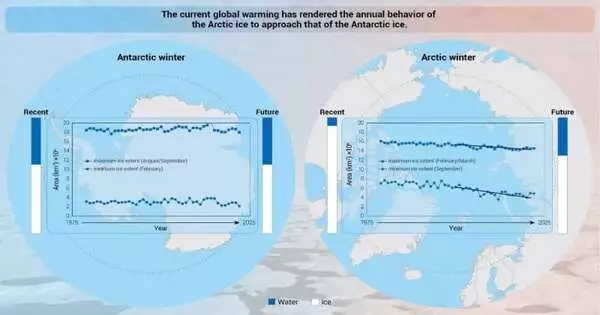
Scientists have utilized information from past distributions to address the subject of why the icy ocean ice is responding significantly more rapidly and clearly to environmental change than the Antarctic ocean ice, which has remained somewhat stable as per the drawn-out investigations checking the Antarctic area’s ocean ice designs. Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research was the journal that published their findings.
“The distinctions in reactions are made sense of regarding geographic, climatic, and meteorological contrasts between the two locales. According to Mohammed Shokr, the paper’s first author, “Arctic sea ice is located in the polar area and is surrounded by land, whereas sea ice in the Antarctic is located far from the polar area outside the Antarctic circle.”
Although Arctic sea ice appears to be melting and thinning on an annual cycle, Antarctic sea ice is still being affected by calving (the formation of icebergs by the splitting of glaciers) and ice shelf melting. Normally, this prompts more conversation encompassing the applicable liquefying in the ice, where its effects are all the more quickly observable because of the population thickness in the northern half of the globe.
“It is expected that Arctic sea ice will follow the seasonal pattern of Antarctic sea ice, forming in winter and nearly completely disappearing in summer.”
Yufang Ye, author and researcher at Sun Yat-sen University.
According to author and Sun Yat-sen University researcher Yufang Ye, “it is expected that Arctic sea ice will mimic the seasonal behavior of the Antarctic sea ice, namely forming in winter and almost completely vanishing in summer.”
The occasional softening of cold ocean ice and Antarctic ice racks can differ with air and maritime circumstances, the two of which can prompt less beneficial consequences for transportation, economies, and the climate. Melting incidences exist in both regions, but their causes are distinct. This would suggest that every issue has the potential for its own response and that the two shouldn’t really be checked through a similar focal point.
Instead of asking why Arctic sea ice is more sensitive to climate change than Antarctic sea ice, the authors propose an alternative inquiry: How did the effects of global warming cause the ice patterns in the Arctic to become similar to those in the Antarctic?
To acquire a thorough comprehension of how ocean ice acts in light of environmental change in both the Icy and Antarctic districts, nonstop observation is fundamental. In order to better answer the question of how global warming has triggered the shift in the patterns of Arctic sea ice, it is essential to investigate each region separately due to its own peculiarities. Addressing these explicit district inquiries might prompt further examination and bits of knowledge on the effects of environmental change on ocean ice.
More information: Mohammed Shokr et al, Why Does Arctic Sea Ice Respond More Evidently than Antarctic Sea Ice to Climate Change?, Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research (2023). DOI: 10.34133/olar.0006