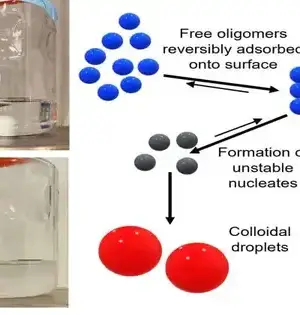
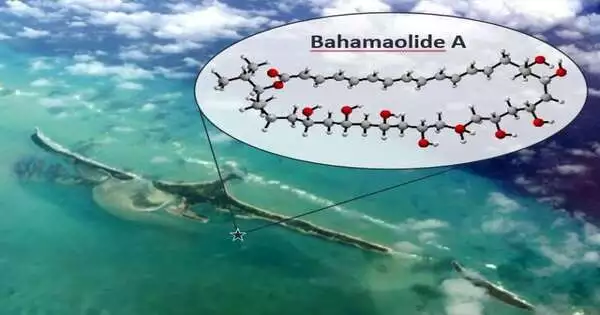
Researchers created a spearheading method to build particles found in uncommon silt from the Bahamas with the possibility of assisting with treating illness and disease. Researchers have developed a much faster method for producing specific complex particles, which are widely used in anti-toxins and anti-parasitic medicines. The first-of-its-kind revelation by physicists at the College of Bristol can possibly accelerate the creation of such medications, making them less expensive and more accessible. The leap forward, published in Nature Science, denotes the zenith of a five-year research project that has at last figured out how to remake in a lab an especially
Biochemistry
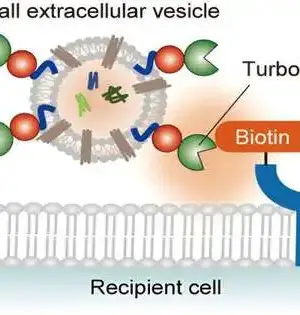
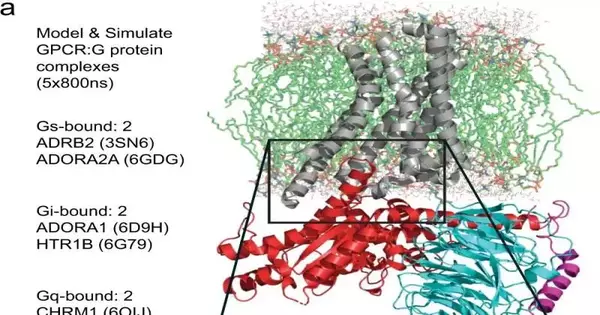
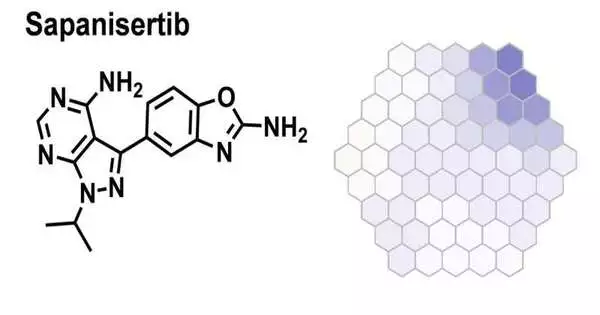
Scientists from the City of Trust, one of the biggest disease exploration and treatment associations in the US, have recognized how a protein receptor designated by around 33% of all governmentally endorsed drugs works. The disclosure could work with drug research since how and why this protein decides to connect to different proteins is basic to how cells will respond to medications. The recently distributed Nature Interchanges study, "Dynamic spatiotemporal determinants tweak GPCR:G protein coupling selectivity and wantonness," revealed a phone flagging system for the biggest superfamily of medication target proteins, called G-protein coupled receptors. GPCRs in the cell film
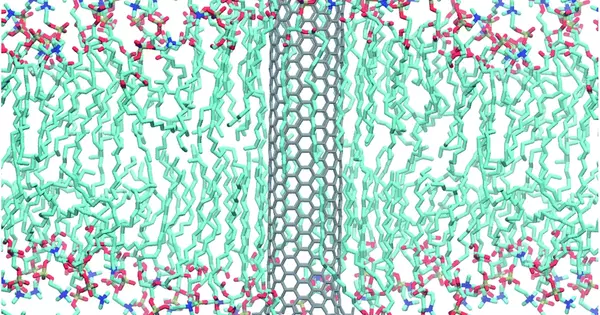
Heavy metal toxicity Mercury (Hg) is a global pollutant that has an impact on both human and ecosystem health. Despite the fact that it occurs naturally in the earth's crust, human activities such as mining and coal combustion add mercury to the environment. Once in the air, it settles into water or land and can be washed into the water, where it enters the food chain. Metarhizium robertsii, a fungus discovered by researchers, removes mercury from soil around plant roots as well as fresh and saltwater. The fungus was also genetically modified by the researchers to enhance its mercury detoxification
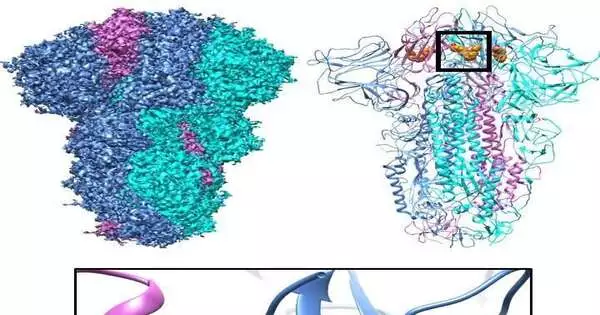
