A huge step in the right direction in the protein plan from Create Biomedicines, Massachusetts, has fostered an artificial intelligence that can produce practical protein structures and foresee the possible usefulness of the proteins produced.
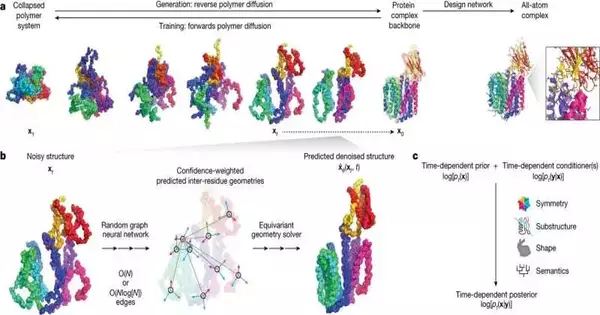
In a paper, “Enlightening protein space with a programmable generative model,” distributed in Nature, the group presents Chroma, a flexible artificial intelligence equipped for creating different proteins with determined properties.
Proteins are the amino-corrosive mixtures that make up every living thing, and these proteins complete most of the capabilities that make life conceivable. Practically all drug drugs target proteins in the body, and numerous drugs are themselves proteins or made utilizing proteins.
With proteins at the center of human wellbeing and the drug reaction to illness, having the option to make novel proteins with explicit properties could open a fountain of new medication targets. By having a more adaptable command over proteins, existing medications could be made more secure, and right now, untreatable illnesses could get sufficiently close to previously un-druggable targets.
Chroma’s uniqueness lies in its programmability, permitting clients to determine a wide cluster of properties, from buildup distances to semantic particulars, through classifiers.
The group performed exploratory approval tests to challenge Chroma’s viability in producing protein plans that express well and display stable collapsing and underlying adjustments to the planned plan.
Under the most safe evaluation, Chroma showed a triumph pace of roughly 3% in effectively described and decontaminated proteins. Chroma displayed capability in creating proteins with different designs and properties, taking care of perplexing shapes, and exhibiting productive plans, featuring its true capacity in custom-fit protein design.
Numerous untreatable illnesses are undruggable, implying that the proteins inside the body that could be actuated or deactivated to counter the infection are excessively mind-boggling or testing to tie with utilizing existing drug proteins.
By back-designing the properties these objectives would expect to restrict as a beginning stage for a generative protein gathering, specialists could find medicines for a huge number of illnesses. Current endeavors are in progress to produce varieties of attainable protein designs and, afterward, search for potential objective matches.
Chroma’s capacity could move the concentration from producing plausible protein structures towards stressing the planned usefulness of a protein and constraining the primary development to follow that expected capability.
More information: John B. Ingraham et al, Illuminating protein space with a programmable generative model, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06728-8