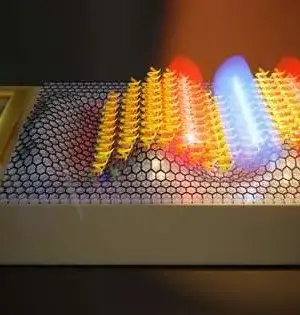
A group of specialists from the Organization for Optoelectronic Frameworks and Microtechnology at the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM) has planned a biosensor equipped for distinguishing proteins and peptides in amounts as low as a solitary monolayer. For that, a surface acoustic wave (SAW), a sort of electrically controlled nanotremor on a chip, is produced with an incorporated transducer to follow up on a pile of 2D materials covered with the biomolecules to be distinguished. As they report in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics in an article named "Surface-acoustic-wave-driven graphene plasmonic sensor for fingerprinting ultrathin biolayers down to as far
Bio & Medicine
In a paper distributed in Science Jan. 18, researchers Chad Mirkin and Sharon Glotzer and their groups at Northwestern College and the College of Michigan, separately, present discoveries in nanotechnology that could affect how best-in-class materials are made. The paper portrays a huge leap forward in gathering polyhedral nanoparticles. The scientists present and show the force of an original engineered procedure that grows potential outcomes in a metamaterial plan. These are the strange materials that support "intangibility shrouds" and ultrahigh-speed optical registering frameworks. "We control macroscale materials in their regular daily existence by utilizing our hands," said Mirkin, the George
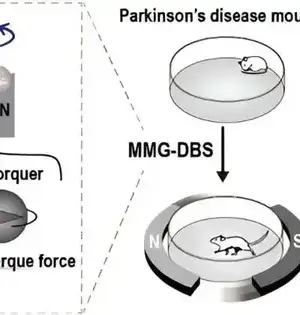
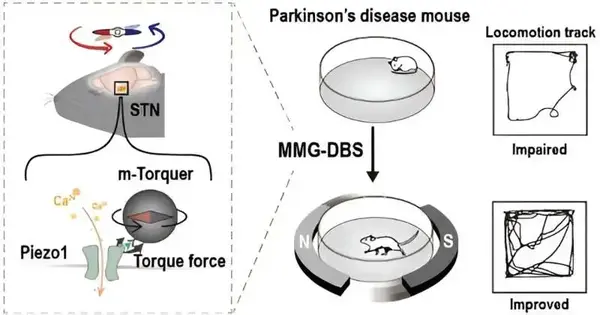
Electrical profound mind feeling (DBS) is a deep-rooted technique for treating scattered development in Parkinson's illness. Be that as it may, embedding terminals in an individual's cerebrum is an obtrusive and loose method for animating nerve cells. Specialists report in Nano Letters on another application for the strategy, called magnetogenetics, that utilizes tiny magnets to remotely set off unambiguous, quality-altered nerve cells in the mind. The treatment actually had better engine side effects in mice without harming the encompassing cerebrum tissue. In customary DBS, a battery pack remotely conveys electrical messages through wires, enacting nerve cells in a district of
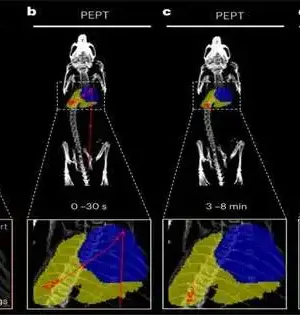
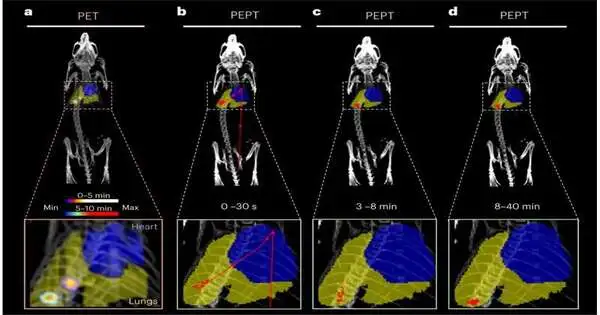
