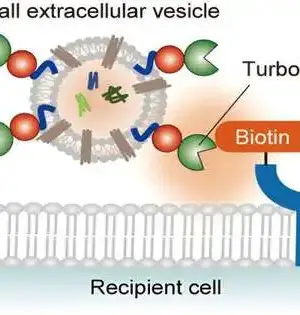
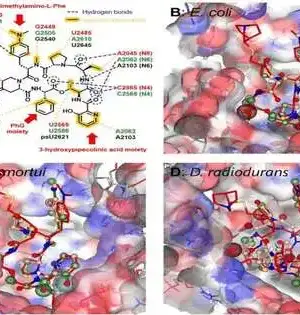
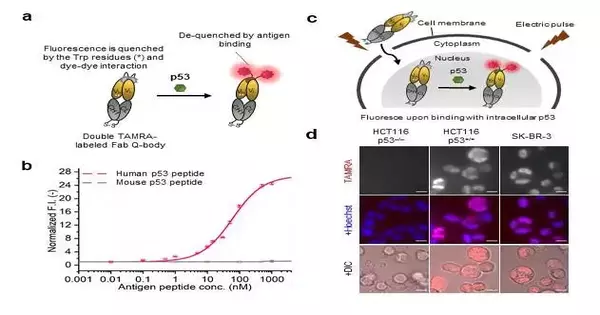
Late advances in imaging innovation have made it conceivable to picture intracellular elements, which offers a superior understanding of a few vital organic standards for speeding up helpful turns of events. Fluorescent naming is one such method that is utilized to recognize intracellular proteins, their elements, and brokenness. Both inner as well as outer tests with fluorescent colors are utilized for this reason, albeit outside tests can more readily visualize intracellular proteins when contrasted with the inward tests. However, their application is limited by a vague restriction to intracellular parts, resulting in low objective explicit flagging and higher foundation clamor.
Biochemistry
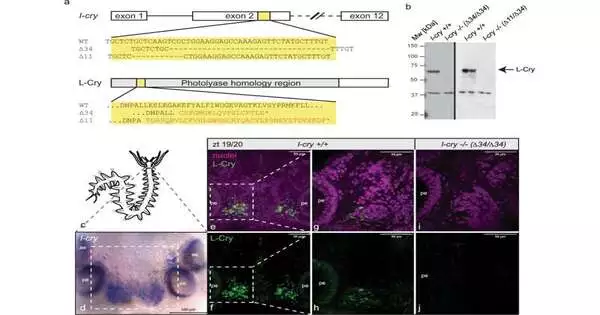
How creatures can decipher normal light sources to change their physiology and conduct is inadequately perceived. The labs of Kristin Tessmar-Raible (Max Perutz Labs Vienna, Alfred Wegener Institut, College of Oldenburg) and Eva Wolf (Johannes Gutenberg College and Foundation of Sub-atomic Science Mainz) have now uncovered that a particle called L-cryptochrome (L-Cry) has the biochemical properties to separate between various moon stages, as well as between sun and twilight. Their discoveries, published in Nature Correspondences, demonstrate the way that L-Cry can decipher twilight to entrain the month-to-month (circalunar) clock of a marine worm to control sexual development and generation. Numerous
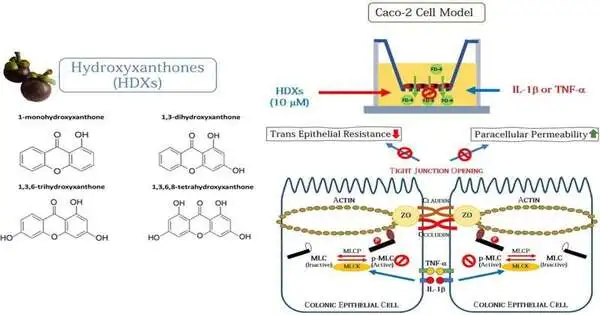
A gathering of specialists in Thailand has imitated "Hydroxy-xanthones," the cell reinforcement-rich fundamental concentrates found in mangosteen strips that kill microorganisms and end contaminations in the gastrointestinal mucosa. In addition to the fact that mangosteen is the sovereign of Thai natural products—a scrumptious and solid organic product—its strip is likewise bountiful with helpful concentrates. Nearby, insight considered mangosteen strips a decent treatment for upset stomachs, skin irritation, and wounds. There have been endeavors to apply mangosteen strip concentrates to different prescriptions and items like mortars, gels, and careful covers. Academic administrator Dr. Suthasinee Poonyachoti of the Department of Physiology, Faculty
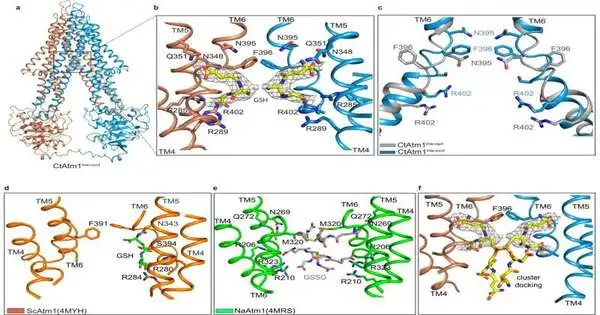
