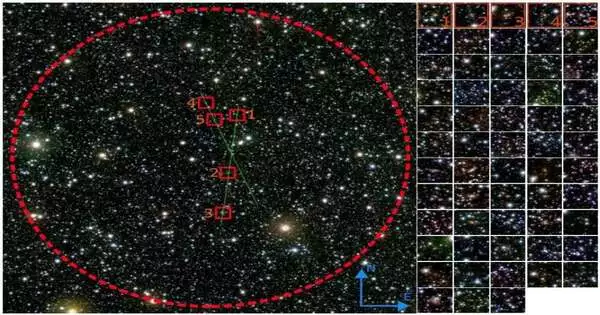
A group of scientists with individuals from Universidad Nacional de San Juan, Universidade Government do Rio Grande do Sul and Universidad Andres Bello has found proof of a huge extragalactic gathering taking cover behind one piece of the Smooth Way world. The gathering has distributed a paper depicting their discoveries on the arXiv preprint server while anticipating distribution in the diary Cosmology and Astronomy. Space researchers have known for quite a while that there is one piece of the night sky that is generally clouded from view because of a lump in the world. Known as the "zone of evasion,"
Astronomy & Space
The earliest morphological hints of life on Earth are frequently profoundly dubious, both on the grounds that non-natural cycles can create somewhat comparable designs and on the grounds that such fossils have frequently been exposed to cutting-edge change and transformation. Stromatolites, layered organo-sedimentary designs reflecting complex exchanges between microbial networks and their current circumstances, have for some time been viewed as key macrofossils for life location in old sedimentary rocks; in any case, the natural beginning of old stromatolites has regularly been censured. An article delivered Friday in the journal Geography utilizes a scope of cutting-edge two- and three-layered logical
Another review from the College of Focal Florida has areas of strength, finding that the outgassing of atoms from comets could be the consequence of the piece from the start of our planetary group. The outcomes were distributed today in The Planetary Science Diary. The review was driven by Olga Harrington Pinto, a doctoral competitor in UCF's Branch of Physical Science, part of the School of Sciences. Estimating the proportion of specific atoms present subsequent to outgassing from comets can give experiences to the compound piece of early planetary groups and the actual handling of comets after they are framed,
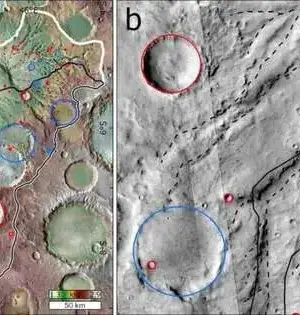
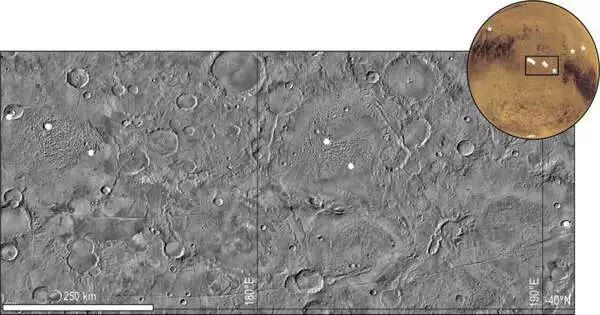
Early habitation on Mars might be surprisingly intricate—aand it might try to be like our own planet's unique exterior. The Martian surface is consistently basaltic, a result of billions of long periods of volcanism and streaming magma on a superficial level that at last cooled. Since Mars didn't go through full-scale surface rebuilding like the moving of continents onto the planet, researchers had believed Mars' crustal history was a somewhat basic story. Yet, in another review, scientists tracked down areas in the Red Planet's southern half of the globe with more prominent groupings of silicon, a compound component, than what
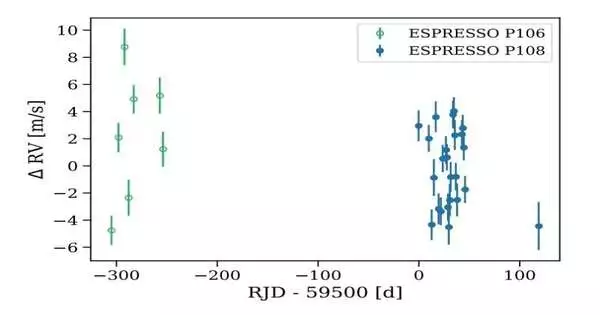
Involving the Echelle SPectrograph for Rough Exoplanets and Stable Spectroscopic Perceptions (Coffee), stargazers from Switzerland and Austria have found another outsider world. The newly discovered exoplanet circles a close by M small star and is no less than multiple times more huge than the Earth. The finding is accounted for in a paper distributed October 23 on arXiv.org. Coffee is the cutting edge super stable high goal spectrograph introduced at the Huge Telescope (VLT) in Chile, covering the phantom reach from around 380 nm to 788 nm. The instrument can arrive at an accuracy permitting it to identify Earth-like planets