Researchers have found the reason why some COVIDs are bound to cause serious sickness, which has remained a secret until recently. Specialists of the College of Bristol-Davie study, distributed in Science Advances today (November 23), say their discoveries could prompt the improvement of a dish Covid treatment to overcome all Covids—from the 2002 SARS-CoV episode to omicron, the ongoing variation of SARS-CoV-2, as well as perilous variations that might arise in the future. In this new review, a worldwide group led by Bristol's teacher Christiane Schaffitzel examined the spike glycoproteins brightening all COVIDS. They uncover that a tailor-made pocket highlight
Real-time monitoring of biochemical reactions, biomolecular and microbial changes in land, water, food, and the environment has made significant progress thanks to advances in nanotechnology and biosensing technology. Nano-biosensors are made up of a biological molecule capable of recognizing analyte/target molecules when coupled with a receptor molecule and a transducer that converts the recognizing event into readable signals that quantify the analyte molecules. Two new low-cost tests that detect chemicals using nanoparticles can accurately measure trace amounts of two potentially harmful herbicides in fruits, vegetables, and their products. A Washington State University research team used two testing methods to measure
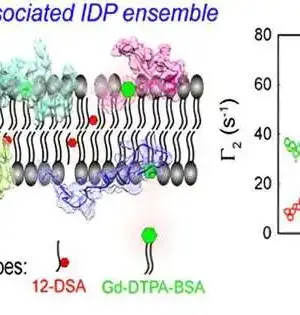
Plant mitochondria are complex organelles that perform a variety of metabolic processes including the generation of energy for cellular functions as well as the synthesis and degradation of various compounds. Mitochondria are semiautonomous, dynamic organelles that change shape, number, and composition according to tissue or developmental stage. Coordination of genes present in both the nucleus and the organelle is required for the biogenesis of functional mitochondria. RIKEN biologists have discovered an effective method for smuggling genetic material into the energy generators of plant cells, opening the door to coaxing plants to produce commercially useful compounds. Their findings were published in
A disease drug currently in clinical trials has demonstrated the ability to protect against, treat, and prevent the spread of jungle fever.The cutting-edge discovery by a global group that includes Penn State scientists offers new hope against a disease that kills over a portion of a million people each year, primarily affecting children under the age of five, pregnant women, and HIV patients. The exploration group, led by specialists at the College of Cape Town (UCT), distributed their outcomes in another paper dated Oct. 19 in the journal Science Translational Medication. "Interruptions in jungle fever immunizations, treatment, and care during