Scientists from the School of Biomedical Designing and Imaging Sciences have distributed another review investigating the utilization of positron emanation molecule following (PEPT) in a living subject. PEPT innovation takes into consideration the 3D limitation and following of a solitary radioactive molecule inside huge, thick, or potentially optically murky frameworks, which makes it challenging to concentrate on utilizing different techniques. The innovation is currently used to concentrate on streams inside complex mechanical frameworks like enormous motors, modern blenders, and so on; however, it has not yet been deciphered for use in biomedical applications. PEPT has recently been a neglected region
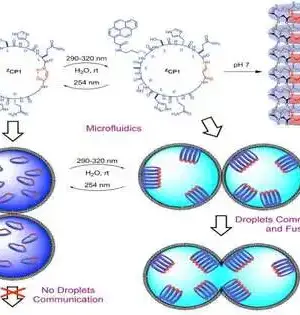
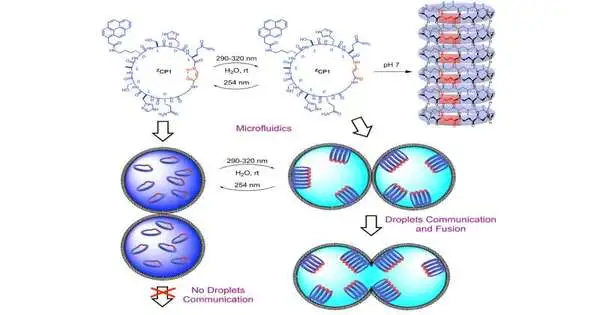
Peptide nanotubes are cylindrically molded structures shaped by the controlled stacking of cyclic peptide parts. These empty biomaterials show inward and external countenances, permitting command over their properties. Driven by Juan R. Granja, specialists from the Middle for Exploration in Natural Science and Sub-atomic Materials (CiQUS) introduced a clever sort of cyclic peptide that, when light-illuminated, prompts the development or integration of nanotubes on request. The peptide changes from collapsed to level compliance at the fitting frequency. At the point when the planar compliance is embraced, the peptide rings gather to form cylindrical structures, while in the collapsed course of
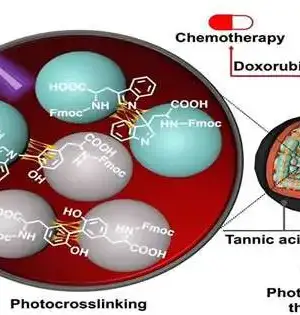
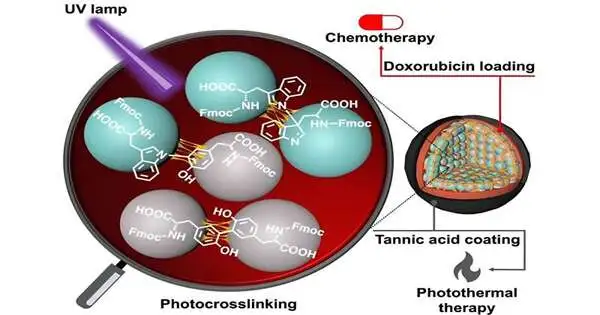
Amino acids, like tyrosine and tryptophan, are the central structures that make proteins. These biomolecules have different substance bunches on each end and side chain and, thus, have the inherent capacity to shape a chain through the development of an amide (peptide) bond. Notwithstanding, such linkages are frail and effectively debased under physiological circumstances. This is where the Fmoc-safeguarded amino acids come into the image. In another concentrate now, an examination group led by Dr. Eijiro Miyako, Academic Administrator, Japan Progressed Foundation of Science and Innovation (JAIST), Dr. Alberto Bianco, and Dr. Cécilia Ménard-Moyon from the Middle Public de la
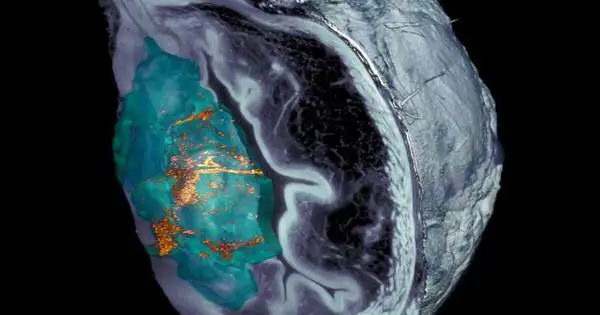
Bladder disease has one of the greatest occurrence rates on the planet and ranks as the fourth most normal growth in men. Notwithstanding its somewhat low death rate, almost 50% of bladder cancers reemerge in no less than 5 years, requiring continuous patient observation. Continuous emergency clinic visits and the requirement for rehash therapies add to making this kind of malignant growth one of the most costly to fix. While current medicines, including direct medication organization into the bladder, show great endurance rates, their remedial viability stays low. A promising option includes the utilization of nanoparticles equipped for conveying remedial
