Melbourne scientists have worked on how we might interpret how the resistant framework is directed to forestall infection, recognizing the formerly obscure job of “normal executioner” (NK) safe cells.
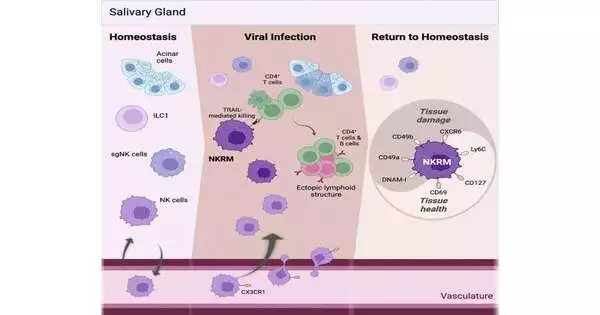
The Monash College focused on recognizing another gathering of resistant cells, known as tissue-inhabitant memory regular executioner (NKRM) cells. NKRM cells restricted resistant reactions in tissues and forestalled autoimmunity, which is the point at which the safe framework commits an error and assaults the body’s own tissues or organs.
While extra exploration is required, the revelation may eventually be utilized to deal with immune system sicknesses like Sjogren’s syndrome and perhaps constant incendiary circumstances.
“This is critical for retaining tissue function and preventing the development of autoimmunity. While long-lived tissue resident memory T cells (TRM) have been identified, their major purpose is to protect the host from reinfection.”
Dr. Iona Schuster from the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute (BDI)
Distributed in Resistance, the preclinical examination is driven by senior creator Teacher Mariapia Degli-Esposti and first creator Dr. Iona Schuster from the Monash Biomedicine Revelation Establishment (BDI), in close coordination with the Lions Eye Organization.
Initially, NK cells were believed to be brief cells that flow in the blood with the sole capability of recognizing and rapidly killing virally tainted or damaged cells.
The group’s previous research established that NK cells’ jobs are undeniably more complex, and the most recent review demonstrates intriguingly that a subset of NK cells, NKRM, are critical in managing resistant reactions in tissues.
“This is critical to safeguarding tissue capability and keeping autoimmunity from forming,” Dr. Schuster said. “While seemingly perpetual tissue occupant memory (TRM) immune system microorganisms have been portrayed, the essential known capability of these cells is to safeguard the host against reinfection.”
“Our revelation of tissue-occupant memory normal executioner (NKRM) cells demonstrates that the capability of some memory cells that live in tissues is to shield from unnecessary irritation as opposed to safeguard against repeat contamination.”
Teacher Degli-Esposti, BDI Head of Trial and Viral Immunology, said the discoveries together worked on our essential comprehension of how the resistant framework is controlled to forestall sickness.
“One of the primary impediments in malignant growth immunotherapy… is the development of safety-related unfavorable events, which incorporate the turn of events or the discharge of immune system confusions,” she explained.”These occasions are because of the “uncontrolled” or “superior” enactment of the resistant framework because the brakes have been eliminated by the remedial procedure.”
“Besides, numerous treatments cause blow-back tissues where growths are limited.” Along these lines, NKRM might be an assistant or follow-up treatment to reestablish resistant equilibrium and bring back tissue wellbeing.
More information: Iona S. Schuster et al, Infection induces tissue-resident memory NK cells that safeguard tissue health, Immunity (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.01.016. www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext … 1074-7613(23)00026-2