Sulfate-decreasing microscopic organisms (SRB), an anaerobic bacterium, have for quite some time been viewed as the fundamental guilty party in causing the erosion disappointment of metal materials.
Past investigations generally utilized nanozymes as antibacterial materials. Be that as it may, nanozymes depend on H2O2, O2, superoxide and hydroxyl extremists to deliver receptive oxygen species, which thwarts their usage in anoxic conditions.
As of late, an exploration group led by Prof. Zhang Dun from the Organization of Oceanology of the Chinese Institute of Sciences (IOCAS) has found that a MoS2 nanosheets-based opportunity material enacted by permonosulfate empowers productive anaerobic microorganism sanitization.
The review was published in the Diary of Perilous Materials on August 9.
“MoS2 has highly exposed active sites and adjustable S vacancies, combining physical harm and chemical removal to create a platform for accelerating the production of “nano killers.” As a result of their increased production of free radicals and intimate contact with bacteria, diverse surroundings might be sterilized quickly and consistently.”
Wang Jin, first author of the study.
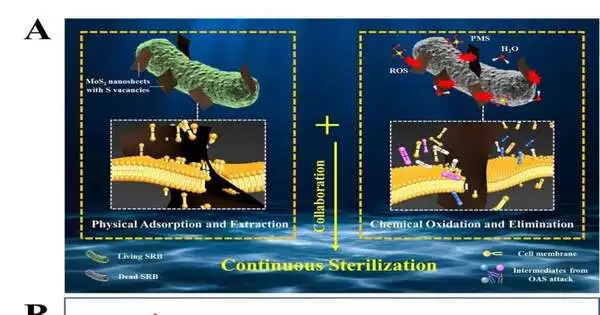
The specialists built a quick and proficient anaerobic bacterial disinfection framework with MoS2 nanosheets by means of the synergistic impact between actual harm and compound oxidation.
For actual harm, the negative sulfur of MoS2 can undoubtedly bond with hydrophilic heads of lipids, and the edges of MoS2 can act as a “blade” to slice through the cell layer.
In view of thickness utilitarian estimations, the specialists found that MoS2 nanosheets could catalyze permonosulfate and H2O to create oxidation dynamic species (OAS). These OAS could be pictured as “nano executioners,” which continually oxidize the lipids around MoS2, re-discharge the outer layer of the “sharp blade,” and cause cell demise.
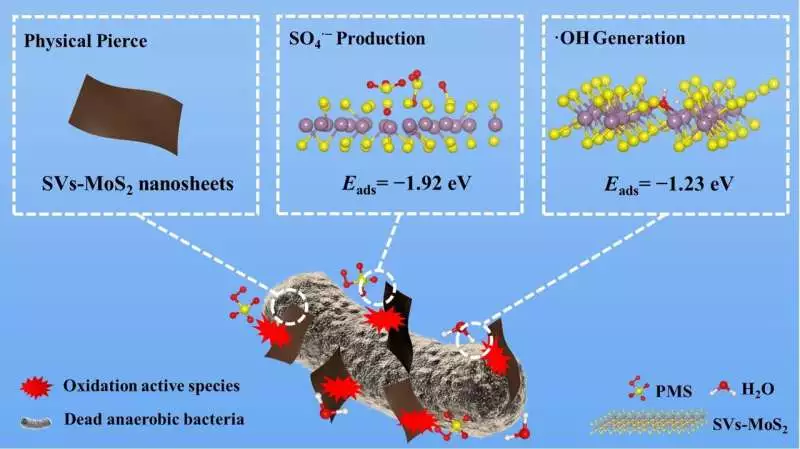
Fig. 2: The plan of the coordinated effort of actual puncture and compound injury of MoS2 nanosheets Credit: IOCAS
“With the coordinated effort of actual injury and compound disposal, MoS2 includes profoundly uncovered dynamic locales and tunable S opportunities, developing a stage for helping the age of ‘nano executioners.’ The expanded creation of these free revolutionaries combined with their nearby contact with microorganisms enables fast and stable cleansing in different conditions,” said Wang Jin, the first creator of the review.
“This work will create new skylines in anaerobic bactericidal systems and creative sanitization procedures,” said Prof. Zhang.
The course of actual extraction in a joint effort with compound oxidation unequivocally positions the phone film as well as considers constant sanitization. “This work dives into the component of anaerobic bacterial cleansing, which reveals insight into organic investigation, antibacterial, malignant growth treatment, and hostile to microbiologically impacted consumption,” said Prof. Wang Yi, the comparing creator of the review.
More information: Jin Wang et al, “Nano Killers” Activation by permonosulfate enables efficient anaerobic microorganisms disinfection, Journal of Hazardous Materials (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129742
Journal information: Journal of Hazardous Materials