Pseudoviruses look like shams. Albeit innocuous, they are planned so that they can scarcely be recognized by their hazardous family members. This makes them an important apparatus in infection research. They can be utilized to definitively break down disease pathways and risky infection variations.
A significant test in this examination region up to this point has been to make the pseudoviruses dependably noticeable under the magnifying lens. This is on the grounds that customary marking techniques hinder the movement of the “fakers” and hence distort the imaging.
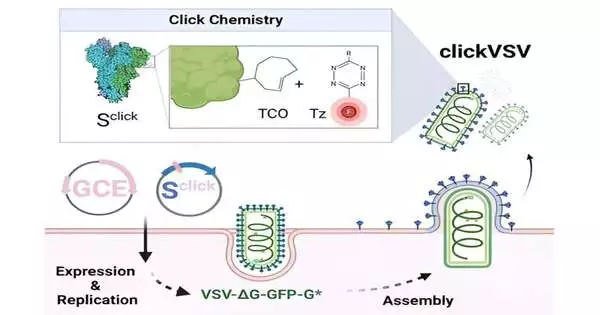
A group from the Rudolf Virchow Center—Place for Integrative and Translational Bioimaging at Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg, driven by Teacher Markus Sauer and Dr. Gerti Beliu, has now fostered an answer: By joining hereditary code development and snap science, an interesting acknowledgment highlight for pseudoviruses was made that leaves their action unaffected. These discoveries are currently distributed in the journal ACS Nano.
“This method opens up completely new vistas in virus research for us. It represents a significant advancement in our ability to use high-resolution microscopy to observe the complex dynamics of viral infections in living organisms.”
led by Professor Markus Sauer.
“Interactive” pseudoviruses are exceptionally fluorescent. Nonetheless, as far as restricting and entering cells, they have similar properties as their pathogenic family members. When inside the cells, nonetheless, they don’t cause illness—this permits them to be taken care of under decreased organic gamble levels in S1/2 standard research facilities.
“This technique opens up totally new skylines for us in infection research. It’s a jump forward in our capacity to notice the mind-boggling elements of viral contamination in living organic entities utilizing high-goal microscopy strategies,” Sauer says.
One more benefit of the new technique is its high locational productivity. Contrasted with customary immunostaining techniques, the JMU group found location proficiency to be commonly higher. This makes the subtleties and unpretentious cycles of the contamination interaction more apparent.
“The interactive pseudoviruses can possibly upset the manner in which we concentrate on infection-cell collaborations. Maybe we are utilizing our magnifying instruments to plunge into a formerly imperceptible world,” makes sense to Dr. Beliu.
More information: Marvin Jungblut et al. Re-Engineered Pseudoviruses for Precise and Robust 3D Mapping of Viral Infection, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c07767