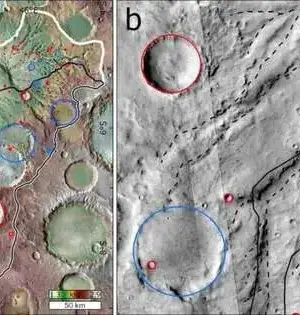
Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun and are mostly found between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt. These objects, which are remnants of the early solar system, are made up of a variety of materials, including organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules made up of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen that serve as the foundation for life as we know it. Analyses of organic compounds known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) extracted from the Ryugu asteroid and the Murchison meteorite revealed that certain PAHs formed in cold areas of space between stars rather than hot regions near
Astronomy & Space
Astronomers studying James Webb Space Telescope images have identified an object as a 'dusty star-forming galaxy' from nearly 1 billion years after the Big Bang. They have also discovered more than a dozen additional candidates, implying that these galaxies are three to ten times more common than previously thought. If that conclusion is correct, it indicates that the early universe was much dustier than previously thought. It first appeared as a glowing blob in ground-based telescope images before disappearing completely in Hubble Space Telescope images. The ghostly object has reappeared as a faint but distinct galaxy in a James Webb
Astronomers have observed water and other molecules for the first time in the highly irradiated inner, rocky-planet-forming regions of a disk in one of our galaxy's most extreme environments. These findings suggest that the conditions for the formation of terrestrial planets can occur in a broader range of environments than previously thought. An international team of astronomers used NASA's James Webb Space Telescope to observe water and other molecules for the first time in the highly irradiated inner, rocky-planet-forming regions of a disk in one of our galaxy's most extreme environments. These findings suggest that the conditions for the formation
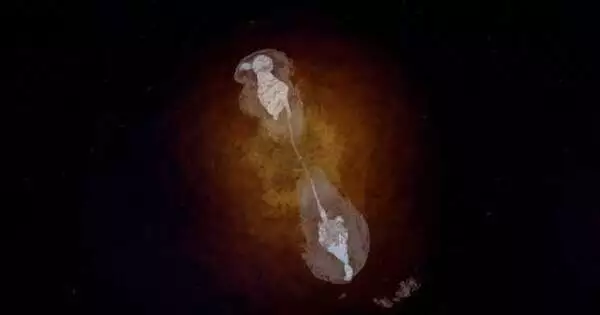
Astronomers have discovered a disc around a young star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a neighboring galaxy to our own. It's the first time such a disc, similar to those that form planets in our own Milky Way, has been discovered outside of our galaxy. The new findings show a massive young star growing and accreting matter from its surroundings to form a rotating disc. The detection was made with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, a collaboration with the European Southern Observatory (ESO). "When I first saw evidence for a rotating structure in the ALMA data, I
Denoting its 1,000th Martian day on the Red Planet, NASA's Diligence Meanderer, a late-finished investigation of the old stream delta, holds proof of a lake that filled Jezero Cavity billions of years prior. The six-wheeled researcher needs to gather a total of 23 examples, uncovering the geologic history of this district of Mars all the while. One example called "Lefroy Straight" contains an enormous amount of fine-grained silica, a material known to protect old fossils on the planet. Another, "Otis Pinnacle," holds a lot of phosphate, which is frequently connected with life as far as we might be concerned. Both
Nearly 300 gamma ray pulsars have been discovered, according to scientists. In their Third Catalog of Gamma Ray Pulsars, the United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) and the international Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration announce the discovery of nearly 300 gamma ray pulsars. This achievement comes 15 years after Fermi's launch in 2008, when there were fewer than ten known gamma-ray pulsars. "Work on this important catalog has been going on in our group for years," said Paul Ray, Ph.D., head of the High Energy Astrophysics and Applications Section at NRL. "Our scientists and postdocs have been able to both
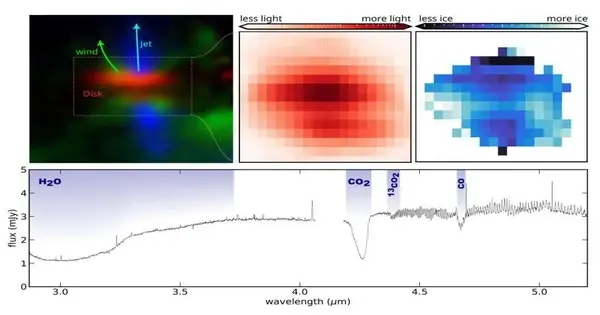
A Dutch-drove global group of cosmologists has made the initial two-layered stock of ice in a planet-shaping plate of residue and gas encompassing a youthful star. They utilized the James Webb Space Telescope and have distributed their discoveries in the journal Cosmology and Astronomy. Ice contributes quite a bit to the development of planets and comets. Because of ice, strong residue particles cluster together into bigger pieces, out of which planets and comets form. Moreover, the effects of ice-bearing comets likely contributed altogether to how much water is on our planet, framing its oceans. This ice likewise contains particles of
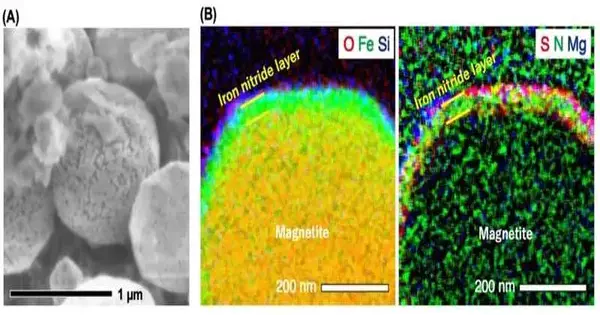
Micrometeorites starting from frigid divine bodies in the external planetary group might be responsible for moving nitrogen to the close Earth locale at the beginning of our planetary group. That disclosure was distributed in Nature Space Science by a global group of specialists, including College of Hawai'i at Mānoa researchers, driven by Kyoto College. Nitrogen compounds, for example, ammonium salts, are bountiful in material brought into the world in locales a long way from the sun; however, proof of their vehicle to Earth's orbital district has been inadequately perceived. "Our new discoveries recommend the likelihood that a more noteworthy measure
State-of-the-art programmatic experiences joined with hypothetical computations are assisting astronomers with better grasping the beginning of a portion of the universe's most fiery and secretive light shows—gamma-beam explosions, or GRBs. The new brought-together model affirms that some durable GRBs are made as a consequence of enormous consolidations that produce a baby dark opening encompassed by a goliath plate of natal material. Stargazers recently felt that dark openings that create long GRBs regularly structure when gigantic stars breakdown. In any case, the new model demonstrates the way that they can likewise emerge when two thick items blend, for example, a couple
A recently constructed Global Fluid Mirror Telescope (ILMT) in India has distinguished its most memorable cosmic explosion—assigned SN 2023af. The finding, revealed on November 8 on the pre-print server arXiv, demonstrates that ILMT might be equipped to distinguish many new supernovae before long. Supernovae (SNe) are strong and brilliant heavenly blasts that could end up being useful to us in better grasping the development of stars and cosmic systems. Stargazers partition supernovae into two groups in light of their nuclear spectra: Type I and Type II. Type I SNe need hydrogen in their spectra, while those of Type II grandstand