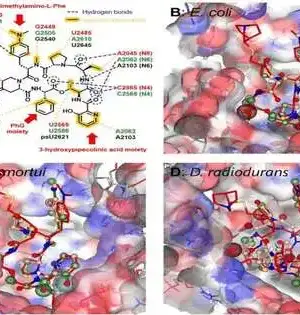
A large number of the medications we use in present day medication are normally created by organisms. Penicillin, an anti-microbial gotten from specific molds, is one of the most prominent regular items because of its acknowledgement as perhaps the greatest development in medication and human wellbeing. As DNA sequencing has become less expensive and quicker, researchers are presently approaching a huge number of microbial genomes and the regular items they produce. In any case, Doug Mitchell (MMG), the John and Margaret Witt Teacher of Science at the College of Illinois, says this could not hope to compare to the quantity
Biochemistry
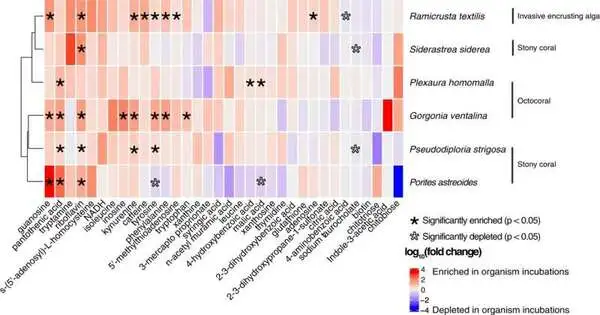
The impact of coral chemical compounds on reef composition and health is investigated in this study.
Coincidentally, finding another wellspring of submerged caffeine was only a special reward of another review inspecting the effect of synthetic mixtures that corals discharge into the seawater. The investigation discovered that the natural substances intensified through digestion — known as metabolites or exudates — shift altogether by coral species and that the mixtures influence the overflows and pieces of reef microorganisms in an unexpected way. This differential arrival of metabolites from benthic reef creatures is especially huge in the Caribbean, where coral strength is shifting from hard stony corals to delicate octocorals because of human-caused stressors like eutrophication, overfishing, and
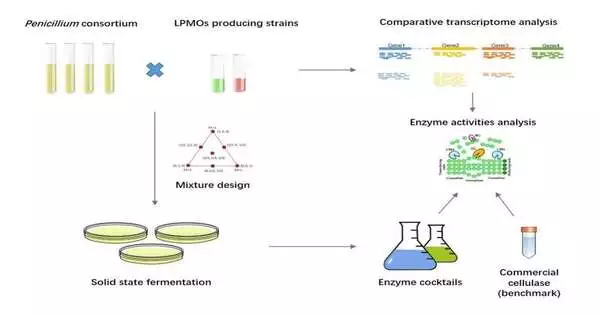
A powerful enzyme ‘cocktail’ from the Penicillium consortium improves lignocellulose biodegradation.
Lignocellulosic biomass is the most bountiful feedstock for bio-based fills and materials. The protein "mixed drink" is considered a useful asset to dispense different explicit exercises within a single grid. As of late, analysts led by Prof. Qi Wei from the Guangzhou Foundation of Energy Change of the Chinese Institute of Sciences have detailed an effective cellulase "mixed drink" created by the co-development of a few Penicillium strains with lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) delivering strains, which accomplishes a great hydrolysis yield of pretreated poplar materials. The review was published in the Compound Designing Diary on September 22. The author of
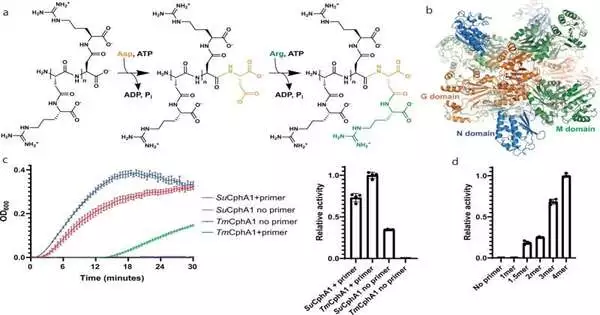
Blue green growth (Otherwise known as cyanobacteria) have a superpower which probably assists them with finding success as intruders of streams. They have an uncommon capacity to store energy and nitrogen in their cells for critical crossroads. Yet, how precisely they do so stays just mostly gotten it. Presently scientists from McGill College and their partners at ETH Zurich have revealed a charming until now obscure capacity of the proteins (known as cyanophycin synthetases) that are dynamic in making these food saves. Their discoveries, depicted in a new paper in Nature Correspondences, are logically amazing, yet make us a stride
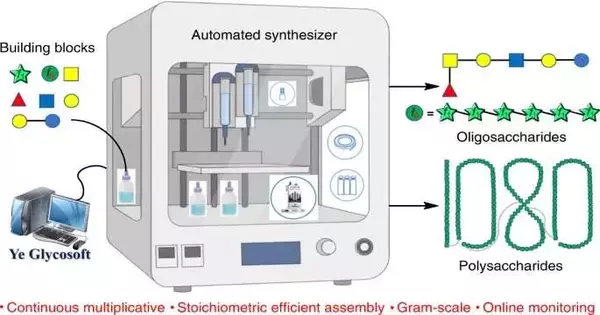
A group of scientists, including individuals from Peking College and WuXi AppTec (Tianjin) Co., Ltd., has planned and fabricated a robotized carbohydrate synthesizer that creates polysaccharides of record-breaking length. In their paper distributed in the diary Nature Blend, the gathering depicts how they assembled their gadget and its potential purposes. Hanchao Cheng and Peng George Wang with the Southern College of Science and Innovation in China, have distributed a News and Perspectives piece in a similar diary issue framing the work by the group in China. As Cheng and Wang note, carbs play a vital part in science—they are a
