Another review by researchers at the La Jolla Foundation for Immunology (LJI) shows how ideal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 hit their imprints.
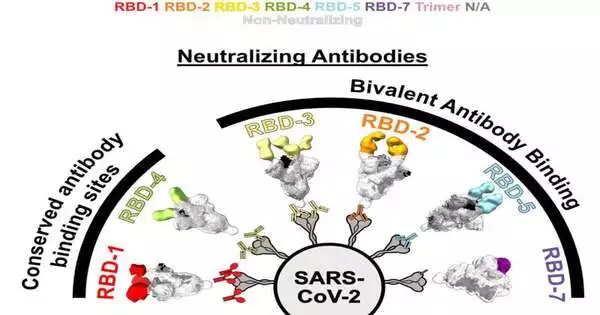
Truth be told, marks Rather than focusing on a single restricting site on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, these strong antibodies tie to two of these locales immediately. Through this “bivalent” restriction, the antibodies can get key viral designs into position, keeping the infection from tainting host cells.
The new findings, published in Cell Reports, suggest that bivalent antibodies are effective against both early SARS-CoV-2 variants and a few later omicron variants.Currently, researchers are taking a gander at how we could outfit their power with new immunizer therapeutics and, surprisingly, more viable coronavirus immunizations.
“The ideal antibodies exist,” says Kathryn Hastie, Ph.D., a LJI teacher and the head of the Immunizer Revelation Center at LJI. LJI Postdoctoral Analyst Heather Callaway, Ph.D., Sharon Schendel, Ph.D., and LJI President and Chief Erica Ollmann Saphire, Ph.D. assisted Hastie in bringing the new concentration to a close.”Presently, the inquiry is, how would we specially help those?”
“It became evident that there was a trend. The effective antibodies bypass omicron affinity loss by concurrently binding two RBDs in the Spike.”
Postdoctoral Researcher Heather Callaway, Ph.D.,
The new exploration was made conceivable through the Covid Immunotherapy Consortium (CoVIC), a worldwide effort with Saphire as Chief and Schendel as Program Director.
Antibodies versus omicron
Current coronavirus antibodies are intended to help the body perceive the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Spike is significant because it perceives and attaches to specific cells via a region known as the receptor restricting space (RBD).Each spike has three duplicates of the RBD. An immunizer that can tie to an objective (called an epitope) on the RBD gets an opportunity to stick up this hardware and stop disease.
The issue is that SARS-CoV-2 continues to change, and some once-strong antibodies can’t perceive their typical foci on RBDs. Developing future immunizations and treatments is dependent on determining what enduring antibodies share practically speaking.
Callaway and Hastie examined almost 400 antibodies sent by researchers all over the planet to the CoVIC, which is settled at LJI. They reduced this immense pool and found 66 strong antibodies that could kill omicron ancestry BA.1 and early sub-heredities like BA.1.1 and BA.2. When they tried antibodies against omicron ancestries BA.4/5, just seven antibodies had killing power.
The issue was that these enduring antibodies designated the very spot as different antibodies that didn’t endure the changes in omicron. The time had come to perceive how this novel gathering of killing antibodies was taking care of business. Callaway utilized an imaging method called cryo-electron microscopy and biochemical examination to see precisely the way that these antibodies bound to atoms in the RBD.
“It turned out to be clear that there was an example,” says Callaway. “The beneficial antibodies outperformed omicron aversion by restricting two RBDs in the spike.”
The best killing antibodies held on with two hands. They didn’t tie their objectives together particularly tightly, but by immediately connecting two nearby RBDs, even Omicron made some extreme memories escaping.Increasing immunizer endurance against the most recent variations by bivalently restricting rose.
A more critical glance at bivalent antibodies
An immunizer’s essential design looks like the letter Y. The two arms at the highest point of the Y are known as the antigen-restricting locales (Fabs). The two Fabs on every immunizer have a similar sub-atomic design, and Fabs work like keys looking for a lock (an epitope).
Researchers leading primary examinations of how antibodies tie proteins frequently utilize just the Fab area, and pictures in course books have zeroed in on how single Fabs tie to single locales. According to the new review, this previous center may have left some unfavorable impressions.
All things considered, the LJI group has shown the significance of imaging the flawless, complete immunizer as it exists in nature, a sort of examination just conceivable with a new and strong electron magnifying lens. Thusly, the group could recognize what endured versus what tumbled into the endless supply of omicron. Antibodies that utilized both their arms to bind two RBDs immediately endured viral development.
Proceeding, the analysts will keep on testing the CoVIC pool of antibodies against new SARS-CoV-2 variations. This data is vital for the advancement of better antibodies that will evoke resistance that endures various times of viral development. The Saphire Lab is likewise designing such immunogens that will hold wide action over time.
The force of CoVIC
The very fact that scientists had the option to examine a wide pool of almost 400 antibodies has been a significant step in the right direction for science.
According to Saphire, the broad scope of the CoVIC immunizer board, which included many helpful competitors and was contributed by nearly 60 gatherings in both corporate and scholarly settings, joined with each other through examinations utilizing a variety of methods, uncovered enough of this uncommon neutralizer populace to comprehend what made them unique.
“The size of the review permitted the group to concentrate on sufficient omicron “survivors” to find basic guidelines about what made them fruitful,” says Saphire.
“CoVIC showed that cooperation permitting concentration on a bigger scope can prompt better experiences,” Schendel adds.
Schendel says that having both the Salt Lake City-based biotech organization Carterra and the lab of Teacher Georgia Tomaras, Ph.D., at Duke College as accomplice reference labs in the CoVIC was particularly significant for arranging the different killing antibodies into epitope-restricting “networks,” in view of where they target SARS-CoV-2.
The study of these antibodies can guide the development of cutting-edge immunizer mixed drinks that are more resistant to always arising.SARS-CoV-2 variations.
Moving forward, it is critical to understand whether promising antibodies are competing or supplementing one another.According to the LJI analysts, it is also critical to investigate how new immunizations present the spike protein to the safe framework.The more precise the immunogen form of Spike is, and the more precisely it presents the plan and division of the parts, the more likely it will elicit killing antibodies.
“We truly need to ponder saving the crease, math, and general appearance of the spike protein,” Schendel says.
More information: Heather M. Callaway et al, Bivalent intra-spike binding provides durability against emergent Omicron lineages: Results from a global consortium, Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112014. www.cell.com/cell-reports/full … 2211-1247(23)00025-6