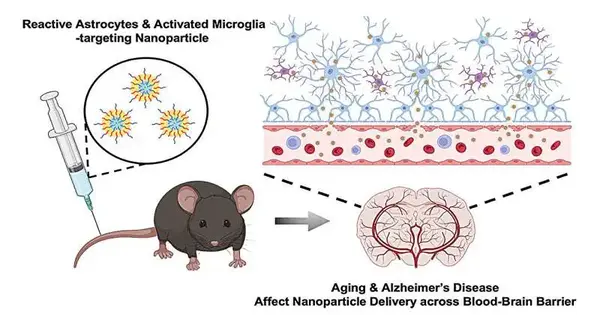
Neurodegenerative problems, for example, Alzheimer's disease, influence in excess of 270 million individuals around the world. Promotion is the main source of dementia, bringing about cognitive decline because of the decay of neurons in the hippocampus, which is the piece of the cerebrum that controls learning and memory. Nanoparticles intended to convey drugs have arisen as a methodology for treating various sicknesses, yet with regards to neurodegenerative infection, a significant part of the examination has zeroed in on creating systems for getting nanoparticles across the blood-mind obstruction and into designated districts of the cerebrum. In another review, an interdisciplinary group
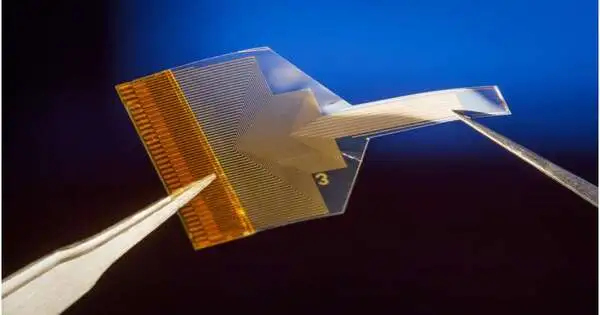
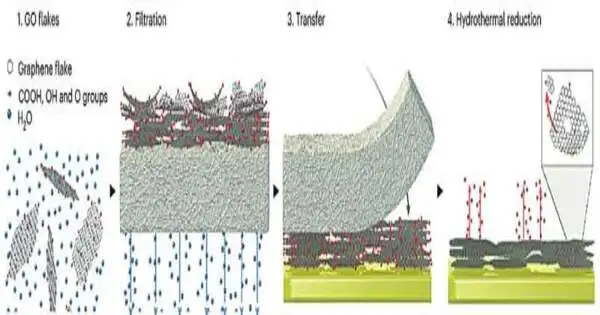
Specialists at the College of California, San Diego, have fostered a brain embed that gives data about action somewhere inside the mind while sitting on its surface. The embed is comprised of a slight, straightforward, and adaptable polymer strip that is loaded with a thick cluster of graphene terminals. The innovation, tried in transgenic mice, carries the specialists a bit closer to building a negligibly obtrusive cerebrum PC interface (BCI) that gives high-goal information about profound brain movement by utilizing accounts from the mind surface. The work is distributed in Nature Nanotechnology. "We are extending the spatial reach of brain
Long stretches of examination have prompted the improvement of EGNITE (Designed Graphene for Brain Connection Points), a clever class of adaptable, high-goal, high-accuracy graphene-based implantable neurotechnology. The review distributed today (Jan. 11) in Nature Nanotechnology adds a creative innovation to the blossoming scene of neuroelectronics and cerebrum PC interfaces. EGNITE expands on the huge experience of its creators in the manufacture and clinical interpretation of carbon nanomaterials. This imaginative innovation in view of nanoporous graphene coordinate creation processes is standard in the semiconductor business to collect graphene microelectrodes of a simple 25 µm in breadth. The graphene microelectrodes display low