The profoundly infectious canine sickness infection is hazardous to dogs and other animals. It is likewise firmly connected with the similarly infectious measles infection. Specialists at the College of Bern and the Zurich College of Applied Sciences have now interestingly resolved the structure of the canine sickness infection “docking protein” and portrayed it at the sub-atomic level. This lays the groundwork for fostering novel treatments for a superior administration of the illnesses instigated by CDV and related infections, like the measles infection.
Measles infection and canine sickness infection (CDV) have a place in the family Morbillivirus. Both irresistible microorganisms are profoundly infectious RNA infections encompassed by an envelope on which their “docking proteins” distend, like the spike protein in Covid. Both infections actuate respiratory contaminations as well as destructive encephalitis, although the high frequency of mind diseases is exceptional to CDV.
Notwithstanding the accessibility of a productive immunization, measles actually kills in excess of 100,000 individuals every year. As far as canine sickness infection is concerned, it causes enormous scourges, particularly in natural life creatures, including imperiled species like specific tiger species. There is likewise a high risk of overflow to other creature species; in nations with substandard immunization inclusion, the infection can seriously influence canines.
“A promising antiviral method is to simultaneously inhibit the cell entry process in distemper and measles virus using several distinct neutralizing molecules.”
Philippe Plattet. Currently, researchers from the Plattet and Fotiadis consortium
No antiviral medication is currently supported.
For measles, antivirals would go about as an appealing supplement to immunization crusades. Also, for CDV, antiviral medications might uphold illness across the board in defenseless imperiled species that are in prison, e.g., pandas. In any case, no antiviral morbillivirus drug is right now supported.
To foster successful antiviral medications, a superior comprehension of the design of the measles and canine sickness infections and the instruments that permit them to enter human and creature cells is required.
Specialists led by Dimitrios Fotiadis of the Foundation of Natural Chemistry and Sub-atomic Medication (IBMM) of the Clinical Workforce of the College of Bern and Philippe Plattet of the Division of Neurological Studies of the Vetsuisse Staff of the College of Bern have now prevailed without precedent in deciding the design of the “docking protein” of the canine sickness infection and portraying it at the atomic level.
These discoveries make it conceivable to create “custom” dynamic substances against the “docking protein” that keeps the infection from entering host cells. The review was distributed in the journal Procedures of the Public Foundation of Sciences.
Designated as obstructing the ‘docking protein.”
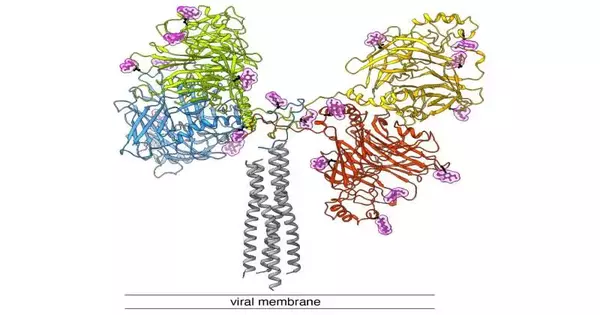
The component by which measles and canine sickness infections enter cells depends on two proteins on the viral envelope: a “docking protein” (likewise called H-protein) and a “combination protein” (F-protein). In light of past exploration, it is expected that upon connection with a host cell receptor, the H-protein will communicate a sign that will enact the F-protein.
This results in the viral envelope combining with the host cell film.In this cycle, a purported combination pore is framed, which enables the infusion of the viral genome into the host cell. Presently, the group led by Dimitrios Fotiadis and Philippe Plattet, along with analysts from the Zurich College of Applied Sciences (ZHAW), has had the option to decide the design of this H-protein, interestingly utilizing cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and guiding it at a sub-atomic level.
In cryo-electron microscopy, organic examples are imaged at cryogenic temperatures (around -180 °C) and amplified multiple times. This uncovered that the protein is described by three fundamental spaces (heads, neck, and tail) that structure a “Y.” ” The fact that we had the option to decide the design represents a major leap forward.
This presently permits us to comprehend how the different subdomains spatially sort out with one another — and gives us an important plan to foster cutting-edge antiviral medications that block the ‘docking protein’,” says Dimitrios Fotiadis.
Novel helpful methodologies
“All the while impeding the cell-section process in sickness and measles infection with a few different killing particles is a promising antiviral methodology,” makes sense to Philippe Plattet. At present, scientists from the Plattet and Fotiadis consortium and the College of Marseille have effectively distinguished antibodies that kill CDV in an exceptionally viable way.
In additional exploration, the recently settled cryo-EM stage at the College of Bern will offer valuable types of assistance: the underlying examinations for CDV and related infections can now be expanded and sped up, for instance, to determine the designs of the H-proteins of measles and sickness infections when bound to killing antibodies. “Because cryo-EM is not set in stone, we can create and further develop antiviral medications utilizing purported structure-based drug configurations,” says Fotiadis.
More information: David Kalbermatter et al, Structure and supramolecular organization of the canine distemper virus attachment glycoprotein, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2208866120