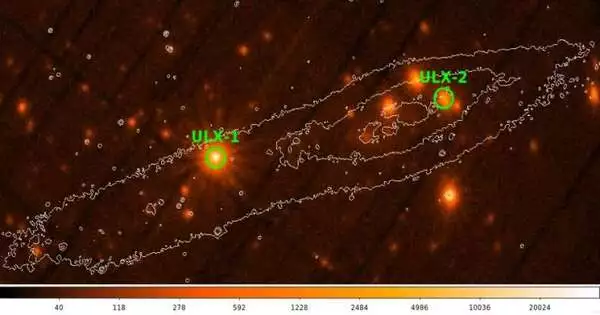
Utilizing ESA's XMM-Newton and NASA's Swift space telescopes, a global group of stargazers have noticed a nearby cosmic system known as NGC 55. They found another transient ultraluminous X-beam source in this cosmic system. The finding is accounted for in a paper distributed July 19 on the arXiv pre-print server. Ultraluminous X-beam sources (ULXs) are point sources overhead that are so splendid in X-beams that each produces more radiation than 1 million suns discharge at all frequencies. They are less brilliant than dynamic cosmic cores but more reliably iridescent than any known heavenly cycle. Although various investigations into ULXs have
Astronomy & Space
A thick, imploded star turning 707 times each second — making it one of the quickest turning neutron stars in the Milky Way cosmic system — has destroyed and drunk almost the whole mass of its heavenly sidekick and, all the while, developed into the heaviest neutron star known to date. Gauging this unparalleled neutron star, which beats out all competitors at 2.35 times the mass of the sun, assists cosmologists with understanding the odd quantum condition of issues inside these thick items, which—assuming they get a lot heavier than that—breakdown totally and vanish as a dark opening. "We know
Planetary researchers from Rice University, NASA's Johnson Space Center and the California Institute of Technology have a solution to a secret that has bewildered the Mars research local area since NASA's Curiosity meanderer found a mineral called tridymite in Gale Crater in 2016. Tridymite is a high-temperature, low-pressure type of quartz that is very uncommon on Earth, and it wasn't immediately clear how a concentrated piece of it wound up in the pit. Curiosity's arrival site was picked because of the probability that it once held fluid water, and Curiosity found proof that affirmed Gale Crater was a lake as
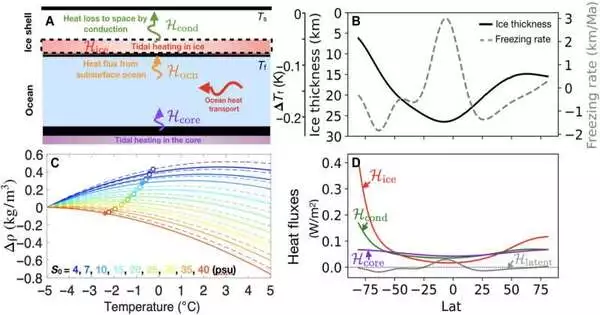
A theoretical model suggests that the oceans of Enceladus may be sufficiently salty to support life.
