Disease immunotherapy is a treatment methodology against cancer development and metastasis by means of invigorating host safe reactions. Phototherapy, including photodynamic treatment (PDT) and photothermal treatment (PTT), is a less obtrusive treatment compared with chemotherapy. To be explicit, PDT and PTT-prompted immunogenic cell passage can deliver growth-related antigens and harm-related atomic examples, invigorating an insusceptible reaction.
Photoimmunotherapy, the blend of phototherapy and immunotherapy, can really improve treatment viability compared to a solitary treatment methodology. Up to now, the multifunctional, photo-resistant framework is still in its early stages. Subsequently, the improvement of a multifunctional and safe phototherapy framework for proficient growth treatment is earnestly required.

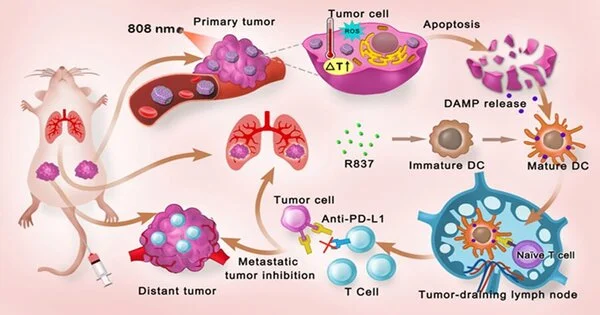
Dong Wenfei’s group from the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has as of late fostered a multifunctional nanoplatforms in view of mesoporous hexagonal center shell zinc porphyrin-silica nanoparticles (MPSNs) stacked with R837 (a cost-like receptor-7 agonist), which can be utilized to coordinate PDT, PTT, and growth explicit immunotherapy for bosom disease.
As indicated by the specialists, MPSNs with zinc phosphide (ZnP) as the center and a mesoporous silica structure as the shell could really produce singlet oxygen and convert photons to warmth with a solitary light source.
In the meantime, the mesoporous design of the silica shell can work with proficient R837 stacking. Thus, the restorative system in view of MPSNs@R837 not only killed essential growth by means of phototherapy modalities (PDT and PTT), but in addition, successfully repressed far-off metastasis because of the solid safe reaction set off by the two-way robotic cooperation.
This study has been published in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology.