Galactic explosions, also known as supernovae, are some of the most powerful and energetic events in the universe. They occur when a star reaches the end of its life and explodes, releasing a tremendous amount of energy and matter into the surrounding space. For astrophysicists, these events offer valuable insights into the workings of the universe. They can help us understand the lifecycle of stars, the distribution of elements in the universe, and the formation of galaxies. An international team of researchers was able to view an exploding supernova in a distant spiral galaxy by chance using data from the
Astronomy & Space
Estimating the fuel supply on Odyssey, a decades-old shuttle without a fuel check, is no simple errand. Since NASA sent off the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to the Red Planet nearly a while ago, the space apparatus has circled around Mars multiple times. That is about what could be compared to 1.37 billion miles (2.21 billion kilometers), a distance that has required incredibly cautious administration of the rocket's fuel supply. This accomplishment is even more great given that Odyssey has no fuel check; engineers have needed to depend on math, all things considered. Their work has assisted Odyssey with building
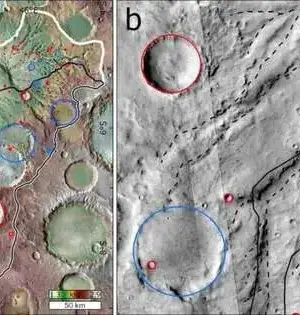
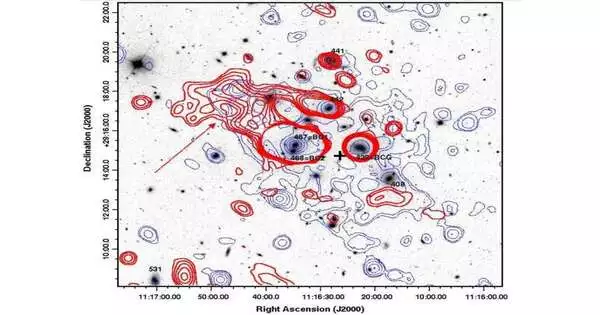
European stargazers have noticed a universe bunch known as Abell 1213 that utilizes different shuttles and ground-based offices. The perceptions divulged fundamental data about the diffuse radio emanation from this source. The discoveries are accounted for in a paper distributed with Walk 4 on the arXiv pre-print server. Many systems are bound together by gravity in universe clusters.They are the biggest known gravitationally bound structures known to man and could act as magnificent labs for concentrating on system development and cosmology. At a redshift of 0.047, Abell 1213 is an unfortunate low-mass cosmic system group ruled in its focal district
Four space station explorers got back to Earth late Saturday after a fast SpaceX flight home. Their case was scattered down in the Bay of Mexico simply off the Florida coast close to Tampa. The U.S.-Russian-Japanese team burned through five months at the Global Space Station, showing up last October. Other than evading space garbage, the space explorers needed to manage a couple of releasing Russian containers docked to the circling station and the critical conveyance of a substitution for the station's other group of individuals. Driven by NASA's Nicole Mann, the main local American lady to fly in space,
DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) is a space mission led by NASA that aims to test whether it is possible to deflect an asteroid on a collision course with Earth. The mission involves the launch of a spacecraft, which will collide with the moon of an asteroid system called Didymos, located about 11 million kilometers away from Earth. The collision is expected to change the orbit of the moon, thus testing the effectiveness of the impact as a means of asteroid deflection. In 2022, NASA embarked on a risky experiment to see if they could change the velocity of an
Today Venus has a dry, oxygen-unfavorable environment. In any case, late examinations have suggested that the early planet might have had fluid water and intelligent mists that might have supported tenable circumstances. Scientists at the University of Chicago's Division of Geophysical Sciences have constructed another time-subordinate model of Venus' air structure to investigate these cases. Their discoveries have been distributed in the Procedures of the Public Foundation of Sciences. Water is wherever in our planetary group, as a rule as ice or barometrical gas, but occasionally in fluid structure. On the planets in general, a significant number of the moons,
Researchers have made a huge, engineered study that shows what we can anticipate from the Nancy-Beauty-Roman Space Telescope's future perceptions. However, it addresses simply a little lump of the genuine future study. This mimicked form contains a stunning number of worlds—33 million of them, alongside 200,000 forefront stars in our home system. The recreation will assist researchers with arranging the best noticing systems, testing various ways of mining the mission's huge amounts of information, and investigating what we can gain from pairing perceptions with different telescopes. "The volume of information Roman will return is uncommon for a space telescope," said
Researchers examining a nearby protostar have recognized the presence of water in its circumstellar plate. The novel perceptions made with the Atacama Huge Millimeter/Submillimeter Cluster (ALMA) mark the main location of water being acquired into a protoplanetary plate without massive changes to its piece. These outcomes further propose that the water in our planetary group shaped billions of years before the sun. The novel perceptions are distributed today in Nature. V883 Orionis is a protostar found about 1,305 light-years from Earth in the star group Orion. The novel perceptions of this protostar have assisted researchers in finding a likely connection
Far faster than one would anticipate for a collapsing star, millisecond pulsars spin. Finding a black widow system where the pulsar has vaporized and consumed much of its companion star offers the finest chance to investigate these neutron stars. Astronomers were only able to weigh the pulsar of one of these companions thanks to the Keck I telescope's ability to catch its spectrum. It is the heaviest known object and may be getting close to the maximum limit for neutron stars. The Milky Way galaxy's fastest spinning neutron star, a compact, collapsed star that spins 707 times per second, has
On the top right shoulder of the winter constellation Orion the Hunter, there is a dazzling, ruby-red, sparkling speck of light that is the star Betelgeuse. Astronomers, however, recognize it as a seething monster with a 400-day-long heartbeat of regular pulsations when they look at it closely. This old star is a supergiant because of its astounding expansion to a diameter of almost 1 billion miles. If placed at the center of our solar system it would reach out to the orbit of Jupiter. The star will eventually undergo a supernova explosion. When that eventually occurs, it will be momentarily