Space experts have found in excess of 200 far-off factor stars known as RR Lyrae stars in the Smooth Manner's heavenly radiance. The most distant of these stars is more than 1 million light years away from Earth, which is close to a quarter of the distance to our neighboring cosmic system, Andromeda, which is approximately 2.5 million light years away. The trademark throbs and brilliance of RR Lyrae stars make them incredible "standard candles" for estimating cosmic distances. These groundbreaking perceptions have permitted the analysts to follow the furthest reaches of the Smooth Way's corona. "This rethinking review includes
Astronomy & Space
A newfound comet could be noticeable to the unaided eye as it shoots past Earth and the Sun before long, without precedent for 50,000 years, stargazers have said. The comet is known as C/2022 E3 (ZTF) after the Zwicky Transient Office, which discovered it passing Jupiter in spring last year. Subsequent to leaving the cold spans of our planetary group, it will come nearest to the sun on January 12 and pass closest to earth on February 1. It will be easy to detect with a decent set of optics and logical even with the unaided eye, if the sky
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are some of the most energetic and luminous explosions in the universe. They are thought to be caused by the collapse of massive stars or the merger of neutron stars, and are often associated with black holes. However, it is possible for GRBs to be caused by other mechanisms as well. For example, some GRBs may be produced by the collapse of extremely massive and rapidly rotating stars called magnetars. There is still much that we don't understand about the precise mechanisms that produce GRBs, and ongoing research is aimed at better understanding these mysterious and powerful
The Big Bang Theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the origin and evolution of the universe. It proposes that the universe was once a singularity, or a point in space with infinite density and temperature, that began expanding 13.8 billion years ago. An international team of astrophysicists, including Prof. Rennan Barkana from the Sackler School of Physics and Astronomy at Tel Aviv University, has managed for the first time to statistically characterize the first galaxies in the Universe, which formed only 200 million years after the Big Bang. The ground-breaking findings indicate that the earliest galaxies were small
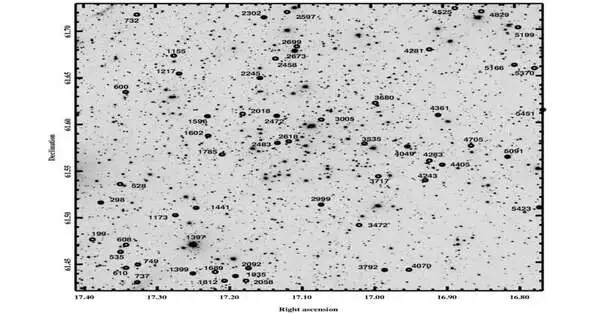
Stargazers from the Aryabhatta Exploration Foundation of observational science (ARIES) and from the Actual Exploration Lab in India report the location of 57 variable stars in the field of open group NGC 381. The disclosure was itemized in a paper distributed on December 19 on the arXiv preprint server. Open bunches (OCs), shaped from a similar goliath sub-atomic cloud, are gatherings of stars freely gravitationally bound to one another. Up to this point, more than 1,000 of them have been found in the Smooth Manner, and researchers are still searching for more, wanting to track down various of these heavenly
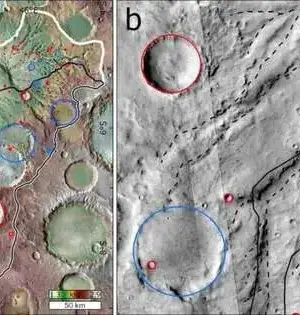
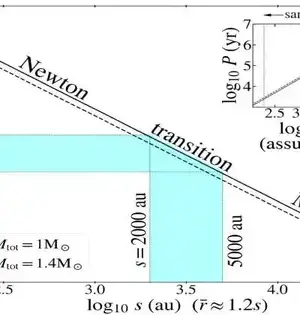
Although dull matter is a central component of the standard cosmological model, it is not without flaws.There are still annoying secrets about the stuff, not the least of which is that no immediate molecule proof of it has been discovered. Regardless of various inquiries, we can't seem to identify dull matter particles. So a few space experts favor another option, like changed Newtonian elements (MoND) or an altered gravity model. What's more, another investigation of the cosmic pivot appears to help them. The cosmic turn sparked the possibility of MoND.The majority of the noticeable matter in a world is bunched
Lunar Pioneer, NASA's main goal driven by Caltech in Pasadena, California, to comprehend lunar water and the moon's water cycle, is one bit nearer to sending off the following year. Recently, the office's Fly Drive Lab in Southern California conveyed a key science instrument to Lockheed Martin Space in Colorado, and the groups coordinated it with the little satellite, or SmallSat. The instrument, called the High-goal Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM3), is one of two on the Lunar Pioneer. HVM3 will identify and plan water on the moon's surface to decide its overflow, area, structure, and how it changes
At the point when NASA's Mars wanderers found manganese oxides in rocks in the Storm and Try pits on Mars in 2014, the disclosure led a few researchers to propose that the red planet could have once had more oxygen in its air billions of years prior. The minerals likely needed plenty of water and firmly oxidizing conditions to take shape, the researchers said. Using examples from Earth's geologic record, researchers hypothesized that the presence of manganese oxides indicated that Mars had previously experienced occasional increases in air oxygen — prior to declining to the current low levels. Yet, another
Interestingly stargazers have recognized a planet that is spiraling towards a disastrous crash with its maturing sun, possibly offering a brief look into how Earth could end one day. In another review distributed on Monday, a group of generally US-based scientists said they trust the bound exoplanet Kepler-1658b can assist with revealing insight into how universes pass on as their stars age. Kepler-1658b, which is 2,600 light a long time from Earth, is known as a "hot Jupiter" planet. While comparable in size to Jupiter, the planet circles its host star an eighth of the distance between our Sun and
It is no distortion to say the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) addresses another time in current cosmology. Sent off on December 25 of last year and completely functional since July, the telescope offers looks at the universe that were previously distant to us. Like the Hubble Space Telescope, the JWST is in space, so it can take pictures with dazzling subtlety liberated from the bends of Earth's air. In any case, while Hubble is in a circle around Earth at a height of 540 kilometers, the JWST is 1.5 million kilometers away, a long way past the moon. From