A manageable synthetic division strategy that utilizes films, microalgae, and man-made brainpower has been created by a group drawn from various KAUST bunches whose individuals have different strengths in bioengineering, layers, water reuse, and reusing.
Such layer-based ceaseless detachment and fixation cycles will assist with understanding the maximum capacity of microbial substance creation for use in medication and industry.
“The upside of our technique is that items can be persistently separated from fluid microbial societies, for example, microalgae, in a cycle known as “draining,” as opposed to being removed difficult from the biomass toward the finish of a group culture,” says postdoc and first creator Sebastian Overmans.
Microalgae are single-celled photosynthetic organisms that normally produce numerous valuable synthetic compounds. They can likewise be hereditarily designed to discharge other special particles. Green growth is progressively being outfitted as reasonable and harmless to the ecosystem’s bio-manufacturing plants. However, it is trying to isolate the valuable atoms.
This venture exhibited a low-energy and proficient method for collecting and concentrating these items. This interaction is more practical than other division processes since it is low energy, the microorganisms can be developed on squander materials, and the atomic focus process doesn’t deliver squander.
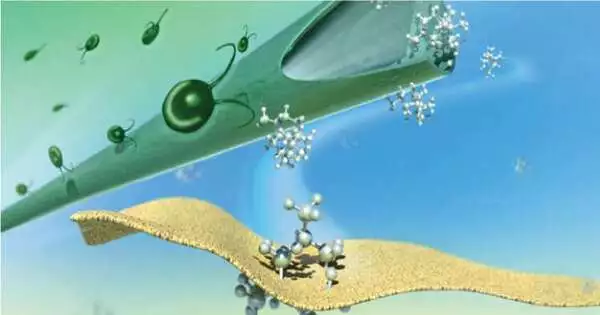
The framework depends on a film made from empty microfibers that isolates the way of life liquid that contains microalgae from a dissolvable where the ideal item collects. The item is then isolated and thought utilizing other specific films chosen and planned by artificial intelligence that permit reusing of the dissolvable without harming the framework.

delineation of the empty fiber arrangement utilized for the extraction of the ideal concentrate (patchoulol) from the microalgae culture. Patchoulol is an important compound generally utilized in the scent business.
The group exhibited the capability of their strategy by ceaselessly separating patchoulol, a compound broadly utilized in perfumery. These film blends could likewise be applied to numerous other specialty synthetic compounds.
“The advancement of the extraction interaction was a totally new area,” says Overmans.
“This is invigorating,” recommends biotechnologist Kyle J. Lauersen, “on the grounds that it very well may be executed in huge scope bio-plants utilizing different microorganisms, not just green growth, to change over squander into important items.”
Compound designer Gyorgy Szekely adds that the analysts utilized the man-made brainpower instruments and AI abilities accessible at KAUST to direct the turn of events and refinement of the film interaction.
The following stage is to exhibit increasing to modern levels. The group additionally plans to foster films with bigger surface regions and to investigate the utilization of various algal strains to deliver a lot more building blocks of revenue.
The exploration was published in Green Chemistry.
More information: Sebastian Overmans et al, Continuous extraction and concentration of secreted metabolites from engineered microbes using membrane technology, Green Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1039/D2GC00938B
Journal information: Green Chemistry