Trinitarian geoscientists have fostered a modest and harmless technique for the union of the uncommon earth mineral, which holds guarantee for the therapy of illnesses related to irritation, including malignant growth.
The review, distributed for this present week in the RSC Advances diary, additionally gives new understandings of the event and conduct of cerianite in regular stores. The examination additionally extends our insight about the investigation, double-dealing, and extraction of interesting earth minerals (REEs).
The discoveries likewise have suggestions for biomedical exploration, the creation of carbon-neutral advancements, and the material sciences.
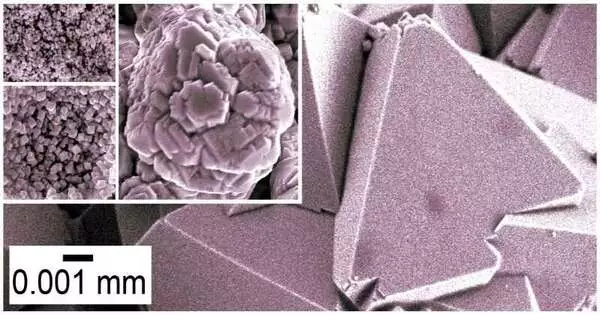
“Our simple approach enables the synthesis of cerianite in a variety of sizes and shapes. The smallest particles are a few nanometers in size, while the largest are 50 micrometers. This will be important in medicinal sciences, carbon-neutral technology development, and material sciences.”
Dr. Juan Diego Rodriguez-Blanco, Associate Professor in Nanomineralogy in Trinity’s School of Natural Sciences,
Adrienn Maria Szucs, Ph.D. scientist in geochemistry in Trinity’s School of Innate Sciences and lead writer of this review, made sense of, “We solved two problems at once on the grounds that we figured out why cerianite is related to REE-carbonates and how precisely it structures in nature, and simultaneously we delivered a cooking book for material designers with simple recipes for the combination of REE-carbonates and cerianite in various sizes and shapes. On the highest point of that, the combination strategies are cost- and earth-productive. Exceptionally advantageous.”
Cerianite or cerium-oxide (CeO2) is a broadly utilized compound utilized in many areas (e.g., energy, transportation, hardware, and medical services). It is likewise an exceptionally encouraging material for biomedical exploration because of its cell-reinforcing properties. For instance, cerianite nanoparticles are being researched as remedial specialists for the therapy of illnesses related to oxidative pressure and irritation, including disease.
Dr. Juan Diego Rodriguez-Blanco, academic partner in nanomineralogy at Trinity’s School of Innate Sciences and lead creator, added, “Our straightforward technique considers the development of cerianite in various sizes and shapes. The smallest particles are only a couple of nanometers, and the biggest are 50 micrometers. This will be helpful in biomedical sciences, the creation of carbon-neutral advances, and material sciences.”
What have the scientists found?
In the review, the analysts synthesized cerianite utilizing different techniques with different shapes and sizes by utilizing different crystallization courses, some of them copying regular cycles.
They consolidated two straightforward creation techniques at low temperatures. By changing boundaries, for example, temperature, length of the trial, and focus, they found that cerianite can be shaped by means of cerium carbonates, acting in basically the same manner as other uncommon earths (e.g., La, Pr, Nd, and Dy); in any case, cerium carbonates ultimately decarbonize and frame cerianite.
Their techniques give essential data on the combination of nanometric and micrometric cerium carbonate and cerianite. These techniques are non-poisonous and utilize normal synthetic compounds; consequently, they are energy- and material-productive and can be effectively duplicated.
More information: Adrienn Maria Szucs et al, The role of nanocerianite (CeO2) in the stability of Ce carbonates at low-hydrothermal conditions, RSC Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3RA00519D. pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articl … g/2023/ra/d3ra00519d