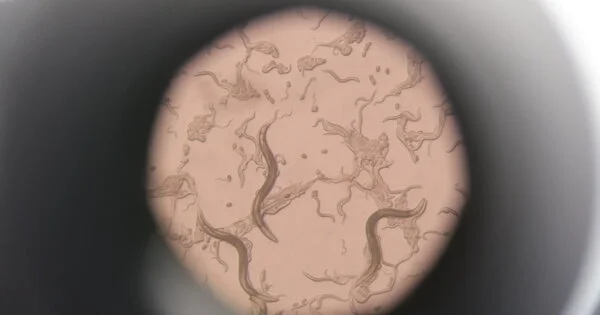
Aging is not a disease in and of itself. Aging, on the other hand, is a major risk factor for the development of many major chronic diseases. Furthermore, many diseases appear to hasten the aging process, manifesting as functional decline and reduced quality of life. Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) discovered that a stress response in cells, when 'turned on' at a post-reproductive age, could be the key to slowing ageing and promoting longevity. The NTU Singapore team discovered that switching on this stress response in aged worms by feeding them a high-glucose diet extended their lifespan
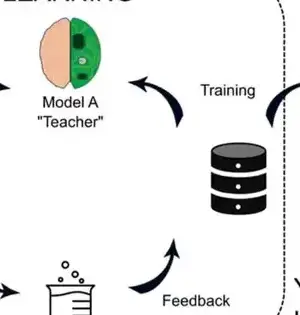
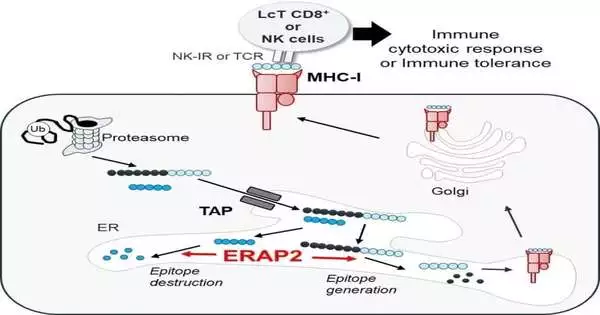
Specialists at the College of Illinois Chicago have found a little particle equipped for controlling a resistant cycle that plays a significant part in malignant growth and immune system illnesses. Their revelation is accounted for in an Angewandte Chemie paper titled "Disclosure of the First Specific Nanomolar Inhibitors of ERAP2 by Motor Objective Directed Union." They found the atom—and compound inhibitor—after first concentrating on how the invulnerable framework functions and why a few illnesses can be impervious to medicines. Growths can introduce cell-surface markers as non-self peptide antigens, or neoantigens, which renders them perfectly delicate to acknowledgment and disposal by
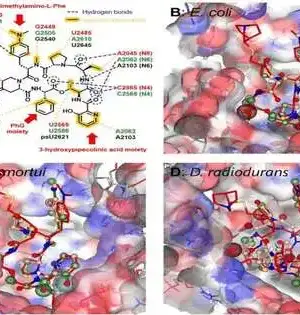
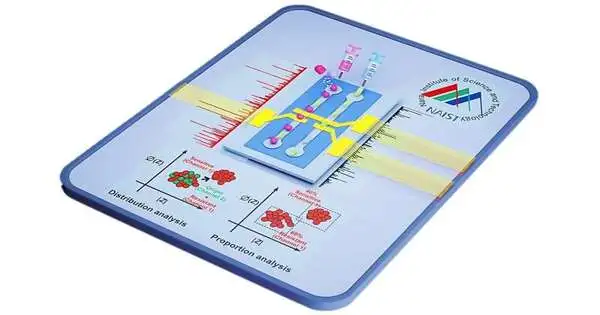
A huge amount of time is expected to decide the medication weakness profile of a bacterial disease. Presently, scientists from the Nara Foundation of Science and Innovation and their teaming up accomplices have developed an innovation that will decisively accelerate this generally sluggish cycle and perhaps assist in saving lives. The CDC states that anti-toxin safe diseases are liable for killing north of 1,000,000 individuals overall consistently. The key to overseeing safe diseases is rapidly recognizing the proper treatment to which the infective microbes are helpless. "As a rule, weakness results are required a lot quicker than regular tests can