The mass of thick gas and residue looks like a gigantic winged animal, its sparkling throat lit by a brilliant star as it takes off through vast fibers. A worldwide examination group on Monday uncovered the main pictures of the Orion Cloud caught with the James Webb Space Telescope, leaving stargazers "blown away." The heavenly nursery is arranged in the group of stars Orion, 1,350 light-years from Earth, in a comparable setting in which our own nearby planet group was born more than 4.5 billion years ago. "In this image, we see how the first generation of stars is effectively
Astronomy & Space
Utilizing the Exceptionally Enormous Telescope and the radio telescope ALMA in Chile, a group of cosmologists, including scientists from the Niels Bohr Organization, has found a multitude of worlds circling the environmental elements of a hyper-brilliant and enthusiastically star-shaping system in the early universe. The perception gives significant insights into how uncommonly brilliant systems develop and how they advance into lively quasars, radiating light across the vast majority of the discernible universe. The subject of how systems structure, develop, and advance is a critical issue in cosmology. As a piece of their development, most universes appear to encourage a supermassive
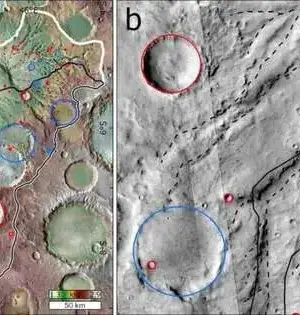
Scientists have mapped out the dark matter around some of the earliest, most distant galaxies yet. The 1.5 million galaxies appear as they were 12 billion years ago, or less than 2 billion years after the Big Bang. Those galaxies distort the cosmic microwave background — light emitted during an even earlier era of the universe — as seen from Earth. That distortion, called gravitational lensing, reveals the distribution of dark matter around those galaxies, scientists report in the Physical Review Letters. Understanding how dark matter collects around galaxies early in the universe’s history could tell scientists more about the
Earth, of all the planets mentioned, is as welcoming to life as any other—or is it?In the event that Jupiter's circle changes, another review shows Earth could be more cordial than it is today. At the point when a planet has a totally round circle around its star, the distance between the star and the planet won't ever change. In any case, most planets have "offbeat" circles around their stars. It is oval-molded to mean the circle. At the point when the planet draws nearer to its star, it gets more intense, influencing the environment. Using definite models in view
A global group of scientists has found proof showing that in spite of the unfriendly natural circumstances on Mars, the gear utilized by wanderers on its surface ought to be fit for recognizing proof of life assuming it at any point existed there. In their paper distributed in the diary Science Advances, the gathering depicts how they exposed example materials to Mars-like circumstances and afterward tried them to perceive how well they endured the maltreatment. In spite of a ton of testing by wanderers shipped off Mars to both review the planet and to find evidences of life past or
Maser outflows, "vast lasers" from the interstellar and circumstellar medium, are created by the enhancement of animated emanations. The Splendid and smaller maser sources are great focuses for high-accuracy astrometry in the kinematic investigation of the Smooth Way. An examination group from the Public Time Administration Center (NTSC) of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences led a 22 GHz water maser study towards the O-rich asymptotic goliath branch (AGB) stars in the Sagittarius heavenly stream. Utilizing the Nobeyama 45-m and Tidbinbilla DSS-43 70-m telescopes, 21 maser outflows were found, of which 20 were recognized interestingly. The outcomes were distributed in the
Dark openings are cosmic items with very amazing gravitational pulls from which not even light can escape. While bodies that would trap light have been around since the eighteenth century, the main direct perception of dark openings occurred in 2015. From that point forward, physicists have led endless hypothetical and trial studies focused on better grasping these entrancing cosmological items. This has prompted numerous disclosures and hypotheses about the novel qualities, properties, and elements of dark openings. Scientists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität and Max-Planck-Institut für Physik have as of late put together a hypothetical report investigating the conceivable presence of vortices in
Cosmologists utilizing the W. M. Keck Observatory on Hawaii Island have captured from Maunakea the most point-by-point and complete pictures at any point taken of the zone where the renowned heavenly body of Orion gets destroyed by bright (UV) radiation from enormous young stars. This illuminated nonpartisan zone, called a Photo-Dissociation Region (PDR), is situated in the Orion Bar inside the Orion Nebula, a functioning star-shaping site found in the "sword" swinging from Orion's "belt." When seen with the unaided eye, the cloud is frequently confused with one of the stars in the heavenly body; when seen with a telescope,
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) caught pictures of an earthy-colored predominate with silicate particles in its environment. In their paper posted on the arXiv preprint server, space experts describe their examination of the earthy-colored overshadow and its exceptional climate. Earthy-colored diminutive people are space protests that some have named bombed stars. They start their reality similarly to different stars, yet neglect to develop sufficient hydrogen to induce a combined response. Thus, they don't develop to the size of stars; consequently, their name Earthy colored diminutive people can meld deuterium, but the temperature and tension are a lot lower than
An interdisciplinary group revolved around a Jena astrophysicist used perceptions from times long past to demonstrate that Betelgeuse — the dazzling red monster star in the upper left of the heavenly body Orion — was yellow-orange quite a while back. As atomic combinations in the focal point of a star advance, brilliance, size, and variety likewise change. Astrophysicists can get from such properties significant data on the age and mass of a star. Those stars with essentially more mass than our sun are blue-white or red; the progress from red to yellow and orange is generally quick for cosmic time-scales.