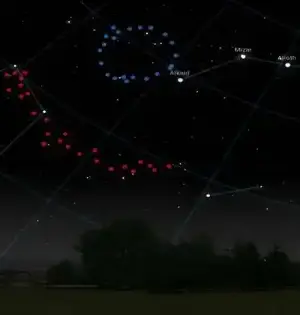
The Hubble Space Telescope's recent discovery of a baffling trail of stars that formed eight billion million years ago has presented a challenge to numerous research teams. This very long, narrow structure, whose size is comparable to that of the Milky Way, has sparked a number of theories regarding its origin. This trail of stars could be caused by a massive gas cloud passing through a supermassive black hole, according to a controversial initial hypothesis. The astronomical community was immediately captivated by this concept because it requires a large number of complex and exceptional circumstances. As a result, a number
Astronomy & Space
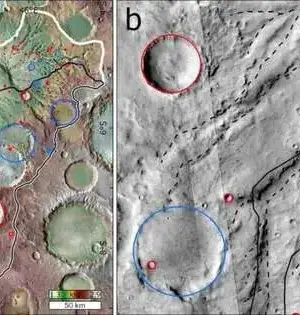
NASA's Opportunity rover spent 14 years exploring Mars' Meridiani Planum region for a reason: The district could hold vital clues about the Red Planet's initial geography and climate. Scientists are particularly interested in the Burns Formation, a layer of sandstone embedded with "blueberries" of hematite, due to its characteristics of liquid water and sulfur-rich composition that are similar to those found on Mars. A new study, which was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research, found that the Grasberg formation, a thin rock layer, is on top of the Burns formation. In Planets, Brian Hynek and Thomas McCollom propose a
At the point when Edwin Hubble noticed far-off cosmic systems during the 1920s, he made the historic revelation that the universe was growing. However, it wasn't until 1998 that researchers who were observing Type Ia supernovae made further discoveries, which revealed that the universe is not only expanding but has also begun a phase of expanding at a faster rate. To make sense of this speed increase, we want a source," says Joseph Mohr, an astrophysicist at LMU. "What's more, we allude to this source as 'dull energy,' which gives a kind of 'repulsive force' to accelerate vast extension." Dark
The Europa Clipper spacecraft, the largest that NASA has ever flown on an interplanetary mission, is getting ready to launch in October 2024. It is meant for Jupiter's icy moon Europa. Once in a while, a very long time of work will go into gathering and testing the rocket to guarantee it's sufficiently solid to endure a six-year, 1.6 billion-mile (2.6 billion-kilometer) venture and sufficiently refined to play out a definite scientific examination of this strange moon. Spacecraft Makers: A New Video Series "Europa Clipper" gives quick updates on how the mission is going and shows how hard work is
It was an astonishing time when, fourteen days prior, SpaceX got the freedom it expected to lead its most memorable orbital flight test with the Starship and Really Weighty Sendoff framework. The long-awaited flight, static fire, stacking, and unstacking tests of the SN24 Starship and BN7 Booster prototypes were completed after years of anticipation. SpaceX hoped to reach an altitude of at least 150 kilometers (90 miles) above sea level for this flight, crossing the official "space" boundary of 100 kilometers (62 miles) (the Karman Line) and passing through a portion of the world before collapsing off Hawaii's coast. Tragically,
Future space missions may make use of a novel method for finding planetary craters that will enable researchers to precisely map the surfaces of planets using a variety of data sources. A group of scientists from the College of Aberdeen has fostered another all inclusive cavity recognition calculation (CDA) utilizing META simulated intelligence's Fragment Anything Model (SAM). A brand-new artificial intelligence model known as SAM was unveiled earlier this month. It is capable of automatically "cutting out" any object from any image. The technology has allowed the team to map craters automatically rather than manually, which takes a lot of
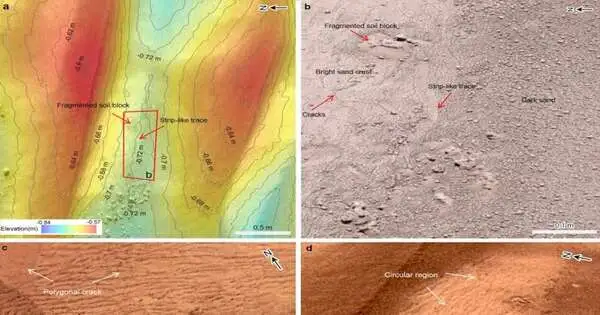
According to a study led by Prof. Qin Xiaoguang from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics (IGG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the Zhurong rover has provided key observational proof of liquid water at low Martian latitudes, which means that it has discovered evidence of water on modern Mars' dune surfaces. The study also involved researchers from CAS's Institute of Atmospheric Physics and the National Astronomical Observatories. The review was distributed in Science Advances on April 28. Studies in the past have shown that early Mars had a lot of liquid water. However, the climate changed a lot
Evidence suggests that planets may have formed during the "cosmic noon," according to a global team of space scientists. The team used data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to study a portion of the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) to learn more about how planets form around young stars. Their findings are published in the journal Nature Astronomy. Astronomers have been studying planet formation and the likelihood of Earth-like planets' existence for a long time. However, the origin of planets in the early universe, when most, if not all, stars were small, is still a mystery. In this new
A bright fireball that could be seen all over Europe resulted from an asteroid hitting Earth just hours after it was discovered on Monday. According to a press release issued by the European Space Agency, astronomer Krisztián Sárneczky discovered an asteroid at Hungary's Piszkéstet Observatory around 12:18 p.m. Eastern Time on Sunday. The object was initially identified as Sar2667. The International Astronomical Union Minor Planet Center was informed shortly after a second observation was made. "100% impact probability" The Vinjan Observatory in Croatia confirmed the asteroid approximately forty minutes after it was discovered. According to the ESA, a number of
In a recent publication, a multidisciplinary group of scientists, led by a researcher at the University of Manchester, developed a novel AI (artificial intelligence) strategy for translating technical astronomy terminology into plain English. The new research, which is the result of the international RGZ EMU (Radio Galaxy Zoo EMU) collaboration, is changing the language of radio astronomy from specific terms like FRI (Fanaroff-Riley Type 1) to simple terms like "hourglass" or "traces host galaxy." The paper has been accepted for publication in the Royal Astronomical Society's Monthly Notices. In astronomy, specific ideas are efficiently and easily understood by professional astronomers