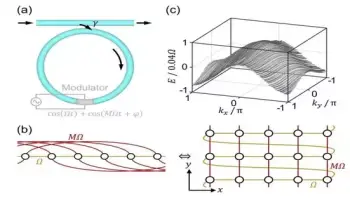
The coupling of internal photon degrees of freedom like frequency, spatial mode, and orbital angular momentum generates extra dimensions in the photonic synthetic dimension in
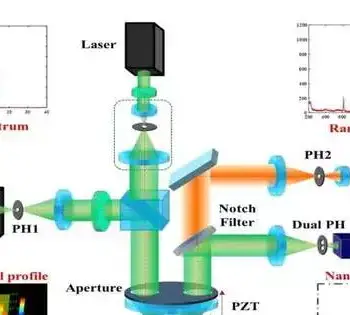
The morphology, chemical properties, and mechanical properties of cancerous cells and normal cells clearly differ. The pathological processes of human cells and tissues can be better understood by analyzing the
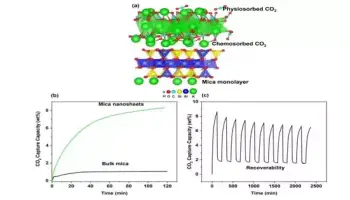
This obvious distinction between the liquid and solid states of substances is something that we all experience on a daily basis—water flows; ice is rigid. It follows from the exceptionally
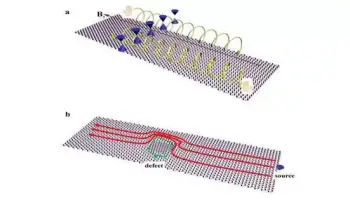
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon that occurs in quantum mechanics where two or more particles become correlated in such a way that the state of one particle cannot be described
Polaritons are a unique state of quasi-particles that are a combination of light and matter. They have the potential to bring novel capabilities to conventional chemical reactions. The polaritons collapse