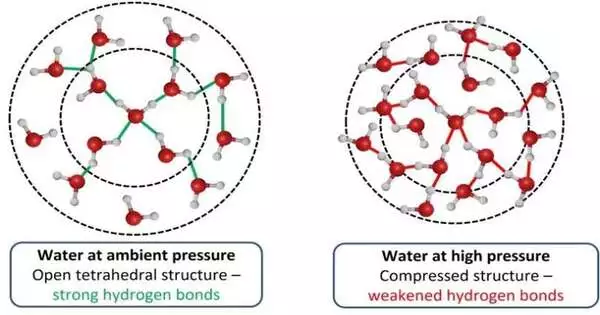
Researchers have found how a compound in the cells of marine creatures empowers them to endure the high tensions tracked down in the profound seas. The further out in the ocean animals live, the colder and more extreme the climate they must adapt to.In quite possibly the most profound point in the Pacific — the Mariana Channel, 11 kilometers beneath the ocean surface — the strain is 1.1 kbar, or eight tons for each square inch. That is a 1,100-fold increase in the strain felt at the Earth's surface. Under typical conditions of air pressure, water particles structure a tetrahedron-like
Cells are continually pursuing choices that lead to separation. For example, cells in an undeveloped organism pursue a progression of choices that decide if they will become neurons at times and muscle cells in others. How do cells settle on these choices? Specialists at Texas A&M College and North Carolina State College are deciding the way in which cells work with dynamic cycles. Through this work, they desire to unequivocally gauge the centralization of explicit indispensable flagging proteins inside cell tissues. Furthermore, they will utilize the estimations to foster numerical models that can foresee and control cell separation. This study
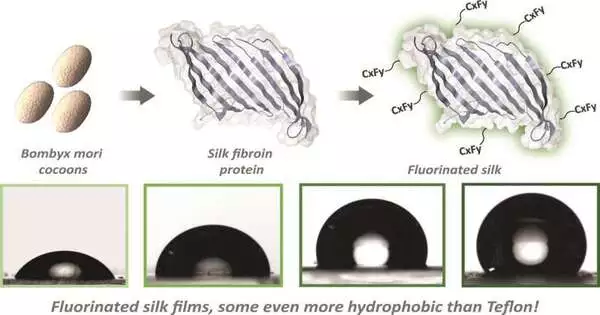
Scientists at Tufts College have fostered a strategy to make silk-based materials that won't adhere to water, or nearly anything else containing water besides. Truth be told, the changed silk, which can be shaped into structures like plastic or covered onto surfaces as a film, has non-stick properties that outperform those of nonstick surfaces commonly utilized on cookware, and it could see applications that reach out into an extensive variety of consumer items as well as medication. Silk is a characteristic fiber turned by moths and has been utilized for millennia to make solid and fine textures, as well as
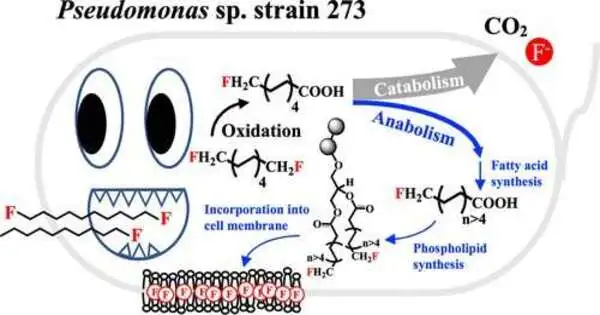
College of Tennessee, Knoxville employees Shawn Campagna, teacher and partner division head in science, and Plain Loeffler, lead representative's seat teacher in microbial science, have made a disclosure that could prompt new capacities for overseeing natural tainting. Monetarily utilized per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) were created in the 1940's and have since evolved into an assortment of normal family items. PFAS are now used in plastic and elastic manufacturing, as well as food coverings, umbrellas, and firefighting foam, among other things. PFAS have likewise been designated "always synthetic" because of their protection from separating in both the climate and the human
Name a natural capability, and proteins called integrins are likely engaged with it. Together, the 24 individuals from the integrin family permit cells to join with each other and with the grid that encompasses them. They assist cells with choosing what to become, where to go, how to respond to their surroundings, and when to develop, gap, or pass on. Integrins' universality and flexibility likewise imply that while cells bearing them turn out badly, these proteins can add to a scope of illnesses, from immune system infections to disease. The FDA has up to this point endorsed six medications that