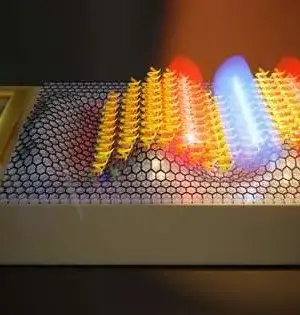
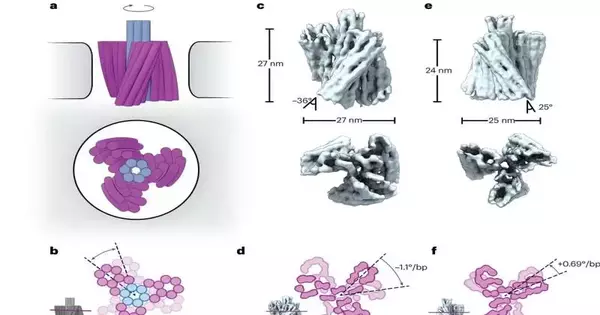
A cooperative group of scientists led by Prof. Cees Dekker at Delft College of Innovation, in association with global partners, have presented a spearheading leap forward in the realm of nanomotors—the DNA origami nanoturbine. This nanoscale gadget could address a change in outlook, saddling power from particle slopes or electrical potential across a strong state nanopore to drive the turbine into mechanical pivots. The center of this revelation is the plan, development, and driven movement of a "DNA origami" turbine, which highlights three chiral sharp edges, all inside a minute 25-nanometer outline, working in a strong state nanopore. By shrewdly
Bio & Medicine
Engineers at the College of California, San Diego, have created secluded nanoparticles that can be handily redone to target different natural elements like growths, infections, or poisons. The outer layer of the nanoparticles is designed to have any natural particles of decision, making it conceivable to tailor the nanoparticles for a wide cluster of utilizations, going from designated drug conveyance to killing organic specialists. The excellence of this innovation lies in its straightforwardness and proficiency. Rather than making totally new nanoparticles for every particular application, specialists can now utilize a secluded nanoparticle base and helpfully join proteins focusing on an
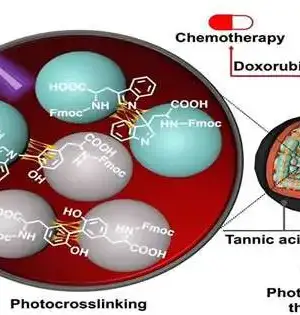
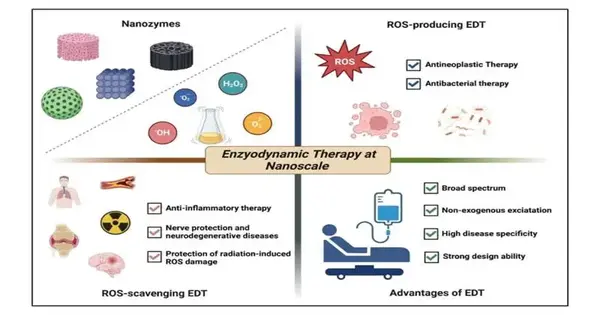
Enzyodynamic treatment (EDT) is another sort of responsive oxygen species (ROS)-related powerful restorative methodology that sufficiently uses the catalyst to set off synergist responses in living life forms and accomplishes illness treatment through controlling the age or disposal of ROS. ROS alludes to an exceptionally dynamic compound substance containing oxygen-free extremists in the body or regular habitat. ROS at physiological fixation is helpful for the advancement of living creatures. Notwithstanding, unreasonable ROS creation causes oxidative harm, which is connected to a huge number of infections, including malignancies, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular illness, irritation, etc. A new survey, distributed in MedComm—Biomaterials and Applications,
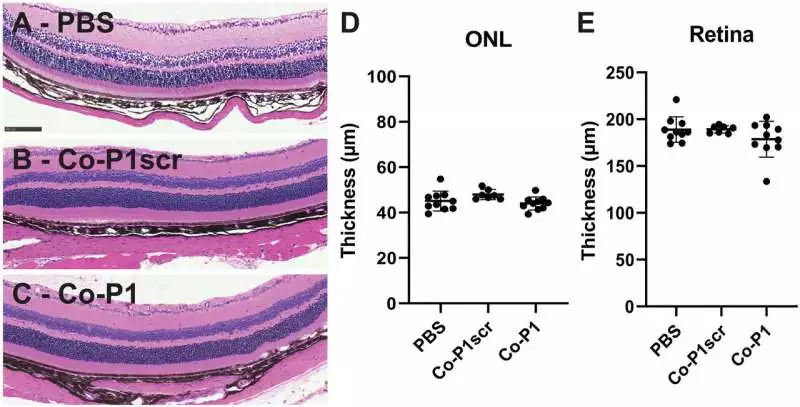
In the most recent step toward battling neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD), a group led by Teacher Nathan Gianneschi from the Global Organization for Nanotechnology at Northwestern College has disclosed an original methodology that could change patients' lives around the world. Their examination, distributed in Science Advances, presents thrombospondin-1 mimetic protein-like polymers (TSP1 PLPs) as an expected major advantage in the battle against this driving reason for visual deficiency. Grasping the test: Neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD)Prior to diving into the development of Gianneschi and his group, grasping the gravity of nAMD was significant. This condition is the essential driver
A global group of researchers has, as of late, fostered a clever kind of nanomotor made of DNA. It is driven by a sharp instrument and can perform beats. The scientists are currently wanting to fit it with a coupling and introduce it as a drive in complex nanomachines. Their outcomes have been distributed in the journal Nature Nanotechnology. Petr Šulc, an associate teacher at Arizona Express College's School of Sub-atomic Sciences and the Biodesign Place for Atomic Plan and Biomimetics, has worked together with teacher Famulok (project lead) from the College of Bonn, Germany, and teacher Walter from the
