Space travelers who have returned from longer-than-90-day spaceflights may show signs of poor bone recuperation even after a year on Earth, but including more opposition-based practices during spaceflight may help limit bone misfortune.The little review, distributed in Scientific Reports, on 17 global space explorers found that while the shinbone somewhat recuperates, the supported bone misfortunes following one year are identical to a decade of typical age-related bone misfortunes on Earth. Steven Boyd and partners imaged 17 space travelers (14 male, three female) before spaceflight, on return to Earth, and following six and a half years of recuperation. They led bone
Astronomy & Space
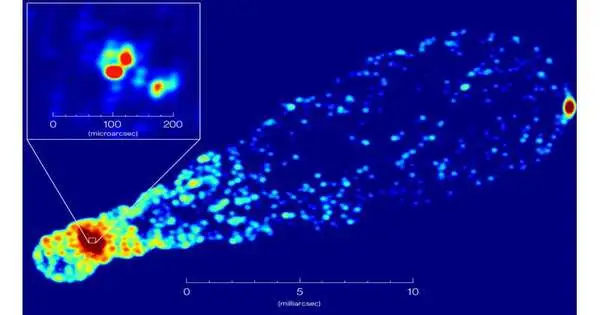
A free reanalysis of the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT's) observational information for the focal point of the curved world M87 has created pictures with various elements, as per another review. This study is essential for the exploration cycle in current science, in which observational information and examination strategies are available to general society and are audited and talked about in different networks of analysts to create more valid outcomes. The radio observational information for the focal point of the curved system M87 that was gotten by the Event Horizon Telescope in April 2017 and the techniques by which the information
Stargazers have made a record-breaking estimation of a dark opening's twist, one of two key properties of dark openings. NASA's Chandra X-beam Observatory shows this dark opening is turning more slowly than the majority of its more modest cousins. This is the biggest dark opening with an exact twist estimation and gives hints about how a portion of the universe's greatest dark openings develop. Supermassive dark openings contain millions or even billions of times more mass than the Sun. Stargazers feel that virtually every large world has a supermassive dark opening at its middle. While the presence of supermassive dark
As telescopes have become more developed and strong, stargazers have had the option of identifying an ever increasing number of far-off worlds. These are probably the earliest worlds to take shape in our universe that started to retreat away from us as the universe extended. As a matter of fact, the more prominent the distance, the quicker the world seems to get away from us. Curiously, we can gauge how quickly a world is moving, and thus, when it was framed in view of how "redshifted" its outflow shows up. This is like a peculiarity called the Doppler impact, where
Ibuprofen tablets altered to get by in space have gotten back to Earth and shown that those with added flavor endure preferred with less corruption over those with no additional taste. Scientists from the International Flavor Research Center at the University of Nottingham worked with the University of Adelaide on the examination that likewise showed that an iron oxide covering framed during tablet production could safeguard Ibuprofen. "Medicines brought on space missions are subjected to cosmic rays, which shorten their'space shelf life' and can even lead to the production of dangerous compounds as the medication content drops," the researchers write."The
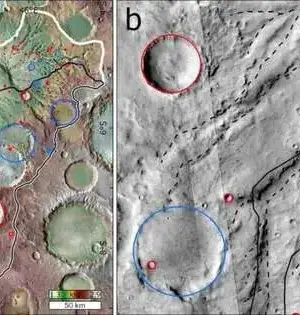
Inside the planetary group, the majority of our astrobiological research is focused on Mars, which is viewed as the next most tenable body after Earth. In any case, future endeavors are pointed toward investigating cold satellites in the external planetary group that could likewise be livable (like Europa, Enceladus, Titan, and then some). This polarity between earthly (rough) planets that circle inside their framework's livable zones (HZ) and cold moons that circle farther from their parent stars is supposed to illuminate future extrasolar planet reviews and astrobiology research. As a matter of fact, some accept that exomoons may play a
Making a 3D guide of our world would be simpler in the event that a few stars acted to allow us to compute the distances to them. In any case, red supergiants are the lively children on the block with regards to nailing down their careful areas. That is on the grounds that they seem to move around, which makes pinpointing their place in space troublesome. That wobble is an element, not a bug, of these huge old stars, and researchers need to grasp why. Thus, likewise with other test objects in the world, stargazers have turned to PC models
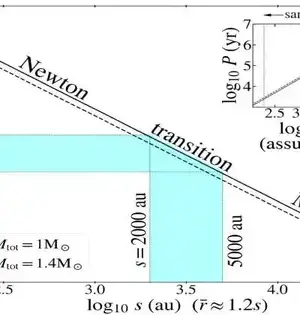
Magnetars are probably the most intriguing cosmic items. One teaspoon of the stuff they are made from would weigh just about one billion tons, and they have attractive fields that are countless times more remarkable than any attractive field that exists today on Earth. Yet, we have hardly any insight into how they are structured. Another paper focuses on one potential source—consolidations of neutron stars. Neutron stars themselves are similarly entrancing by their own doing. As a matter of fact, magnetars are by and large viewed as a particular type of neutron star, with the primary contrast being the strength
Researchers from Skoltech and their partners from the University of Graz and the Kanzelhöhe Observatory (Austria), Hvar Observatory (Croatia), and the Belgian Solar-Terrestrial Center of Excellence (SILSO), Royal Observatory of Belgium, introduced another strategy to foresee the strength of the 11-year sun-based cycle. The outcomes are significant for expecting and relieving space weather conditions' impacts on space travelers, pilots, and current mechanical frameworks both in space and on Earth. The review will be published in Astronomy and Astrophysics. The sun is the wellspring of strong blasts that can influence space travelers and current advances in space and on Earth. Toward
The current scientific theory holds that our Moon was formed by a catastrophic giant impact. Earth was a very different place 4.5 billion years ago, shortly after the planets in our solar system formed, glowing red with rivers and seas of lava. The solar system was still littered with formation debris. Earth and another small planetary body orbited the Sun in the same region of our solar system for millions of years. The orbit of the small planetary body crossed Earth's path, and the two collided, shattering the impactor. A sophisticated analysis of a rock sample collected from the Moon