New exploration gives new insight into how a significant class of atoms are made and moved in human cells. For quite a long time, researchers knew that mitochondria—specific designs inside cells in the body that are fundamental for breath and energy creation—were engaged in the gathering and development of iron-sulfur cofactors, probably the most fundamental mixtures in the human body. Yet, as of recently, analysts didn't see how the very cycle functioned. New exploration, distributed in the journal Nature Communications, observed that these cofactors are moved with the assistance of a substance called glutathione, a cell reinforcement that forestalls specific
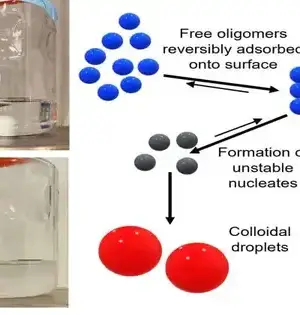
A strange protein structure known as an "undulated beta sheet," first anticipated in quite a while, has been made in the lab and portrayed exhaustively utilizing X-beam crystallography. The new discoveries, published in July in Chemical Science, may enhance the sane design of novel materials in view of the undulated sheet design. "Our review lays out the undulated beta sheet layer setup as a theme with general elements and opens the door to structure-based planning of novel sub-atomic models, with potential for materials improvement and biomedical applications," said Jevgenij Raskatov, academic partner of science and organic chemistry at UC Santa
Drug atoms and biofuels can be specially made by residing cell plants, where organic proteins finish the work. Presently, scientists at Chalmers University of Technology have fostered a PC model that can foresee how quickly proteins work, making it conceivable to track down the most effective living plants as well as to concentrate on complex illnesses. Their outcomes are distributed in Nature Catalysis. "To concentrate on each normal protein with tests in a lab would be unthinkable; they are just too much. Yet, with our calculation, we can foresee which proteins are generally encouraging by simply taking a gander at
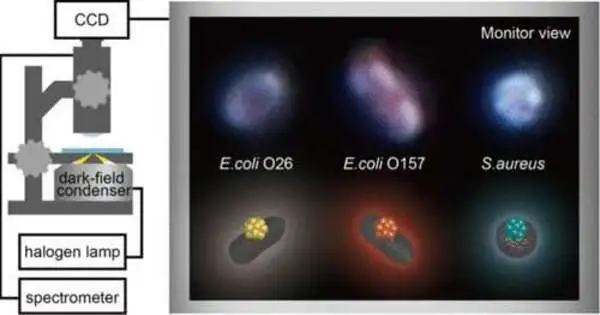
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have fostered a straightforward, fast strategy to all the while recognize various food contamination microbes in view of the variety of contrasts in the dispersed light by nanometer-scaled natural metal nanohybrid structures (NHs) that tight spot through antibodies to those microorganisms. This strategy is a promising device for quickly identifying microbes at food-producing locales and consequently further developing sanitation. The discoveries were published in Analytical Chemistry. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), consistently, food contamination influences 600 million individuals overall—just about 1 in every 10 individuals—of which 420,000 pass on. Bacterial tests are conducted to