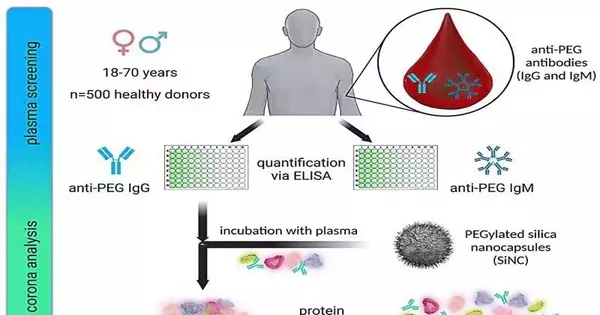
It has, for some time, been realized that individuals can frame safeguards and, accordingly, antibodies against infections. However, antibodies can likewise be created against polyethylene glycol (Stake), a substance utilized in beauty care products, food, and medication. These impact the adequacy of medications. A group of specialists from the Maximum Planck Establishment for Polymer Exploration has now examined how far reaching these antibodies are in German culture and how they could impact clinical treatments utilizing nanocarriers. They have distributed their ongoing outcomes in Nanoscale Skylines. An infection attacks the body, and the insusceptible framework starts to work. Antibodies foster the
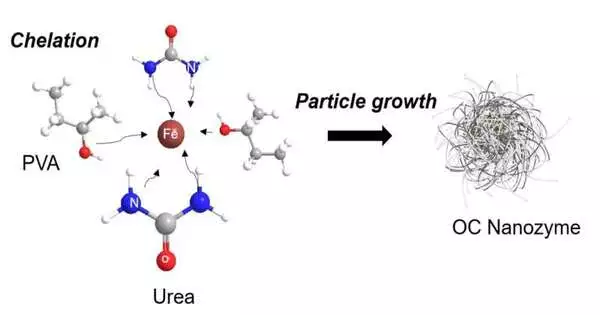
Nanozymes are manufactured materials that copy the properties of regular compounds for applications in biomedicine and synthetic design. By and large, they are, for the most part, thought to be excessively poisonous and costly for use in agribusiness and food science. Presently, specialists from the College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have fostered a nanozyme that is natural, non-harmful, harmless to the ecosystem, and financially savvy. In a recently distributed paper, they portray its elements and its ability to identify the presence of glyphosate, a typical horticultural herbicide. They want to ultimately make an easy-to-use test pack for buyers and farmers. "The
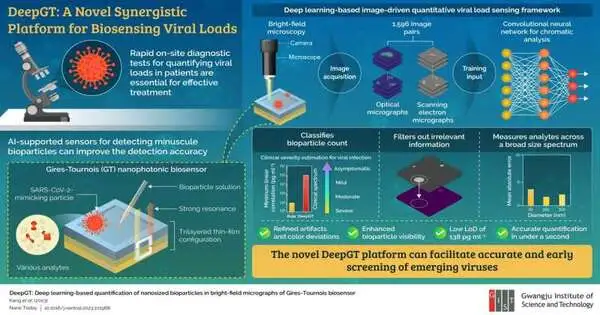
Late examinations have tracked down that Gires-Tournois (GT) biosensors, a sort of nanophotonic resonator, can identify infinitesimal infection particles and produce bright micrographs (pictures taken through a magnifying lens) of viral burdens. However, they experience the ill effects of visual curiosities and non-reproducibility, restricting their usage. In a new leap forward, a global group of specialists, led by Teacher Youthful Min Melody from the School of Electrical Designing and Software Engineering at the Gwangju Foundation of Science and Innovation in Korea, has utilized computerized reasoning (man-made intelligence) to defeat this issue. Their work was distributed in Nano Today. Quick and
Changes in the mechanical properties of cells are among the earliest indications of the improvement of malignant growth. As of recently, one of the significant hindrances to the utilization of mechanics in malignant growth conclusion has been the absence of a normalized estimation strategy that would ensure reproducibility and unwavering quality of results. Because of European logical collaboration, including the establishment of atomic physical science by the Clean Foundation of Sciences in Cracow, this obstruction has now been eliminated. At the point when solid cells change into disease cells, their mechanical properties change. This perception could be utilized to quickly
UCLA scientists have fostered another treatment strategy utilizing a small nanocapsule to assist with the invulnerable reaction, making it more straightforward for the resistant framework to battle and kill strong growths. The examiners found the methodology, portrayed in the diary Science Translational Medication, expanded the number and movement of safe cells that assault the malignant growth, making disease immunotherapies work better. "Disease immunotherapy has reshaped the scene of malignant growth therapy," said senior creator of the review, Jing Wen, a colleague assistant lecturer of microbial science, immunology, and sub-atomic hereditary qualities at the David Geffen Institute of Medication at UCLA