Dusk perceptions with the US Branch of Energy-created Dim Energy Camera at Cerro Tololo The American Observatory in Chile, a program of NSF's NOIRLab, has empowered stargazers to detect three close-to-Earth space rocks (NEA) concealed in the brightness of the sun. These NEAs are essential for a subtle populace that hides inside the circles of Earth and Venus. One of the space rocks is the biggest item that is possibly risky to Earth to have been found over the most recent eight years. A global group utilizing the Dim Energy Camera (DECam) mounted on the Vctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope
It's realized that water ice exists beneath the lunar regolith (broken rock and residue), yet researchers don't yet comprehend whether surface ice covers the floors inside these cool pits. To find out, NASA is sending Lunar Spotlight, a little satellite (or SmallSat) no bigger than a satchel. Diving low over the lunar South Pole, it will utilize lasers to reveal insight into these dim pits—similar to a miner searching for buried treasure by sparkling a spotlight into a cavern. The mission will be sent off on board a SpaceX Hawk 9 rocket in mid-November. "This send off will put the
A branch of astronomy called radio astronomy focuses on the study of celestial objects at radio frequencies. Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation emanating from the Milky Way in 1933, marking the first time radio waves from an astronomical object had been discovered. A variety of distinct radio emission sources have been discovered through further studies. In addition to stars and galaxies, these also contain completely new kinds of phenomena like radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. Radio astronomy was used to make the cosmic microwave background radiation finding, which is viewed as supporting evidence for the Big
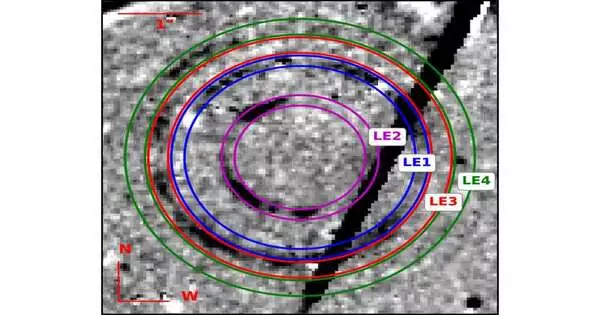
When a star detonates (a cosmic explosion), it sends its serious eruption of light out every which way. Now and again, in the long stretches of time that follow, rings of light, or "light repeats," spread out from the first cosmic explosion position. This is depicted in a new paper in The Astrophysical Diary Letters in view of perceptions with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) by a cooperation of stargazers from Dublin, Barcelona, Aarhus, New York, and Garching. The paper, "Hubble Space Telescope Uncovers Fabulous Light Repeats Related to the Stripped-envelope Cosmic Explosion 2016adj in the Famous Residue Path of
NASA's Knowledge lander recorded a size 4 marsquake last Dec. 24, yet researchers learned just later the reason for that shake: a meteoroid strike assessed to be one of the greatest seen on Mars since NASA started investigating the universe. Likewise, the meteoroid exhumed rock-sized lumps of ice covered nearer to the Martian equator than at any other time found previously — a revelation with suggestions for NASA's likely arrangements to send space travelers to the Red Planet. Researchers decided the shake came about because of a meteoroid influence when they took a gander at pictures from NASA's Mars Observation