Researchers have found evidence of ancient stone tools used for rice harvesting dating back to around 9,000 years ago in the Yangtze River Valley in China. This suggests that rice cultivation began in China around this time, which is earlier than previously believed. The tools were used to thresh and winnow rice, which are important steps in the process of rice cultivation. The discovery provides important insights into the development of agriculture in ancient China. A new Dartmouth-led study of stone tools from southern China finds the earliest evidence of rice harvesting, dating back 10,000 years. The researchers discovered two
Ancient Civilizations
An extinction event is defined as a widespread and rapid decline in Earth's biodiversity. A sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms is indicative of such an event. It occurs when the rate of extinction exceeds the rate of speciation and the rate of background extinction. According to new research from Florida State University, a decline in the element molybdenum across the planet's oceans preceded a significant extinction event about 183 million years ago. The decrease may have contributed to the mass extinction, which killed up to 90% of oceanic species, and it implies that much more
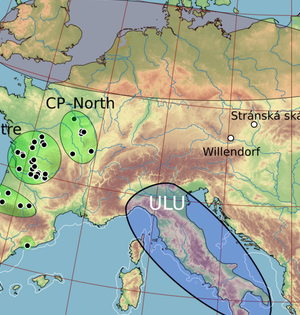
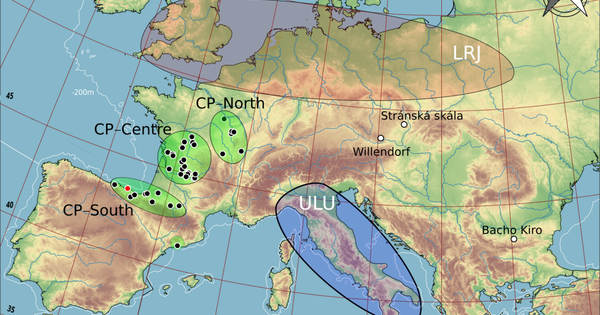
Neandertal populations in the Iberian Peninsula were experiencing local extinction and replacement even before Homo sapiens arrived, according to a study published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Joseba Rios-Garaizar of the Archaeological Museum of Bilbao, Spain and colleagues. Neandertals disappeared around 40,000 years ago, but many details of their extinction remain unclear. To elucidate the situation, it is useful to explore how Neandertal populations were changing during their final millennia. In this study, researchers examined the distribution of a tool complex known as the Châtelperronian, which is thought to be unique to certain populations of Neandertals in France
New genetic research from remote islands in the Pacific offers fresh insights into the ancestry and culture of the world's earliest seafarers, including family structure, social customs, and the ancestral populations of the people living there today. The work, described in the journal Science, reveals five previously undocumented migrations into a subregion of this area and suggests that about 2,500 to 3,500 years ago early inhabitants of these Pacific islands - including Guam in the northern region and Vanuatu in the southwest - had matrilocal population structures where women almost always remained in their communities after marriage while men more
There are traces of Neandertal DNA in the genome of modern humans, according to research. Now, an exploratory study that examined the facial structure of prehistoric skulls provides new information and supports the hypothesis that much of this interbreeding occurred in the Near East, which stretches from North Africa to Iraq. "Ancient DNA caused a revolution in how we think about human evolution," says co-author and Duke University professor of evolutionary anthropology Steven Churchill. "We often think of evolution as a tree with branches, and scientists have spent a lot of time trying to trace back the path that led
While only four species of slow-moving aquatic herbivores of the order Sirenia remain on the planet, many different types of sea cows have existed for the past 47 million years. Sea cows have lived along the coasts of every continent except Antarctica, and multiple species have coexisted at times. A new article has compiled the most complete history of these strange creatures' ancestors to date. Manatees and dugongs are referred to as "sea cows" by zoologists, but a quick internet search may yield the more amusing moniker "floaty potatoes." Imagine a 24,000-pound version swimming in the Bering Sea, twice the
Because of the geography of Greece, Ancient Greece was made up of hundreds of essentially independent city-states. Communities were separated by mountains, hills, and water. Rather than a unified nation, Ancient Greece was more like a network of communities with a shared religion and language, which sometimes led to a sense of common belonging. A modern scientific analysis of ancient stone tools is challenging long-held beliefs about what caused radical change on the island of Crete, where the first European state flourished during the Bronze Age: the 'Minoan civilization.' Crete underwent significant cultural transformations around 3,500 years ago, including the
Archaeologists from the University of Cincinnati discovered, using new scientific tools, that an ancient Greek leader known today as the Griffin Warrior grew up near the seaside city he would one day rule. The findings are part of three new studies published in the journal Science that looked at the ancient DNA of the Griffin Warrior and 726 other people who lived before and during the Bronze Age to learn more about their origins and movements across three continents surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. The papers, led by Harvard University researchers and co-authored by experts from around the world, show that
Researchers have successfully sequenced the genomes of ancient human fossils from the Late Pleistocene in southern China for the first time. According to the findings, which were published in the journal Current Biology, the mysterious hominin belonged to an extinct maternal branch of modern humans that may have contributed to the emergence of Native Americans. Su describes the ancient DNA technique as a "really powerful tool. Despite their unusual morphological features, it tells us quite definitively that the Red Deer Cave people were modern humans rather than an archaic species like Neanderthals or Denisovans," he says. The genomes of these
Widespread volcanic eruptions around 202 million years ago had a significant impact on Earth's climate, triggering a mass extinction event that wiped out three-quarters of the planet's species, including many large reptiles. Dinosaurs, on the other hand, survived and thrived. Dinosaurs are frequently thought to be heat-loving creatures, perfectly suited to the steamy greenhouse environment of the Triassic Period. But, unlike other reptiles of the time, their ability to adapt to cold temperatures may have been the key to their survival. Researchers report in Science Advances that the dinosaurs' warm feather coats may have helped the creatures weather relatively brief