The family Quercus, usually known as oaks, is one of the most developmentally fruitful genera in the Northern Hemisphere as far as species variety, biomass and conveyance range. Oaks can normally satisfy two or three hundred years, and during the long life expectancy they show high resistance to different abiotic and biotic dangers. In the interim, oaks are likewise notable for their broad interspecific quality stream, which is accepted to be useful for their wide dispersal. These qualities make Quercus an optimal family for concentrating on versatile introgression.
As of late, the exploration group drove by Prof. Chen Jun at the Zhejiang University College of Life Sciences distributed an article named “far reaching examinations of introgression between two sympatric Asian oak species” in Nature Ecology and Evolution. Their examination zeroed in on two sympatric Asian oak types of wide dissemination ranges — Quercus acutissima and Q. variabili — to investigate how introgression can help with quickly adjusting to different ecological circumstances.
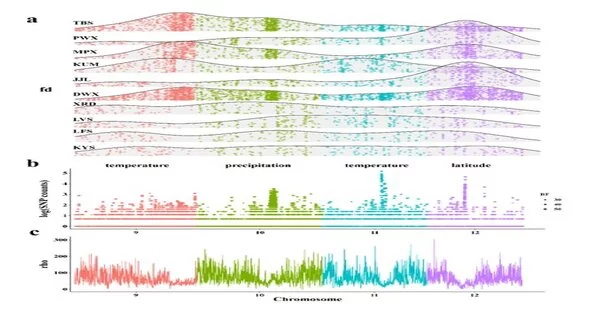
In this review, Ph.D. understudies gathered examples in 15 territories of China and produced a chromosomal-level genome gathering of superior grade, populace genomic re-groupings and transcriptome information to explore the connection between’s introgression designs, the recombination rate, hereditary varieties of nearby transformation, and quality articulation guideline.
Introgressed locales across the genome were viewed not entirely set in stone by hereditary difference and ecological circumstances. The more comparable their current circumstance, the more probable the two oak species were to trade in the equivalent genomic areas. Versatile introgressed transformations were kept up with by normal choice in four long chromosomal stretches because of stifled recombination rate, which might be brought about by chromosome reversals actuated by the addition of transposable components. Most versatile introgressed transformations were situated in cis-administrative components framed by TE additions and changed quality articulation level because of natural upgrade. In outline, comparable ecological circumstances prompted comparable hereditary trade and to comparable articulation profiles between oaks.
This study gives another knowledge into the hereditary systems of introgression and natural variation in sympatric species.
More information: Ruirui Fu et al, Genome-wide analyses of introgression between two sympatric Asian oak species, Nature Ecology & Evolution (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41559-022-01754-7