About 10 years after the role of pyramidal neurons in mental portrayals of room and area was found, a gathering of Brazilian and American specialists has made a significant commitment to how researchers might interpret the mind’s route framework by recognizing a subtype of these neurons that can check speed with extraordinary accuracy.
In tests including creatures, we showed a relationship between the electrical action of inhibitory interneurons and speed portrayals in the mind,” Alexandre Kihara, a neuroscientist at the Government College of the ABC in So Paulo state, Brazil, told Agência FAPESP. Kihara is a co-writer of an article on the review distributed in Logical Reports.
Excitatory neurons and inhibitory interneurons are situated in the hippocampus, a two-sided mind structure in the worldly curve (behind the ears) that is related to the development of new recollections, learning, feelings, and, as has as of late been found, spatial portrayal. Excitatory neurons enact different neurons, while inhibitory interneurons ruin or block them. Together, they can modify movement in brain areas to avoid the excess of action associated with seizures, for example.
“Despite the fact that they all assume a part in encoding space, we found that inhibitory neurons have a few extra capabilities,” said Juliane Midori Ikebara, who holds a four-year certification in science and innovation and a Ph.D. in neuroscience and perception from UFABC.
Ikebara is the lead writer of the article, followed by Peter Schuette, a scientist in the Brain Science Division at the College of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) in the US.
“A crew at UCLA opened it up around seven years ago, examined what was inside, and then released a free blueprint with extremely detailed instructions for building and using it. This accomplishment has made the technology accessible to hundreds of researchers in other nations,”
Adhikari, who has lived in São Paulo.
Examining video pictures of brain action in mice, the group likewise saw that inhibitory neurons responded diversely to changes in the environment like turning or size. “They were more steady than excitatory neurons, which at times adjust position encoding because of natural changes,” Kihara said.
This conduct was obscure and might be related to spatial memory. “These more steady neurons might be connected to the memorable capacity courses or the area of the parlor or washroom when we awaken in a similar house, for instance,” said Kihara, who managed Ikebara’s Ph.D. research.
By and by, Ikebara noticed, this is the main review to prove the elements of inhibitory cells, which represent under 10% of pyramidal neurons. Concentrating on these cells emerged while she was doing a sandwich doctorate in the US in 2020–21. Having been granted a grant by FAPESP, she went to work for a period at the UCLA lab driven by Teacher Avishek Adhikari, the related writer of the Logical Reports article, to figure out how to construct the small magnifying lens used to record neuronal electrical action.
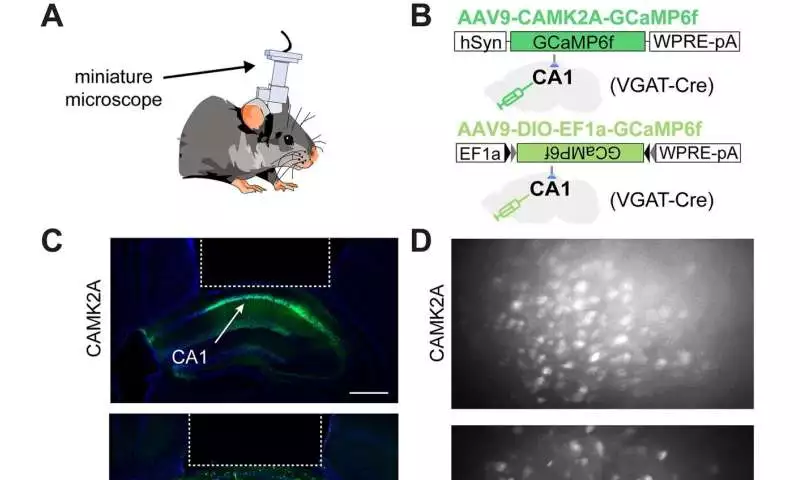
Keep calcium drifters in CAMK2A-and VGAT-communicating cells in the dorsal hippocampal region of CA1. (A) Plan showing a mouse with a scaled down magnifying lens to record calcium drifters from either CAMK2A-or VGAT-communicating cells in the dorsal hippocampal region CA1. (B) Plan showing viral development used to target articulation of the calcium marker GCaMP6f to either CAMK2A-or VGAT-communicating cells in CA1. VGAT-cre driver mice were utilized in the two cases. (C) Agent histology demonstrating GCaMP6f articulation in CAMK2A- and VGAT-communicating cells.The area involved by the scaled down magnifying instrument focal point is framed by a ragged white line (scale bar = 500 m). (D) Agent greatest projection showing perspectives on CAMK2A-(top) and VGAT-(base) communicating cells through the embedded focal point. (E) Miniscope post-handling technique(F) Agent hints of CAMK2A (top) and VGAT (bottom) cells from the dorsal hippocampus’s region CA1.(G) Shown are models CAMK2A and VGAT, which follow when z-scoring. (H) The bars represent the rate of calcium tops for CAMK2A and VGAT cells (left; CAMK2A rate = 0.11 0.001 pinnacles/s; VGAT rate = 0.17 0.004 pinnacles/s) and pinnacle width (right; CAMK2A top width = 0.77 0.007 s; VGAT top width = 1.34 0.09 s).CAMK2A n = 2303 (from 8 mice); VGAT n = 937 (from 12 mice); t-measurement = 17.7 (left), t-measurement = 10.1 (right).***p 0.001.Logical Reports (2022) is credited.DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13799-6
The standard gadget utilized in this kind of trial, the Miniscope, created at Stanford College, likewise in California, sells at a restrictive cost. “Around a long time back, a gathering at UCLA opened it up, concentrated on what it contained, and distributed a plan for nothing, with very much indicated directions for building and utilizing it. Because of this accomplishment, many analysts in different nations have had the option to get the innovation, “said Adhikari, who has lived in So Paulo.
Biosensors and calculations are also used in the study of neuronal electrical action in mice.Most importantly, the mice were infused with an infection bearing directions to taint the phones and make them produce a protein that becomes fluorescent in the sight of expanded degrees of calcium, which happens when the phones are enacted,” Ikebara made sense of.
A tube-shaped focal point was then positioned over the hippocampus, and the small magnifying lens was fixed to the skull surface to report neuronal activity. During the tests, the creatures were put in nooks that were turned and made to change size or shape.
Subsequent to recording many long periods of recordings, the analysts utilized data hypotheses and calculations to plan the enacted neurons related to the places of the mice in the nooks.
“We found it was feasible to foresee exactly where a mouse was situated in the climate by simply taking a gander at the guide of electrically enacted neurons, without watching the recordings,” Adhikari told Agência FAPESP.
As per Ikebara, the discoveries add to a superior understanding of how individuals track and hold data about courses and learn new areas. In view of past examination into the impacts of oxygen hardship upon entering the world on the minds of grown-up rodents, Ikebara said these most recent disclosures highlight ways forward in the examination of troubles to learn new courses and areas in individuals with Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative illnesses.
Oxygen hardship upon entering the world can prompt spatial memory shortages, an issue that has likewise been related to changes in inhibitory neurons.
Ikebara led her Ph.D. research under the aegis of UFABC’s Alumni Program in Neuroscience and Perception, with Kihara and teacher Silvia Takada managing.
More information: Peter J. Schuette et al, GABAergic CA1 neurons are more stable following context changes than glutamatergic cells, Scientific Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13799-6
Journal information: Scientific Reports





