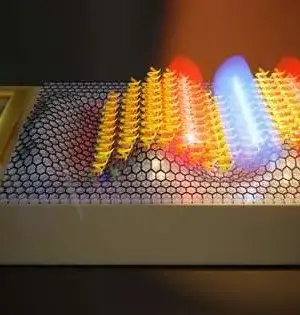
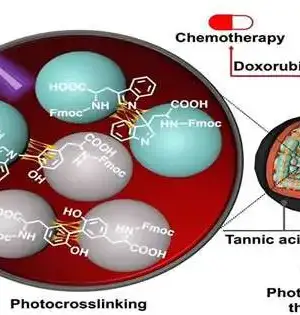
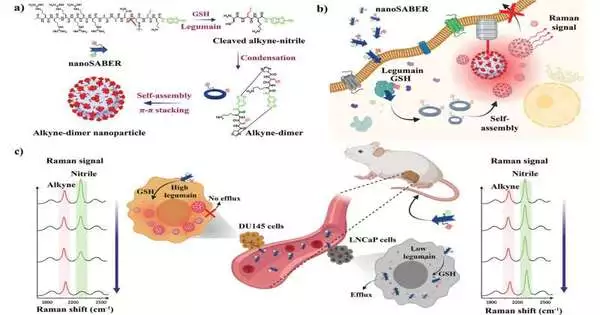
At the point when Jedi Knights need to vanquish an adversary, they whip out their dependable lightsabers. Later on, because of Johns Hopkins specialists, specialists trying to pulverize malignant growth might use microscopic sub-atomic nanoSABERs that permit them to check out cancers in manners never before conceivable. Motivated by the interaction cells use to gather proteins, a group led by two specialists—Ishan Barman at the college's Whiting School of Designing and Jeff W. Bulte, a teacher of radiology and radiological science at the Institute of Medication who is likewise partnered with JHU's Establishment for NanoBioTechnology—has made minute tests that light
Bio & Medicine
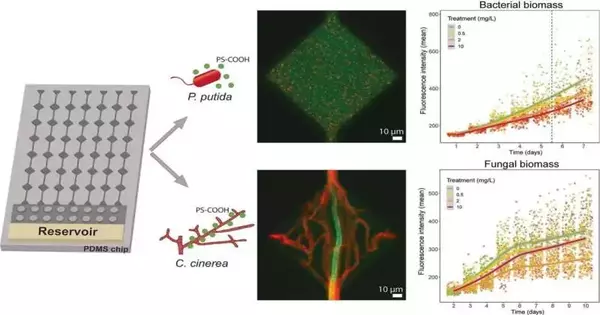
Utilizing miniature-designed soil models, scientists at Lund College in Sweden have examined the impact of minuscule polystyrene particles on microbes and growths. While these nanoplastics decreased both bacterial and contagious development, the parasite really figured out how to "tidy up" their environmental factors, accordingly facilitating the impact of the plastics. Their work has been distributed in The Study of the All-Out Climate. "Plastic waste is a gigantic worldwide issue. Whether recklessly disposed of into nature, spilling from landfills, or scoring from materials, for example, vehicle tires and manufactured garments, a lot of miniature and nanoplastics end up in our dirt,"
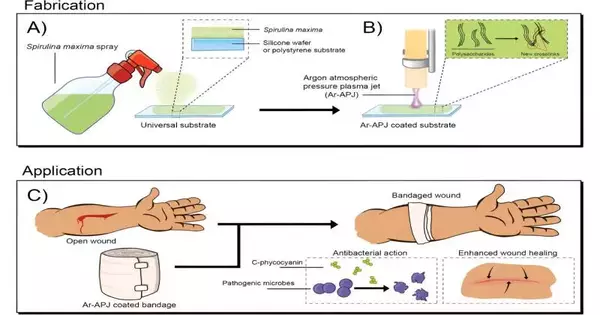
Specialists at Flinders College have taken a huge leap in the field of wound care, utilizing a creative methodology. By sending an argon barometrical plasma stream, they have effectively changed Spirulina maxima, a blue-green microalgae, into ultrathin bioactive coatings. These coatings tackle bacterial diseases, advance quicker wound recovery, and have powerful calming properties. This holds particularly for the therapy of ongoing injuries, which frequently present difficulties because of drawn-out healing times. The original methodology could diminish the risk of harmful responses to silver and other nanoparticles and increase anti-infection protection from normal business coatings utilized in injury dressing. The most
The sex chemical, usually known as estrogen, assumes a significant role in numerous aspects of ladies' wellbeing and richness. Elevated degrees of estrogen in the body are related to bosom and ovarian malignant growths, while low degrees of estradiol can bring about osteoporosis, coronary illness, and even sadness. Estrogen is a class of chemicals that incorporates estradiol as its most intense structure. Estradiol is likewise important for the advancement of optional sexual attributes in women and controls the regenerative cycle. Due to its many capabilities, the chemical estradiol is frequently explicitly observed by doctors as a feature of ladies' medical
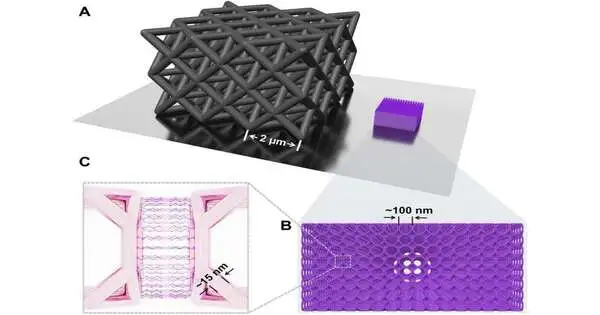
A group of substance and natural designers working with a gathering of nanotechnologists at Northwestern College in Illinois has fostered a sort of area of strength for super precious stone metamaterial by sticking together metal nanostructures utilizing strands of DNA. In their paper distributed in the journal Science Advances, the gathering portrays how they fostered their strategy and potential purposes for the kinds of items they made. Earlier exploration has shown that extremely few metamaterials can be utilized for a wide assortment of purposes. In this new exertion, the examination group made the following stride in such exploration by building