A group of specialists at MIT has found through hypothetical display that the pungency of the seas on Saturn's moon, Enceladus, might be the right level to support life. In their paper distributed in the journal Science Advances, the gathering depicts the variables that went into building their model and the highlights of Enceladus that were utilized to quantify the pungency of its seas. The joined information from the Cassini and Galileo missions showed that Saturn's moon Enceladus and Jupiter's moon Europa both hold potential for fulfilling three of the principal highlights accepted to be important for supporting life on
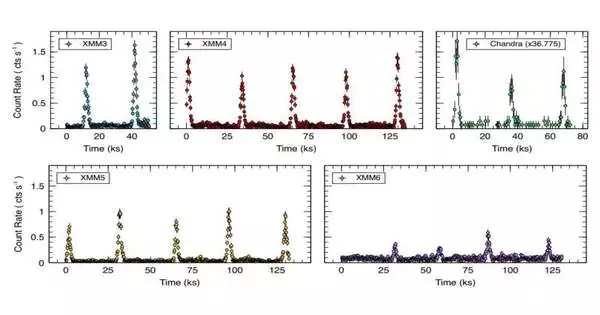
Utilizing ESA's XMM-Newton satellite and NASA's Chandra shuttle, a global group of cosmologists has researched an exceptional way of behaving semi-occasional ejections (QPEs) in a functioning system known as GSN 069. The consequences of the review, distributed July 15 on arXiv.org, shed all the more light on the idea of the QPE peculiarity. X-beam semi-occasional ejections are a recently discovered peculiarity related to supermassive dark openings at system focuses.They are outrageous high-sufficiency explosions of X-beam radiation, repeating like clockwork and starting close to the focal supermassive dark openings (SMBHs) in cosmic cores. Found about 250 million light years away in
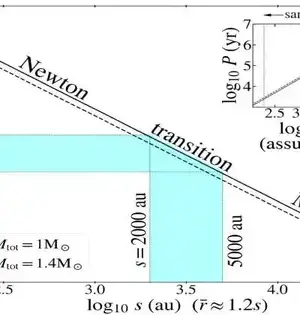
A group of worldwide specialists who are known for exposing dark opening revelations have found a torpid heavenly mass dark opening in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a system that neighbors the Milky Way. The group incorporates Kareem El-Badry — nicknamed by individual stargazers as the "dark opening destroyer" — of the Center for Astrophysics at Harvard and Smithsonian (CfA). "Interestingly, our group got together to provide details regarding a dark opening disclosure, rather than dismissing one," says concentrate on lead Tomer Shenar, a Marie-Curie Fellow at Amsterdam University in the Netherlands. The group found that the star that led to
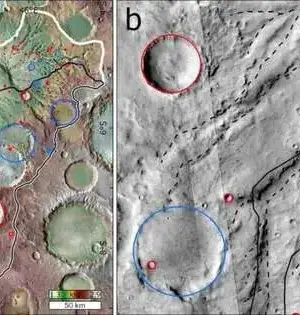
A group led by Prof. Toru Misawa of the School of General Education at Shinshu University figured out for the primary opportunity that the inward doughnut molded construction of the focal cores of splendid cosmic systems in the far off universe can have an "anisotropic" impact on the gas circulated over an immense region around them. Since the brilliant cores of far-off cosmic systems (quasars) discharge solid-bright radiation, they ionize hydrogen gas (intergalactic gas) around them. Assuming that the quasar's UV radiation is isotropic, the "ionization level" of intergalactic gas ought to be practically steady no matter what the course
Scott Sheppard, a cosmologist with the Institute of Astronomy at the University of Hawaii, has distributed a Perspective piece in the journal Science proposing that it is the ideal opportunity for the space science local area to investigate Earth objects (NEOs) that lie toward the sun. In his paper, he takes note of the innovation presently existing to search for and find such NEOs, essentially during the dusk hours. As Sheppard notes, most spherical looking is fixed on the dull night sky, when the sky isn't overpowered by light from the sun. In any case, subsequently, space researchers have disregarded
The National Science Foundation said Tuesday it intends to direct a review to assess the ecological impacts of building one of the world's biggest optical telescopes on destinations chosen in Hawaii and Spain's Canary Islands. The organization distributed a notification in the Federal Register of its expectations to set up an ecological effect proclamation for the $2.65 billion Thirty Meter Telescope. The telescope's allies have sought after plans to fabricate it on their favored site on the highest point of Mauna Kea, Hawaii's tallest mountain and one of the world's best areas for reviewing the night sky, for more than
A small space pebble has had a large impact on NASA's newly operating deep-space telescope. Between May 22 and 24, a micrometeoroid damaged the James Webb Space Telescope, damaging one of the observatory's 18 hexagonal golden mirrors. NASA announced the micrometeoroid strike in June, stating that the debris was larger than pre-launch modeling had predicted. In a report released on July 12 explaining what scientists on the project learned about operating the observatory during its first six months in space, experts on the expedition have shared an image that emphasizes the gravity of the blow. Fortunately, the total impact on