A group led by Prof. Guang Shouhong and Prof. Feng Xuezhu from the College of Science and Innovation (USTC) of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences (CAS) uncovered, interestingly, the structure and administrative system of the atomic vacuole in C. elegans. The review was distributed in Cell Reports.
The core contains a noticeable organelle called the nucleolus, which is fundamentally responsible for the get-together and creation of ribosomes, which are fundamental cell structures engaged in protein blend. Expanding proof demonstrates that the nucleolus is a dense biomolecular structure that structures through stage detachment; it shows three or two gradually working isolated subcompartments in mammalian cells and C. elegans, individually.
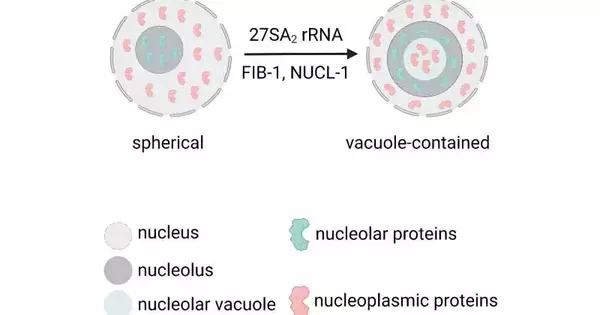
Nonetheless, there is a profoundly moderated focal locale, called the nucleolar depressions or vacuoles (a comparative nucleolar vacuole [NoV] has been seen in mammalian cells), present in the nucleoli of different plants and creatures.
Utilizing differential impedance contrast (DIC) microscopy and fluorescent microscopy, the group pictured the nucleolar design of C. elegans. What’s more, it was observed that there were two sorts of nucleoli: round and vacuole-contained nucleoli. Up-and-comer-based RNAi screening was utilized, and it was tracked down that knockdown of an unmistakable class of ribosomal proteins of the enormous subunit (RPLs) reshaped circular nucleoli into vacuole-contained nucleoli, joined by the unusual gathering of 27SA2 rRNAs.
Another two profoundly moderated nucleolar proteins with inwardly cluttered groupings, NUCL-1 and Lie-1, are likewise expected for the arrangement of NoVs. All in all, these discoveries suggest major areas of strength for the association of the nucleolus and the handling and development of rRNA.
The scientists observed that the presence of NoVs is dynamic in C. elegans, and that implies the presence of NoVs changes in various states during improvement. Likewise, the scientists additionally guessed that the articulation and handling of rRNAs are differentially managed across various cell types and all through improvement and maturing, which would incite the arrangement of cell-type-explicit nucleolar structures and the difference in NoVs during germline development and maturing of the creatures.
More information: Demin Xu et al, rRNA intermediates coordinate the formation of nucleolar vacuoles in C. elegans, Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112915