UMass Amherst scientists have pushed forward the limits of biomedical design one hundredfold with another strategy for DNA location with phenomenal responsiveness. "DNA discovery is the focal point of bioengineering," says Jinglei Ping, lead creator of the paper that appeared in Procedures of the Public Foundation of Sciences. Ping is an associate teacher of mechanical and modern design, an assistant colleague teacher in biomedical design, and a subsidiary of the Middle for Customized Wellbeing Observing of the Organization for Applied Life Sciences. "Everybody needs to distinguish the DNA at a low fixation with a high responsiveness. What's more, we just
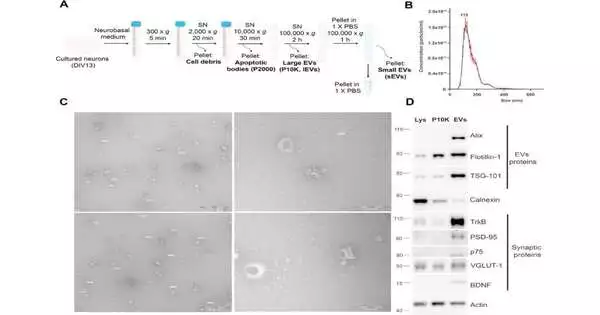
Another study by the College of Barcelona could drive the development of future systems to recover damaged brain regions in neurodegenerative illnesses. The review underscores the role of neuron-determined extracellular vesicles in the cycles that adjust synaptic pliancy and neuronal flagging pathways. Likewise, the outcomes frame another situation for utilizing these extracellular vesicles from solid neurons—equipped for shipping atoms between cells—in medicines against neurodegenerative illnesses. The review, distributed in the Diary of Extracellular Vesicles, whose first creator is the predoctoral understudy Julia Solana-Balaguer, was driven by Teacher Cristina Malagelada, from the Personnel of Medication and Wellbeing Sciences and the Foundation
Researchers at the Materials Exploration Center (MRC), Indian Establishment of Science (IISc), have fostered another kind of compound mimetic that can corrupt harmful synthetics in modern wastewater, really within the sight of daylight. Chemicals are proteins that catalyze a greater part of organic responses in living frameworks. In any case, the reasonable utilization of normal catalysts is extraordinarily thwarted by specific innate restrictions. These limits incorporate aversion to denaturation (breakdown or harm), complex creation strategies, significant expenses, and hardships in reusing, says Subinoy Rana, Aide Teacher at MRC, and relate to the creator of the paper distributed in Nanoscale. Efficiently
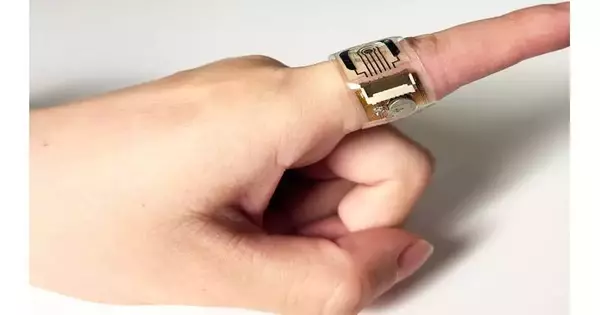
Since the revelation of penicillin in 1928, microbes have advanced various ways of sidestepping or by and large, overlooking the impacts of anti-infection agents. Fortunately, medical services suppliers have a stockpile of rarely utilized anti-infection agents that are as yet compelling against any safe types of microorganisms. Scientists at Sandia Public Research facilities have joined before work on easy microneedles with nanoscale sensors to make a wearable sensor fix able to do ceaselessly observing the degrees of one of these anti-infection agents. The particular anti-microbial they're following is vancomycin, which is utilized as a last line of safeguard to treat
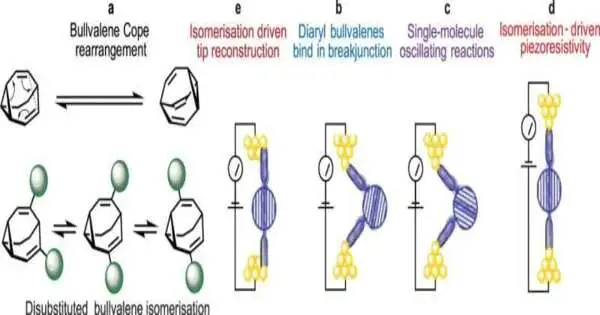
Australian specialists have fostered a sub-atomic, measured, and more productive form of a generally utilized electronic sensor at a leading edge that could bring far and wide advantages. Piezo resistors are usually used to distinguish vibrations in hardware and vehicles, like in advanced cells for counting steps and for airbag sending in vehicles. They are likewise utilized in clinical gadgets like implantable tension sensors, as well as in aeronautics and space travel. In a cross-country drive, specialists led by Dr. Nadim Darwish from Curtin College, Teacher Jeffrey Reimers from the College of Innovation Sydney, Academic Administrator Daniel Kosov from James