A headway in neutron safeguarding, a basic part of radiation security, has been accomplished. This advancement is ready to reform the neutron safeguarding industry by offering a financially savvy arrangement relevant to a large number of material surfaces.
An examination group led by Teacher Soon-Yong Kwon in the Master’s level college of Semiconductors Materials and Gadgets Designing and the Division of Materials Science and Designing at UNIST has effectively fostered a neutron safeguarding film fit for obstructing neutrons present in radiation. This imaginative safeguard isn’t just accessible in huge regions; it is additionally lightweight and adaptable.
The group’s paper is distributed in the journal Nature Correspondences.
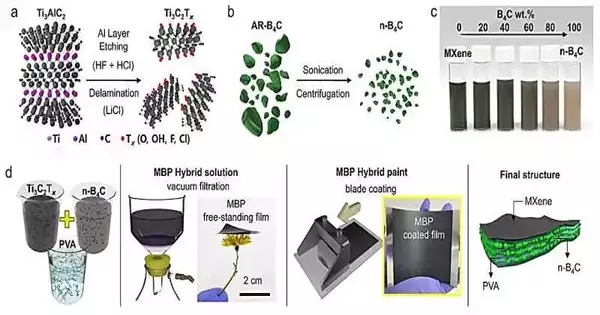
“The created MXene-Boron carbide composite safeguarding film is many micrometers thick, north of 1,000 times more slender than traditional business materials,” noted Teacher Kwon. “It very well may be easily applied to different surfaces, looking like a demonstration of painting.”
“We improved the stability of the two materials’ mixture solution by controlling the properties of MXene and boron carbide. Experiments showed that we effectively generated a light and flexible barrier with a stable MXene-boron mixture that can be sprayed like paint on diverse object surfaces.”
Co-first author Ju Hyoung Han, a researcher in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at UNIST,
Neutrons, which are essential to the atomic power age, clinical gadgets, and aviation businesses, have innate perils when spilled. They can set off startling peculiarities in electronic gadgets or living organic entities through communications with different iotas.
The examination group straightforwardly integrated MXenes, a two-layered nanomaterial, and the parent MAX stages. Furthermore, they formulated a strategy to isolate boron carbide into little pieces fit for engrossing neutrons and integrated them between the maxillary layers. In view of this forward leap, an enormous, adaptable, and lightweight film was created. Moreover, a state-of-the-art procedure was developed to apply the combination to different surfaces.
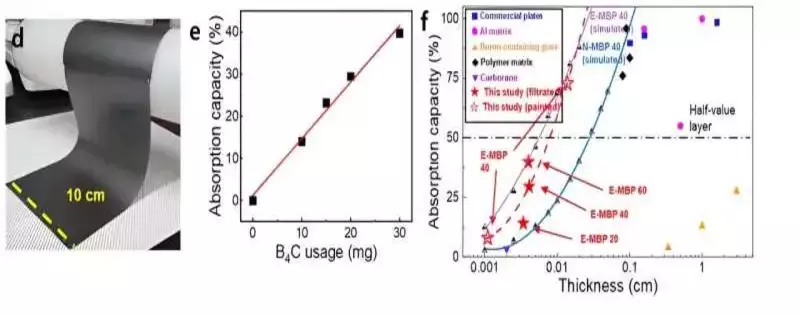
Neutron-safeguarding exhibitions of MBP half-and-half movies (d) Photo of the painted MBP half-breed film on the nylon layer, with a huge area of 10 × 30 cm2. (e) Neutron retention limit of MBP mixture films with various B4C utilizations. (f) Neutron retention limit versus thickness of boron-based composites Credit: Ulsan Public Establishment of Science and Innovation
Co-first creator Ju Hyoung Han, a specialist in the Division of Materials Science and Designing at UNIST, expressed, “By controlling the properties of MXene and boron carbide, we worked on the dependability of the blend arrangement of the two materials. We effectively made a light and adaptable safeguard with a settled MXene-boron blend, which can be applied like paint on different items’ surfaces, as exhibited through tests.”
The created neutron safeguard has a thick construction with negligible air pocket openings, estimating just several nanometers. Subsequently, it shows fantastic mechanical properties compared with recently utilized polymer-based composites. Since extra cycles, for example, heat treatment, are superfluous, an unadulterated blended structure without debasements can be produced.
Co-first creator Si-Hyun Seok, a specialist in the Division of Materials Science and Designing at UNIST, remarked, “Even after north of 20,000 twisting tests, the nylon composite covered with the protecting film kept up with its roundabout shape up to 98%. It exhibited an uncommon neutron-protective rate (40% while utilizing 30mg) even with milligrams of boron carbide, displaying its predominance.”
Teacher Kwon added, “The recently evolved composite assembling innovation is reasonable and requires neither complex hardware nor processes. It empowers the execution of a neutron-shielding film with the ideal thickness and region. This study will grow the conceivable outcomes of MXene material covering innovation and exhibit its application in different fields.”
More information: Ju-Hyoung Han et al. Robust 2D layered MXene matrix-boron carbide hybrid films for neutron radiation shielding, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42670-z