination of mucosal and foundational resistance to SARS-CoV-2 after birth,” distributed in Cell, the exploration group finds that babies and small kids mount strong neutralizer reactions for as long as 300 days.
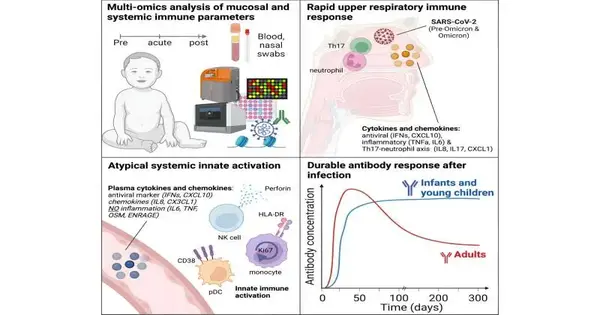
There has been an absence of a complete, framework-wide, longitudinal investigation of how babies and small kids respond to SARS-CoV-2 contamination in regards to their resistant frameworks’ turn of events, neutralizer reactions, and natural safe enactment. Scientists gathered information on kids, adults, and moms to get a near-image of newborn children’s insusceptible responses.
Blood and nasal swab tests were done on babies and small kids in the engraving partner at the Cincinnati Youngsters’ Clinic Clinical Center. Kids were tried week after week for SARS-CoV-2, and the partner included 54 tainted babies and small kids, incorporating 27 newborn children with matched pre-contamination tests. 27 extra-paired control babies and small kids addressed solid controls who reliably tried negative from birth to examination.
Notwithstanding the pediatric companion, 62 blood tests were acquired from 48 adult coronavirus patients, and ten sound control tests were gathered from the Expectation Facility at Emory College in Atlanta and the Stanford College Clinical Center. Blood tests were additionally acquired from 41 moms with gentle coronavirus, incorporating three matched pre-contamination tests and three matched controls.
Rather than adults, babies and small kids showed powerful and solid neutralizer reactions against SARS-CoV-2. These neutralizer titers stayed high for as long as 300 days, though counter-acting agent reactions will generally rot all the more quickly in adults.
In the blood, there was an upregulation of actuation markers on natural cells in the youngsters, yet no critical expansion in provocative cytokines. Memory B and lymphocyte reactions in newborn children were essentially lower than in adults. Notwithstanding, they showed expansions in multifunctional T-aide 17 and 1-type CD4+ white blood cells portrayed by the development of interleukin-2, interferon-gamma, and growth corruption factor-alpha, making them triple-positive.
Babies mounted a hearty mucosal-resistant reaction characterized by provocative cytokines, interferon α, and markers related to T-partner 17 and neutrophil reactions. This mucosal reaction was especially articulated in the nasal mucosa.
While multifunctional CD4 lymphocyte reactions were decreased by approximately two significant degrees in the babies, perceptions of constant immunization reactions endured significantly longer. The review’s discoveries raise the chance of planning immunization definitions to make the most of these inborn resistant framework enactment pathways to try not to cause the guarantee immunopathology frequently connected with undesirable aggravation.
More information: Florian Wimmers et al, Multi-omics analysis of mucosal and systemic immunity to SARS-CoV-2 after birth, Cell (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.044