The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission is designed to test whether a spacecraft impact can deflect an asteroid's trajectory, should a potentially hazardous asteroid be detected in the future. The target of the DART mission is the binary asteroid system Didymos, which consists of a primary asteroid and a smaller moonlet orbiting it. When asteroids collide in space, debris flies away from the point of impact. The asteroid's physical characteristics can be determined by the tail of particles that form. NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test mission in September 2022 provided a unique opportunity for a team of scientists, including
Astronomy & Space
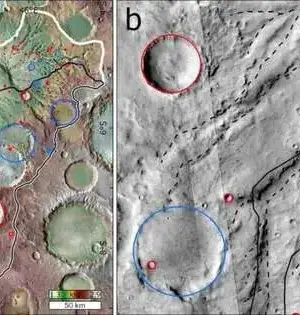
The Earth is shielded from cosmic radiation and the charged particles of solar wind by a geomagnetic field that is created within the planet and extends into space. The convection of charged molten iron fluids in the outer core of the Earth creates the magnetic field. Earth's inner core is inhomogeneous and anisotropic, as opposed to the convective, homogeneous outer core. The seismic velocity is 2–3 percent faster in the polar direction than in the equatorial direction. Researchers led by professors The Earth's anisotropic inner core structure is driven by the dipole geomagnetic field, according to Li Heping and He
On March 30, the newest science campaign for the Perseverance mission's rover cored and stored the first sample. The team investigates and researches a new topic with each campaign. On this one, the rover is investigating the top of Jezero Crater's delta. As part of the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign, Perseverance has returned a total of 19 samples, three witness tubes, and ten backup tubes to the Martian surface. In order to find evidence of prehistoric microbial life and to better understand how the water cycle shaped Mars' surface and interior, researchers want to analyze Martian
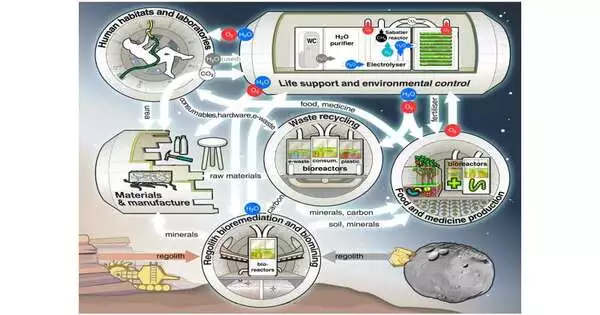
Scientists are under great pressure to find solutions to the problems of global warming, pollution, and depleting resources by pushing the boundaries of exploration and creating new technologies. By doing this, they are thinking broadly: they are considering not only how to address these issues on a domestic level but also how to improve the effectiveness and sustainability of space exploration. But as it turns out, some solutions come from having a limited perspective. This week, researchers from five continents published a report in Nature Communications that claimed microbe-based technologies could increase the sustainability and affordability of future life in
Taking advantage of a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, a group of astronomers has discovered one of the largest black holes ever discovered. Using supercomputer simulations and gravitational lensing on the DiRAC HPC facility, the Durham University, UK-based team was able to examine how light is distorted by a black hole hundreds of millions of light years away from Earth. Gravitational lensing occurs when a foreground galaxy magnifies the light of a more distant object. In the foreground galaxy, they discovered an ultramassive black hole that was larger than 30 billion times the mass of our sun—a scale that astronomers
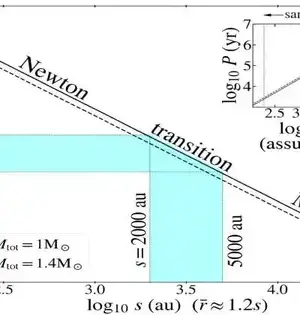
Fast radio bursts, or FRBs, are mysterious bursts of radio waves that come from faraway galaxies. We recently presented evidence for this phenomenon in Nature Astronomy. When two "supermassive" neutron stars collided, they produced a burst of gravitational waves, each of which was the super-dense core of an exploded star. We discovered that when the neutron star collapsed into a black hole two and a half hours later, it produced an FRB. So we believe. An optical or gamma-ray flash coming from the direction of the fast radio burst, which would either support or disprove our theory, vanished almost four
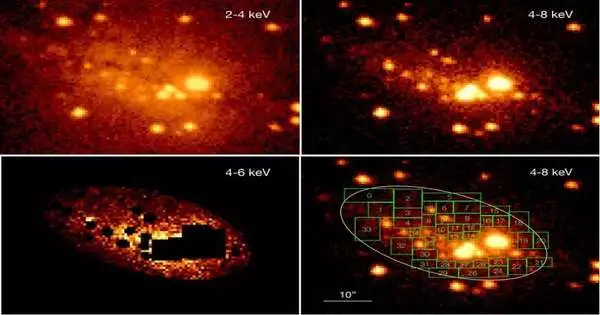
An international group of astronomers has made X-ray observations of the Cigar Galaxy with the help of the Chandra spacecraft from NASA. The observational campaign's findings, which were made public on the arXiv pre-print repository on March 16, provide important information about this galaxy's diffuse emission. The Cigar Galaxy, also known as Messier 82 or M82, is a starburst galaxy that was discovered in 1774. It is 11.73 million light years away in the constellation Ursa Major. It is one of the starburst galaxies closest to Earth and has a size of about 40,800 light years. The Cigar Galaxy is
What gave rise to life? The answer to this question gets right to the heart of why we are here on Earth. Did organic compounds simply react chemically to form life in a primordial soup left over from Earth's collision with space debris? Where did the organic compounds originate, if so? It's possible that the so-called "building blocks of life" were quite common in the beginning of the Solar System. Uracil, one of the five essential bases of the RNA and DNA molecules that are essential to life as we know it, was discovered after samples taken from the asteroid
Since days of yore, people all over the planet have looked up in stand amazed at the night sky. The brilliant night sky has not just roused endless works of music, craftsmanship and verse, yet has additionally assumed a significant part in timekeeping, route and horticultural practices in numerous customs. For some societies, the night sky, with its stars, planets and the Smooth Way, is viewed as similarly as significant a piece of the common habitat as the woods, lakes and mountains beneath. Endless individuals all over the planet look at the night sky: beginner and expert stargazers, yet in
A number of presumptions regarding particle size and their sensitivity to shape can be used to evaluate the impact of the cohesive force of asteroid particles on microgravity. Each day, approximately hundreds of kilograms of material from space enter Earth's atmosphere and settle down as fine dust and grains. Asteroids' fragments make up many of the meteorites that fall to Earth from space. Yuuya Nagaashi and an exploration group in planetology at Kobe College in Japan directed durable power estimations of shooting star pieces in another report currently distributed in Science Advances.The high mobility of asteroid surface particles discovered during