An article by specialists at the Middle for Improvement of Practical Materials (CDMF) in Brazil portrays a fruitful technique to moderate charge limit misfortune in vanadium redox stream batteries, which are utilized by electric influence utilities among different enterprises and can collect a lot of energy. The article is distributed in the Compound Design Diary.
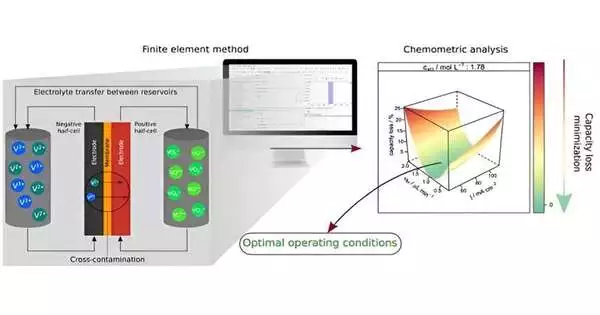
The review included virtual experiences intended to figure out how particle spillage between the anolyte and catholyte—called transport misfortune—prompts battery deactivation and how to alleviate this misfortune in order to keep particle focus consistent over the long run.
At first, the specialists assessed the impacts of current thickness, dynamic species focus, and volumetric stream on limit misfortune. The subsequent stage looked for ideal circumstances to limit misfortune in view of the stream between electrolyte tanks the other way to cross-defilement (transport of electroactive species through the layer).
“Given the slow rate of aging, energy efficiency loss from aging is minimal.”
Ernesto Pereira, senior author of the article and a professor at UFSCar,
The outcomes demonstrated current thickness and dynamic species fixation to be the fundamental factors influencing limit misfortune. As per the specialists, their methodology effectively alleviated cross-pollution in various blends of the two factors, giving an ideal stream between electrolyte tanks under various working circumstances.
Ernesto Pereira, senior writer of the article and a teacher at UFSCar, noticed that the fundamental benefit of redox stream batteries is the absence of cathode maturing as the electroactive parts are broken down in arrangements as opposed to being covered onto terminals.
Business vanadium redox stream batteries are supposed to have a longer lifetime than different sorts, although the review was directed at a limited scale. “Energy effectiveness misfortune because of maturing is negligible, given the sluggish speed of maturing,” he said.
The scientists made sense of the fact that they are investigating and examining stream batteries computationally, with business batteries as a model, as a component of a more extensive system that incorporates the improvement of novel natural substances for this sort of battery.
More information: Luis Felipe Pilonetto et al. Mitigating the capacity loss by crossover transport in vanadium redox flow batteries: A chemometric efficient strategy proposed using finite element method simulation, Chemical Engineering Journal (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145336