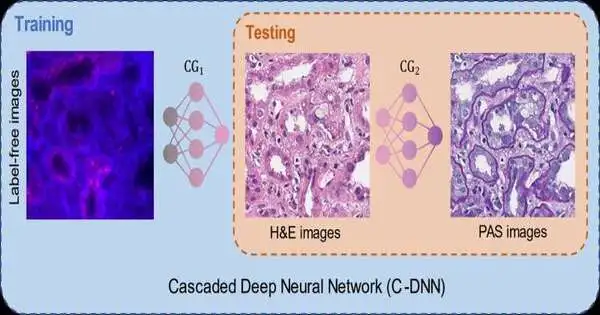
The tissue-put together finding of illnesses depends with respect to the visual review of biopsied tissue examples by pathologists utilizing an optical magnifying lens. Prior to putting the tissue test under a magnifying lens for review, unique compound colors are applied to the example for staining, which improves the picture difference and carries tone to different tissue constituents. This compound staining process is arduous and tedious, performed by human specialists. In numerous clinical cases, notwithstanding the usually utilized hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain, pathologists need extra unique stains and synthetics to work on the exactness of their findings. In any
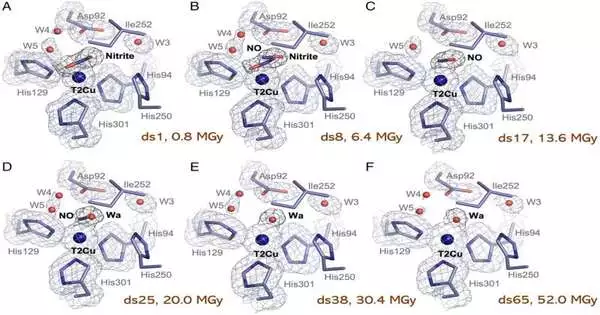
A global team of researchers led by the University of Liverpool has created primary films of a key protein involved in a natural pathway of ozone-harming substance formation, providing new insight into its reactant action. A significant supporter of an unnatural weather change is the ozone-harming substance nitrous oxide, which is multiple times more harmful to the ozone layer than carbon dioxide. Nitrous oxide is a result of the denitrification pathway, which happens when unique sorts of miniature creatures eliminate overabundances of nitrate or nitrite from environments and convert them back to nitrogen gas. The initial step of this cycle
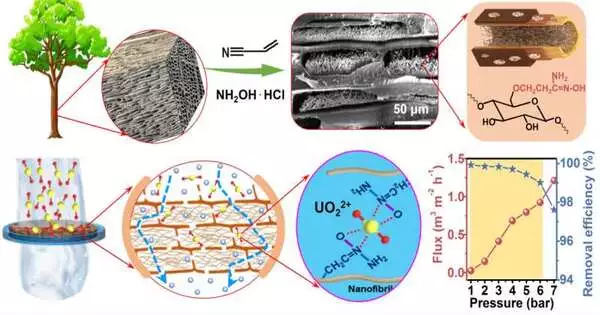
Numerous important metals, like gold, silver, lithium, and uranium, are crucial to high innovation and current industry. The earthly mineral stores of these metals are generally extremely limited or suffer from high mining costs.Although the majority of these important metal particles could be found in the sea, minimal expense and high-proficiency adsorbents are as yet the keys to the improvement of removing these metals from seawater. An examination team led by Prof. Li Chaoxu from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has uncovered that natural nanofibrils could effectively remove important metal components