Geomagnetic storms occur when space weather collides with Earth. Space weather is caused by solar fluctuations that send electrons, protons, and other particles into space. Measuring the speed and size of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) as they erupt from the sun has been found to be critical in providing accurate early warnings that keep astronauts and technology safe. Scientists have discovered that space weather forecasters must predict the speed of solar eruptions as well as their size in order to protect satellites and astronauts' health. NASA has collaborated with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to develop the most
Astronomy & Space
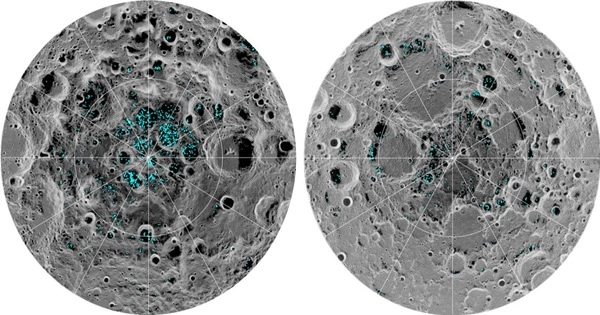
Scientists from the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, have created the first complete map of hydrogen abundances on the Moon's surface using data collected over two decades ago. The map identifies two types of lunar materials containing enhanced hydrogen and confirms previous ideas about lunar hydrogen and water, such as the discovery that water likely played a role in the Moon's original magma-ocean formation and solidification. To create their map, APL's David Lawrence, Patrick Peplowski, and Jack Wilson, along with Rick Elphic from NASA Ames Research Center, used orbital neutron data from the Lunar Prospector mission.
Nebraska Engineering Professor Shane Farritor's scaled-down robot may soon be launched into space to test its capabilities. NASA recently awarded the University of Nebraska-Lincoln $100,000 through the Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR) at the University of Nebraska Omaha to prepare the cautious robot for a test mission aboard the International Space Station in 2024. "NASA has been a long-time ally in this examination and, as a result of that work, our robot will get an opportunity to fly on the International Space Station," Farritor said. Farritor is a prime supporter of Virtual Incision, a new business in view
A review of the zinc isotope composition of shooting stars by scientists from the University of St Andrews proposes that material from the external planetary group was a significant wellspring of unstable components during the development of the Earth. The subject of the beginning of the unstable components present on Earth is key to grasping the advancement of our planet. The review, conducted by scientists in the University's School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, as a team with laborers at the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris and Université Clermont Auvergne, shows, interestingly, that there is a contrast between
The James Webb Space Telescope has looked through time and immense measures of residue to catch another picture of the Cartwheel Galaxy, uncovering the turning ring of variety in uncommon lucidity, NASA and the European Space Agency said Tuesday. Situated around 500 million light-years from Earth in the star group Sculptor, the Cartwheel acquired its shape during a terrific head-on crash between two worlds. The effect sent two rings growing from the world's middle, "similar to swells in a lake after a stone is thrown into it," NASA and the ESA said in a joint explanation. The more modest white
Uncovering the possibly livable environment of old Mars is a vital piece of NASA's main goal to investigate and grasp the obscure, to move and help mankind — and for a long time, the Curiosity wanderer has been working on it on the Red Planet. To check the event, the following are five of the main disclosures that researchers have made utilizing Curiosity's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument suite. SAM is one of NASA's most remarkable astrobiology instruments on Mars. Planned and carried out at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, SAM looks for and measures natural
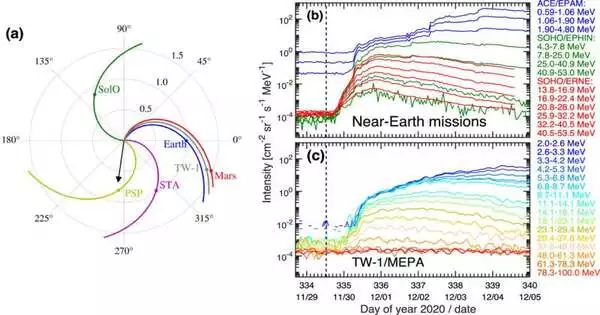
Scientists from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and their partners have revealed a sun-based fiery molecule (SEP) event seen by the Mars Energetic Particle Analyzer (MEPA) carried on China's Tianwen-1 (TW-1) rocket. The paper was distributed in the Astrophysical Journal Letters as the main logical report in view of MEPA. MEPA, mutually created by IMP and the Lanzhou Institute of Physics, is the main logical payload of China pointed toward concentrating on the interplanetary and close-to-Mars space radiation climate. It was sent off with the TW-1 rocket in July 2020 to begin
Nuclear clocks, together with exact cosmic estimations, have revealed that the length of a day is unexpectedly getting longer, and researchers don't have any idea why. This has basic effects on our timekeeping, yet in addition things like GPS and different advances that oversee our cutting edge life. Throughout recent years, Earth's turn around its hub—which decides how long a day is—has been accelerating. This pattern has been shortening our days; in fact, in June 2022, we set a record for the shortest day in the last 50 years, or something along those lines. Yet, in spite of this record,
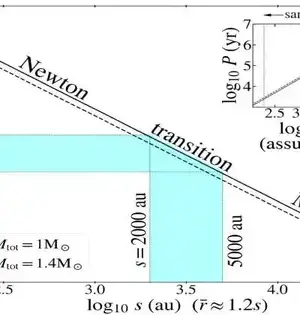
Dark openings with changing light marks yet were believed to be similar items being seen from various points are in various phases of the existence cycle, as per a review led by Dartmouth specialists. The examination of dark openings known as "dynamic cosmic cores," or AGNs, says that it authoritatively shows the need to change the generally utilized "brought together model of AGN" that describes supermassive dark openings as all having similar properties. The review, distributed in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, gives an irritating space secret and ought to permit scientists to make more precise models about the development
NASA-subsidized researchers have found concealed areas inside pits on the Moon that generally drift around an agreeable 63 F (around 17 C) utilizing information from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) shuttle and PC demonstrating. The pits and caverns to which they might lead would make thermally stable locales for lunar investigation contrasted with regions at the moon's surface, which heat up to 260 F (around 127 C) during the day and cool to a mere 280 F (about 173 C) around evening time. Lunar investigation is important for NASA's objective to investigate and grasp the obscure in space, to rouse